Abstract
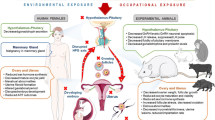
Pesticides are a complex mixture of chemicals used to protect crops from a number of pests and diseases. They have been considered as potential mutagenic agents. This study aims at evaluation of the mutagenic effect of pesticide exposure to agricultural workers through chromosomal aberrations (CA) and micronucleus (MN) assay in peripheral blood lymphocytes and oral mucosal cells, respectively. The exposed group was consisted with 97 farmers, while the control (un-exposed) group consisted of 55. The results showed a significant (p < 0.05) increase in frequency of CA and MN in the exposed group. Both CA and MN profiles were linked to a significant (p < 0.05) co-relation with the confounding factors such as smoking habits, alcohol, vegetables, tea/coffee, vitamins, and sweetener consumptions. More cytogenetic events were denoted in smoking and alcohol consumption as well as non-personal protective equipment (non-PPE) and low/no vegetables user farmers. In conclusion, a deficiency of dietary and medicaments-derived antioxidants, while consumption of alcohol and tobacco, as well as effects of radiation, heavy metal poisoning (especially from sweeteners), and non-PPE using habits, may contribute cytogenetic damage to the workers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavanja MC, Samanic C, Dosemeci M, Lubin J, Tarone R, Lynch CF, Knott C, Thomas K, Hoppin JA, Barker J et al (2003) Use of agricultural pesticides and prostate cancer risk in the agricultural health study cohort. Am J Epidemiol 157:800–814. doi:10.1093/aje/kwg040
Alvarez-Moya C, Silva MR, Ramírez CV, Gallardo DG, Sánchez RL, Aguirre AC, Velasco AF (2014) Comparison of the in vivo and in vitro genotoxicity of glyphosate isopropylamine salt in three different organisms. Genet Mol Biol 37:105–110
Benedetti D, Nunes E, Sarmento M, Porto C, dos Santos CE, Dias JF, da Silva J (2013) Genetic damage in soybean workers exposed to pesticides: evaluation with the comet and buccal micronucleus cytome assays. Mutat Res 752:28–33. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.01.001
Bolognesi C, Perrone E, Landini E (2002) Micronucleus monitoring of a floriculturist population from western Liguria, Italy. Mutagenesis 17:391–397. doi:10.1093/mutage/17.5.391
Bolognesi C (2003) Genotoxicity of pesticides: a review of human biomonitoring studies. Mutat Res 543:251–272. doi:10.1016/S1383-5742(03)00015-2
Bonassi S, Coskun E, Ceppi M, Lando C, Bolognesi C, Burgaz S, Holland N, Kirsh-Volders M, Knasmueller S, Zeiger E et al (2011) The human micronucleus project on exfoliated buccal cells (HUMN(XL)): the role of life-style, host factors, occupational exposures, health status, and assay protocol. Mutat Res 728:88–97. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2011.06.005
Carrano AV, Natarajan AT (1988) International Commission for Protection Against Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens. ICPEMC publication no. 14. Considerations for population monitoring using cytogenetic techniques. Mutat Res 204:379–406. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(88)90036-5
Casida JE (2009) Pest toxicology: the primary mechanisms of pesticide action. Chem Res Toxicol 22:609–619. doi:10.1021/tx8004949
Costa C, Teixeira JP, Silva S, Alves M, Laffon B, Rueff J, Mayan O (2006) Cytogenetic and molecular biomonitoring of a Portuguese population exposed to pesticides. Mutagenesis 21:343–350. doi:10.1093/mutage/gel039
Fujita M, Sasanuma H, Yamamoto KN, Harada H, Kurosawa A, Adachi N, Omura M, Hiraoka M, Takeda S, Hirota K (2013) Interference in DNA replication can cause mitotic chromosomal breakage unassociated with double-strand breaks. PLoS One 8:e60043. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060043
Gaikwad AS, Karunamoorthy P, Kondhalkar SJ, Ambikapathy M, Beerappa R (2015) Assessment of hematological, biochemical effects and genotoxicity among pesticide sprayers in grape garden. J Occup Med Toxicol 10:1–6. doi:10.1186/s12995-015-0049-6
Hu H, Deng Y, Fan Y, Zhang P, Sun H, Gan Z, Zhu H, Yao Y (2016) Effects of artificial sweeteners on metal bioconcentration and toxicity on a green algae Scenedesmus obliquus. Chemosphere 150:285–293. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.043
Islam MT, Leticia Streck L, Paz MFCJ, Sousa JMC, Alencar MVOB, Mata AMOF, Carvalho RM, Santos JVO, Silva-Junior AA, Ferreira PMP, Melo-Cavalcante AAC (2016a) Preparation of phytol-loaded nanoemulsion and screening for antioxidant capacity. Int Arch Med 9(70):1–15. doi:10.3823/1941
Islam MT, Alencar MVOB, Mata AMOF, Paz MFCJ, Matos LA, Sousa JMC, Melo-Cavalcante AAC (2016b) Coffee: a health fuel-blot popular drinking. Int J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci 8:1–7
Islam MT (2016) Concentration-dependent activities of diterpenes: achieving anti-/pro-oxidant links. A-JEMF 2:12–15. doi:10.15272/ajemf.v2016i5.57
Kausar A, Giri S, Roy P, Giri A (2014) Changes in buccal micronucleus cytome parameters associated with smokeless tobacco and pesticide exposure among female tea garden workers of Assam, India. Int J Hyg Environ Health 217:169–175. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2013.04.007
Keller-Byrne JE, Khuder SA, Schaub EA (1995) Meta-analyses of prostate cancer and farming. Am J Ind Med 71:1–10. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0274(199705)31:5<580::AID-AJIM13>3.0.CO;2-V
Kvitko K, Bandinelli E, Henriques JAP, Heuser VD, Rohr P, da Silva FR, da Silva J (2012) Susceptibility to DNA damage in workers occupationally exposed to pesticides, to tannery chemicals and to coal dust during mining. Genet Mol Biol 35:1060–1068
Liu Y, Li CM, Lu Z, Ding S, Yang X, Mo J (2006) Studies on formation and repair of formaldehyde-damaged DNA by detection of DNA-protein crosslinks and DNA breaks. Front Biosci 11:991–997. doi:10.2741/1856
Maryam Z, Sajad A, Maral N, Zahra L, Sima P, Zeinab A, Zahra M, Fariba E, Sezaneh H, Davood M (2015) Relationship between exposure to pesticides and occurrence of acute leukemia in Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16:239–244
Moorhead PS, Nowell PC, Mellman WJ, Battips DM, Hungerford DA (1960) Chromosome preparations of leukocytes cultured from human peripheral blood. Exp Cell Res 20:613–616. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(60)90138-5
Naga MB, Gour S, Nallagutta N, Ealla KK, Velidandla S, Manikya S (2016) Buccal micronucleus cytome assay in sickle cell disease. J Clin Diagn Res 10:ZC62–ZC64. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/19984.7998
Nazam N, Lone MI, Shaikh S, Ahmad W (2013) Assessment of genotoxic potential of the insecticide Dichlorvos using cytogenetic assay. Interdiscip Toxicol 6:77–82. doi:10.2478/intox-2013-0014
Prasad S, Srivastava S, Singh M, Shukla Y (2009) Clastogenic effects of glyphosate in bone marrow cells of Swiss albino mice. J Toxicol 2009:308985. doi:10.1155/2009/308985
Ross AJ, Blair A, Rusiecki JA, Hoppin JA, Svec M, Dosemeci M, Sandler DP, Alavanja MC (2005) Cancer incidence among glyphosate-exposed pesticide applicators in the agricultural health study. Environ Health Persp 113:49–54. doi:10.1289/ehp.7340
Salaija N, Chandrasekhar M, Rekhadevi PV, Mahboob M, Rahman MF, Vuyyuri SB, Danadevi K, Hussain SA, Grover P (2006) Genotoxic evaluation of workers employed in pesticide production. Mutat Res 609:74–80. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.06.022
Silva RG, Alencar MVOB, Teixeira JS, Silva RR, Paz MFCJ, Sousa JMC, Mata AMOF, Santos JVO, Islam MT, Melo-Cavalcante AAC, Picada JN (2016a) Genotoxicity and DNA repair indicative in blood cells after occupational exposure to ionizing radiation. Int Arch Med 9(121):1–13. doi:10.3823/1992
Silva RG, Islam MT, Carvalho RM, Alencar MVOB, Júnior ALG, Aguiar RPS, Mata AMOF, Sousa JMC, Paz MFCJ, Ferreira PMP, Dantas SMMM, Melo-Cavalcante AAC, Picada JN (2016b) Toxicogenetic biomonitoring of workers to the ionizing radiation. Afric J Pharm Pharmacol 10:604–613. doi:10.5897/AJPP2016.4584
Singh VK, Jyoti R, Reddy MM, Kesavachandran C, Rastogi SK, Siddiqui MK (2007) Biomonitoring of organochlorines, glutathione, lipid peroxidation and cholinesterase activity among pesticide sprayers in mango orchards. Clin Chim Acta 377:268–272. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2006.08.037
Sram RJ, Beskid O, Binkova B, Chvatalova I, Lnenickova Z, Milcova A, Solansky I, Tulupova E, Bavorova H, Ocadlikova D et al (2007) Chromosomal aberrations in environmentally exposed population in relation to metabolic and DNA repair genes polymorphisms. Mutat Res 620:22–33. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2007.02.019
Yang HY, Feng R, Liu J, Wang HY, Wang YD (2014) Increased frequency of micronuclei in binucleated lymphocytes among occupationally pesticide-exposed populations: a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:6955–6960
Acknowledgements
We acknowledged the Department of Health, Piauí, through the Laboratory for Toxicology and Molecular Genetics (LABTOXGEN/LACEN-PI) and volunteers from the municipalities of Piauí, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaves, T.V.S., Islam, M.T., de Moraes, M.O. et al. Occupational and life-style factors-acquired mutagenicity in agric-workers of northeastern Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 15454–15461 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9150-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9150-y