Abstract
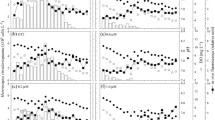
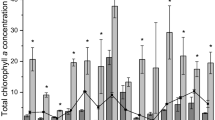
Anthropogenic inputs of chemical environmental contaminants are frequently associated with developing harmful algal blooms, but little is known about how estuarine phytoplankton assemblages respond to multiple, co-occurring chemical stressors in chronically disturbed habitats. The goals of this research were to establish a robust protocol for testing the effects of atrazine on estuarine phytoplankton, and then to use that protocol to compare the effects of atrazine exposure with and without nutrient enrichment on a cosmopolitan estuarine/marine alga, Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyta). Atrazine sensitivity in nutrient-replete media (96-h growth inhibition \( \overline{x} \)) was 159.16 μg l−1, but sensitivity was influenced by exposure duration, and inhibitory effects of herbicide on algal growth decreased under imbalanced nutrient regimes and low nitrogen and phosphorus supplies. These findings advance knowledge about how nutrient regimes and herbicides interact to control estuarine phytoplankton population dynamics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1995) Standard methods for the examination for water and wastewater, 19th edn. Byrd Prepess Springfield, Washington, DC
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) (1996) Standard guide for conducting static 96-h toxicity tests with microalgae vol 11.05. ASTM, West Conshohocken
Behra R, Genoni G, Joseph A (1999) Effect of atrazine on growth, photosynthesis, and between-strain variability in Scenedesmus subspicatus (Chlorophyceae). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 37:36–41
Bérard A, Leboulanger C, Pelte T (1999) Tolerance of Oscillatoria limnetica Lemmermann to atrazine in natural phytoplankton populations and in pure culture: influence of season and temperature. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 37:472–479
Blaise C, Ferard JF, Vasseur P (1997) Microplate toxicity tests with microalgae: a review. In: Wells P, Lee K, Blaise C (eds) Microscale aquatic toxicology—advances, techniques and practice. CRC-Lewis Press, Boca Raton, pp 269–288
Blanck H, Wallin G, Wangberg SA (1984) Species-dependent variation in algal sensitivity to chemical compounds. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 8:339–351
Bricker SB, Longstaff B, Dennison W, Jones A, Boicourt K, Wicks C, Woerner J (2008) Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation’s estuaries: a decade of change. Harmful Algae 8:21–32
Burkholder JM, Glibert PM (2013) Eutrophication and oligotrophication. In: Levin S (ed) Encyclopedia of biodiversity, vol 3, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Waltham, pp 347–371
Carder JP, Hoagland KD (1998) Combined effects of alachlor and atrazine on benthic algal communities in artificial streams. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1415–1420
Chalifour A, Juneau P (2011) Temperature-dependent sensitivity of growth and photosynthesis of Scenedesmus obliquus, Navicula pelliculosa and two strains of Microcystis aeruginosa to the herbicide atrazine. Aquat Toxicol 103:9–17
Chao M-R, Chen C-Y (2001) Discrepancies between different response parameters in batch and continuous algal toxicity tests. J Hazard Mater 82:129–136
Cheung AY, Bogorad L, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1988) Relocating a gene for herbicide tolerance: a chloroplast gene is converted into a nuclear gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:391–395
Choi CJ, Berges JA, Young EB (2012) Rapid effects of diverse toxic water pollutants on chlorophyll a fluorescence: variable responses among freshwater microalgae. Water Res 46:2615–2262
Cook AM, Hutter R (1981) s-triazines as nitrogen sources for bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 29:1135–1143
DeLorenzo ME (2009) Utility of Dunaliella in ecotoxicity testing. In: Ben-Amotz A, Polle JEW, Subba Rao DV (eds) The alga Dunaliella. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 495–512
DeLorenzo ME, Serrano L (2003) Individual and mixture toxicity of three pesticides; atrazine, chlorpyrifos, and chlorothalonil to the marine phytoplankton species Dunaliella tertiolecta. J Environ Sci Health B 38:529–538
DeLorenzo ME, Serrano L (2006) Mixture toxicity of the antifouling compound irgarol to the marine phytoplankton species Dunaliella tertiolecta. J Environ Sci Health B 41:1349–1360
DeLorenzo M, Lauth J, Pennington P, Scott G, Ross P (1999) Atrazine effects on the microbial food web in tidal creek mesocosms. Aquat Toxicol 46:241–251
DeLorenzo ME, Scott GI, Ross PE (2001) Toxicity of pesticides to aquatic microorganisms: a review. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:84–98
DeLorenzo ME, Leatherbury M, Weiner JA, Lewitus AJ, Fulton MH (2004) Physiological factors contributing to the species-specific sensitivity of four estuarine microalgal species exposed to the herbicide atrazine. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 7:137–146
deNoyelles F, Kettle WD, Sinn DE (1982) The responses of plankton communities in experimental ponds to atrazine, the most heavily used pesticide in the United States. Ecology 63:1285–1293
Efron B (1982) The jackknife, the bootstrap and other resampling plans. Conference Board of the Mathematical Sciences - National Science Foundation Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematices Series, vol 38. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), Philadelphia, PA
Eisentraeger A, Dott W, Klein J, Hahn S (2003) Comparative studies on algal toxicity testing using fluorometric microplate and Erlenmeyer flask growth-inhibition assays. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54:346–354
Eisler R (1989) Atrazine hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. Biological Report 85(1.8), Contaminant Hazard Reviews Report No. 18. Laurel: US Fish and Wildlife Service
Fahl GM, Kreft L, Altenburger R, Faust M, Boedeker W, Grimme LH (1995) pH-dependent sorption, bioconcentration and algal toxicity of sulfonylurea herbicides. Aquat Toxicol 31:175–187
Fairchild JF, Ruessler DS, Carlson AR (1998) Comparative sensitivity of five species of macrophytes and six species of algae to atrazine, metribuzin, alachlor, and metolachlor. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1830–1834
Fleeger JW, Carman KR, Nisbet RM (2003) Indirect effects of contaminants in aquatic ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 317:207–233
Flood SL (2017) Ecotoxicology of estuarine phytoplankton growth and toxicity in response to atrazine exposures. Dissertation, North Carolina State University
Forney DR, Davis DE (1981) Effects of low concentrations of herbicides on submersed aquatic plants. Weed Sci 29:677–685
Gaggi C, Duccini M, Bacci E, Sbrilli G, Bucci M, Naby A (1995) Toxicity and hazard ranking of s-triazine herbicides using microtox® two green algal species and a marine crustacean. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1065–1069
Gascón J, Oubiña A, Barceló D (1997) Detection of endocrine-disrupting pesticides by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): application to atrazine. Trends Anal Chem 16:554–562
Geis SW, Fleming KL, Korthals ET, Searle G, Reynolds L, Karner DA (2000) Modifications to the algal growth inhibition test for use as a regulatory assay. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:36–41
Giddings JM (2005) Atrazine in North American surface waters : a probabilistic aquatic ecological risk assessment. Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC), Pensacola 432 p
Gilliom RJ, Barbash JE, Crawford CG, Hamilton PA, Martin JD, Nakagaki N, Nowell LH, Scott JC, Stackelberg PE, Thelin GP, Wolock DM (2006) Pesticides in the nation’s streams and ground water, 1992–2001, vol 1291. U.S. Geological Survey Circular, Reston, p 1291 172 p
Glibert PM, Fullerton D, Burkholder JM, Cornwell JC, Kana TM (2011) Ecological stoichiometry, biogeochemical cycling, invasive species, and aquatic food webs: San Francisco Estuary and comparative systems. Rev Fish Sci 19:358–417
Glotfelty D, Taylor A, Isensee A, Jersey J, Glenn S (1984) Atrazine and simazine movement to Wye River estuary. J Environ Qual 13:115–121
Graymore M, Stagnitti F, Allinson G (2001) Impacts of atrazine in aquatic ecosystems. Environ Int 26:483–495
Guasch H, Sabater S (1998) Light history influences the sensitivity to atrazine in periphytic algae. J Phycol 34:233–241
Guillard RR (1973) Division rates. In: Stein JR (ed) Handbook of phycological methods—culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 239–311
Guillard RR, Hargraves P (1993) Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte. Phycologia 32:234–236
Gustavson K, Wängberg S-Å (1995) Tolerance induction and succession in microalgae communities exposed to copper and atrazine. Aquat Toxicol 32:283–302
Hamala JA, Kollig HP (1985) The effects of atrazine on periphyton communities in controlled laboratory ecosystems. Chemosphere 14:1391–1408
Hatfield PM, Guikema JA, John JBS, Gendel SM (1989) Characterization of the adaptation response of Anacystis nidulans to growth in the presence of sublethal doses of herbicide. Curr Microbiol 18:369–374
Hewitt M, Ellison C, Enoch S, Madden J, Cronin M (2010) Integrating (Q) SAR models, expert systems and read-across approaches for the prediction of developmental toxicity. Reprod Toxicol 30:147–160
Hickey C, Blaise C, Costan G (1991) Microtesting appraisal of ATP and cell recovery toxicity end points after acute exposure of Selenastrum capricornutum to selected chemicals. Environ Toxicol Water 6:383–403
Howard P (1991) Handbook of environmental fate and exposure data for organic chemicals, vol 3. Lewis, Chelsea
Huber W (1993) Ecotoxicological relevance of atrazine in aquatic systems. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1865–1881
Hylland K, Vethaak AD (2011) Impact of contaminants on pelagic ecosystems. Chapter 10 In: Sánchez-Bayo F, van den Brink PJ, Mann RM (eds) Ecological impacts of toxic chemicals. Bentham Science Publishers Ltd, Sharjah, pp 271–287
ISO 10253 (1995) Water quality––marine algal growth inhibition test with Skeletonema costatum and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. International Organization for Standardization, Geneve, Switzerland
Jablonowski ND, Schäffer A, Burauel P (2011) Still present after all these years: persistence plus potential toxicity raise questions about the use of atrazine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:328–331
Janssen CR, Heijerick DG (2003) Algal toxicity tests for environmental risk assessments of metals. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 178:23–52
Jones T, Kemp W, Stevenson J, Means J (1982) Degradation of atrazine in estuarine water/sediment systems and soils. Environ Qual 11:632–638
Kasai F, Takamura N, Hatakeyama S (1993) Effects of simetryne on growth of various freshwater algal taxa. Environ Pollut 79:77–83
Koenig F (1990) Shade adaptation in cyanobacteria. Photosynth Res 26:29–37
Lehotay SJ, Harman-Fetcho JA, McConnell LL (1998) Agricultural pesticide residues in oysters and water from two Chesapeake Bay tributaries. Mar Pollut Bull 37:32–44
Lewis MA (1990a) Are laboratory-derived toxicity data for freshwater algae worth the effort? Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1279–1284
Lewis MA (1990b) Chronic toxicities of surfactants and detergent builders to algae: a review and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 20:123–140
Lewis MA (1995) Use of freshwater plants for phytotoxicity testing: a review. Environ Pollut 87:319–336
Lockert C, Hoagland KD, Siegfried BD (2006) Comparative sensitivity of freshwater algae to atrazine. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 76:73–79
Lytle JS, Lytle TF (2001) Use of plants for toxicity assessment of estuarine ecosystems. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:68–83
McCarthy AM, Bales JD, Cope WG, Shea D (2007) Modeling pesticide fate in a small tidal estuary. Ecol Model 200:149–159
McLachlan J (1960) The culture of Dunaliella tertiolecta Butcher—a euryhaline organism. Can J Microbiol 6:367–379
Mohan B, Hosetti B (1999) Aquatic plants for toxicity assessment. Environ Res 81:259–274
Moreland D, Hill K (1962) Interference of herbicides with the Hill reaction of isolated chloroplasts. Weeds 10:229–236
Norberg-King TJ (1993) A linear interpolation method for sublethal toxicity: the inhibition concentration (ICp) approach. National Effluent Toxicity Assessment Center Technical Report, vol 39. Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Research Laboratory, Duluth, pp 03–93
Nyholm N (1985) Response variable in algal growth inhibition tests—biomass or growth rate? Water Res 19:273–279
Nyholm N (1990) Expression of results from growth inhibition toxicity tests with algae. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:518–522
Nyholm N, Källqvist T (1989) Methods for growth inhibition toxicity tests with freshwater algae. Environ Toxicol Chem 8:689–703
Nyholm N, Lyngby JE (1988) Algal bioassays in eutrophication research—a discussion in the framework of a mathematical analysis. Water Res 22:1293–1300
OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation Development) (1998) Alga, growth inhibition test. OCED Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals. OECD, Paris
Pannard A, Le Rouzic B, Binet F (2009) Response of phytoplankton community to low-dose atrazine exposure combined with phosphorus fluctuations. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57:50–59
Pate AS, De Souza AE, Farrow DRG (1992) Agricultural pesticide use in coastal areas: a national summary. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Rockville
Patlewicz G, Ball N, Booth ED, Hulzebos E, Zvinavashe E, Hennes C (2013) Use of category approaches, read-across and (Q) SAR: general considerations. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 67:1–12
Pennington PL, Scott GI (2001) Toxicity of atrazine to the estuarine phytoplankter Pavlova sp. (Prymnesiophyceae): increased sensitivity after long-term, low-level population exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2237–2242
Pennington PL, Daugomah JW, Colbert AC, Fulton MH, Key PB, Thompson BC, Strozier ED, Scott GI (2001) Analysis of pesticide runoff from mid-Texas estuaries and risk assessment implications for marine phytoplankton. J Environ Sci Health B 36:1–14
Pereira WE, Rostad CE (1990) Occurrence, distributions, and transport of herbicides and their degradation products in the lower Mississippi River and its tributaries. Environ Sci Technol 24:1400–1406
Peterson HG, Healey FP, Wagemann R (1984) Metal toxicity to algae: a highly pH dependent phenomenon. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 41:974–979
Radosevich SR, Holt JS, Ghersa CM (2007) Ecology of weeds and invasive plants: relationship to agriculture and natural resource management. Wiley, New York
Redfield AC (1958) The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am Sci 46:230A–2221
Rohr JR, McCoy KA (2010) A qualitative meta-analysis reveals consistent effects of atrazine on freshwater fish and amphibians. Environ Health Perspect 118:20–32
Rohr JR, Kerby JL, Sih A (2006) Community ecology as a framework for predicting contaminant effects. Trends Ecol Evol 21:606–613
Rojíčková R, Maršálek B (1999) Selection and sensitivity comparisons of algal species for toxicity testing. Chemosphere 38:3329–3338
Ryberg KR, Vecchia AV, Martin JD, Gilliom RJ (2010) Trends in pesticide concentrations in urban streams in the United States, 1992-2008. USGS, Reston
Sanders JG (1979) Effects of arsenic speciation and phosphate concentration on arsenic inhibition of Skeletonema costatum (Bacillariophyceae). J Phycol 15:424–428
Scott GI, Holland AF, Sandifer PA (2006) Afterword—managing coastal urbanization and development in the twenty-first century: the need for a new paradigm. In: Changing land use patterns in the coastal zone. Springer, New York, pp 285–299
Sjollema SB, Vavourakis CD, Geest H, Vethaak AD, Admiraal W (2014) Seasonal variability in irradiance affects herbicide toxicity to the marine flagellate Dunaliella tertiolecta. Front Mar Sci 1:1–5
Solomon KR, Baker DB, Richards RP, Dixon KR, Klaine SJ, La Point TW, Kendall RJ, Weisskopf CP, Giddings JM, Giesy JP (1996) Ecological risk assessment of atrazine in North American surface waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:31–76
Solomon KR, Carr JA, Du Preez LH, Giesy JP, Kendall RJ, Smith EE, Van Der Kraak GJ (2008) Effects of atrazine on fish, amphibians, and aquatic reptiles: a critical review. Crit Rev Toxicol 38:721–772
Sorokin C (1973) Dry weight, packed cell volume and optical density. In: Stein J (ed) Handbook of phycological methods—culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 321–343
Southwick L, Grigg B, Fouss J, Kornecki T (2003) Atrazine and metolachlor in surface runoff under typical rainfall conditions in southern Louisiana. J Agric Food Chem 51:5355–5361
Starr AV, Bargu S, Maiti K, DeLaune RD (2017) The effect of atrazine on Louisiana Gulf Coast estuarine phytoplankton. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 72:178–188
Stauber J (1995) Toxicity testing using marine and freshwater unicellular algae. Australas J Ecotoxicol 1:15–24
Stephan CE, Mount DI, Hansen DJ, Gentile J, Chapman GA, Brungs WA (1985) Guidelines for deriving numerical national water quality criteria for the protection of aquatic organisms and their uses. US EPA, Duluth
Stratton GW, Giles J (1990) Importance of bioassay volume in toxicity tests using algae and aquatic invertebrates. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 44:420–427
Strong LC, Rosendahl C, Johnson G, Sadowsky MJ, Wackett LP (2002) Arthrobacter aurescens TC1 metabolizes diverse s-triazine ring compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5973–5980
Swanson SM, Rickard CP, Freemark KE, MacQuarrie P (1991) Testing for pesticide toxicity to aquatic plants: recommendations for test species. In: Gorsuch JW, Lower WR, Wang W, Lewis MA (eds) Plants for toxicity assessment: second volume, edition ASTM STP 1115. West Conshohocken, ASTM, pp 77–97
Tang J-X, Hoagland KD, Siegfried BD (1997) Differential toxicity of atrazine to selected freshwater algae. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:631–637
Tang J, Hoagland KD, Siegfried BD (1998) Uptake and bioconcentration of atrazine by selected freshwater algae. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1085–1090
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1971) Algal Assay Procedure Bottle Test. National Eutrophication Research Program. Pacific Northwest Environmental Research Laboratory, US EPA, Corvallis
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1974) Marine algal assay procedure: bottle test. US EPA National Environmental Research Center, Corvallis
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1985) Toxic substances control act test guidelines; final rules—environmental effects testing guidelines, algal acute toxicity test. Federal Register, 40 CFR Part 797.1050, pp. 39321–39331
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2007) National water quality inventory: report to Congress, 2002 Reporting Cycle. Report #EPA 841-R-07-011. U.S. EPA, Washington, DC
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2016) Refined ecological risk assessment for atrazine. U.S. EPA, Washington, DC
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2017) ECOTOX User Guide: ECOTOXicology Knowledgebase System. Version 4.0. US EPA, Washington, DC
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) (2017) Census of Agriculture. National Agricultural Statistics Service. USDA, Washington, DC
Van Der Kraak GJ, Hosmer AJ, Hanson ML, Kloas W, Solomon KR (2014) Effects of atrazine in fish, amphibians, and reptiles: an analysis based on quantitative weight of evidence. Crit Rev Toxicol 44:1–66
Van Donk E, Abdel-Hamid M, Faafeng B, Källqvist T (1992) Effects of Dursban® 4E and its carrier on three algal species during exponential and P-limited growth. Aquat Toxicol 23:181–191
Vollenweider RA (ed) (1974) A manual on methods for measuring primary production in aquatic environments, 2nd edn. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Walsh GE, McLaughlin LL, Yoder MJ, Moody PH, Lores EM, Forester J, Wessinger-Duvall PB (1988) Minutocellus polymorphus: a new marine diatom for use in algal toxicity tests. Environ Toxicol Chem 7:925–929
Weiner JA, DeLorenzo ME, Fulton MH (2007) Atrazine induced species-specific alterations in the subcellular content of microalgal cells. Pestic Biochem Physiol 87:47–53
Wells PG, Lee K, Blaise C (1997) Microscale testing in aquatic toxicology: advances, techniques, and practice. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wood RJ, Mitrovic SM, Kefford BJ (2014) Determining the relative sensitivity of benthic diatoms to atrazine using rapid toxicity testing: a novel method. Sci Total Environ 485:421–427
Yates BS, Rogers WJ (2011) Atrazine selects for ichthyotoxic Prymnesium parvum, a possible explanation for golden algae blooms in lakes of Texas, USA. Ecotoxicology 20:2003–2010
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, pp 389–394
Acknowledgements
We thank Geoff Scott, Marie DeLorenzo, Stacy Nelson, Parke Rublee, and Tom Wentworth for their counsel. We also thank the NCSU CAAE staff and students for their many actions in helping to make this research possible. Funding support was provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration—National Ocean Service, the National Park Service, the North Carolina General Assembly, and the Department of Plant and Microbial Biology at North Carolina State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flood, S., Burkholder, J. & Cope, G. Assessment of atrazine toxicity to the estuarine phytoplankter, Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyta), under varying nutrient conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 11409–11423 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1310-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1310-1