Abstract
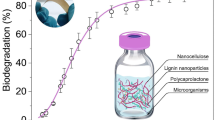
Intensive aquaculture needs to adopt techniques that are able to contribute towards sustainability. Closed systems that employ water recirculation can combine intensive production with environmental sustainability, since there is no exchange of water or discharge of effluents into the environment. In order to achieve this, effective filtration systems are required to ensure that the water quality is satisfactory for the cultivation of aquatic organisms. Chitosan, an industrial waste material derived from crustacean farming, is a renewable natural material that is biodegradable and possesses adsorbent characteristics. In this work, chitosan foam was incorporated in filters and was evaluated as an adsorbent of aquaculture pollutants, adding value to the material and at the same time providing a use for industrial waste. The foam was characterized by scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy, apparent density, and water absorption capacity. It was used to remove ammonia, nitrite, orthophosphate, and turbidity from aquaculture effluents. The foam consisted of a bilayer with smooth and porous sides, which presented low density, flexibility, and high water absorption capacity. The best proportion of the foam, in terms of the mass of foam per volume of solution (% m v−1), was 0.10, which resulted in removal of 32.8, 57.2, 89.5, and 99.9% of ammonia, nitrite, orthophosphate, and turbidity, respectively. This biopolymer produced is biodegradable, and when saturated with organic compounds from aquaculture, and no longer suitable for reuse as a filter material, it can be employed as a fertilizer, hence closing the sustainability cycle of the aquaculture production chain.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 4500-P E. Ascorbic acid method. 21ª ed. Washington, pp.4–153
Ali ZM, Laghari AJ, Ansari AK, Khuhawar MY (2013) Extraction and Characterization of Chitosan from Indian Prawn (Fenneropenaeus indicus) and its Applications on Waste Water Treatment of Local Ghee Industry. IOSR J Engineering (IOSRJEN) 3(10):28–37, e-ISSN: 2250–3021. Available in: http://www.iosrjen.org/Papers/vol3_issue10%20(part-2)/D031022837.pdf. https://doi.org/10.9790/3021-031022837
Arana, L.V., 2010. Qualidade da água em aquicultura: princípios e práticas. 3. ed. rev. e modif. Ed. da UFSC, 238 p., Florianópolis, SC, Brazil, ISBN13:9788532804891
Azevedo VVC, Chaves AS, Bezerra DC, Lia Fook MV, Costa ACFM (2007) Quitina e Quitosana: aplicações como biomateriais. Revista Eletrônica de Materiais e Processos 2(3):27–34 2007. ISSN 1809–8797. Available in: http://www2.ufcg.edu.br/revista-remap/index.php/REMAP/article/viewFile/46/81
Baumgarten, M.G.Z., 1996. Manual de análises em oceanografia química. Ed. Furg,132p., Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, ISBN: 858504246X
Bregnballe, J., 2015. A Guide to Recirculation Aquaculture: An introduction to the new environmentally friendly and highly productive closed fish farming systems. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and EUROFISH International Organisation, 100 p., ISBN 978–92–5-108776-3. Available in: <http://www.fao.org/3/a-i4626e.pdf> Acesso em: 11/08/2016
Carvalho, G., Frollini, E., 1999. Lignina em espumas fenólicas. Polímeros, 9 (1). Available in: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-14281999000100009
Chung YC, Li YH, Chen CC (2005) Pollutant removal from aquaculture wastewater using the biopolymer chitosan at different molecular weights. J Environ Sci Heal A 40(9):1775–1790. https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-200068058
Chung YC (2006) Improvement of aquaculture wastewater using chitosan of different degrees of deacetylation. Environ Technol 27(11):1199–1208. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332708618734
Coelho GF, Gonçalves AC Jr, Sousa RFB, Schwantes D, Miola AJ, Domingues CVR (2014) Use of adsorption techniques utilizing agroindustrial waste in the removal of contaminants in Waters. J Agronomic Sci 3:291–317. Avaliable in: http://www.dca.uem.br/V3NE/21.pdf
Comiotto, C.E.G., Lopes, M.A., Dotto, G.L., Pinto, L.A.A., 2014. Remoção de turbidez e sólidos totais de efluentes do processo de obtenção de quitina. Blucher Chemical Engineering Proceedings, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.5151/chemeng-cobec-ic-01-ea-024
Eddy FB (2005) Ammonia in estuaries and effects on fish. J Fish Biol 67(6):1495–1513. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2005.00930.x
Favere, V.T., Riella, H.G., Rosa, S., 2010. Cloreto de n-(2-hidroxil) propil-3-trimetil amônio quitosana como adsorvente de corantes reativos em solução aquosa. Química Nova [online]. 33(7), 1476–1481, ISSN 0100–4042. Avaliable in: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422010000700010
Gaouar Yadi, M., Benguella, B., Gaouar-Benyelles, N., Tizaoui, K., 2015. Adsorption of ammonia from wastewater using low-cost bentonite/chitosan beads. Desalination and Water Treatment, ISSN: 1944–3994 (Print) 1944–3986 (Online). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1119747
García, M.A., Montelongo, I., Rivero, A., de la Paz, N., Fernández, M., et al., 2016. Treatment of Wastewater from Fish Processing Industry using Chitosan Acid Salts. Int Water Wastewater Treat 2(2), Avaliable in: 10.16966/2381-5299.121
Haseena PV, Padmavathy KS, Rohit Krishnan P, Madhu G (2016) Adsorption of ammonium nitrogen from aqueous systems using chitosan-Bentonite film composite. Procedia Technol 24:733–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2016.05.203
Jabbar Z, Angham A, Sami GHF (2014) Removal of azo dye from aqueous solutions using chitosan. Oriental Journal of Chemistry 30(2): 571-575. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/300222
Jing L, Kaixuan T, Zhipan G (2008) Study on the Adsorption of Nitrite in Water with Crosslinked Chitosan. 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering ICBBE ’08, Shanghai, pp. 3673–3676. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBBE.2008.420
Kyzas GZ, Bikiaris DN (2015) Recent modifications of chitosan for adsorption applications: a critical and systematic review. Mar Drugs 13(1):312–337. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010312
Koroleff, F., 1976. Determination of nutrients. In Methods of seawater analysis (K. Grasshoff, ed.). Verlag Chemie Weinheim, New York, p.117–181
Lazzari R, Baldisserotto B (2008) Nitrogen and phosphorus waste in fish farming. Bol. Inst. Pesca 34(4):591–600 Avaliable in: http://www.pesca.sp.gov.br/34_4_591-600.pdf
Lertsutthiwong P, Boonpuak D, Pungrasmi W, Powtongsook S (2013) Immobilization of nitrite oxidizing bacteria using biopolymeric chitosan media. J. Environ. Sci 25(2):262–267, Avaliable in. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60059-X
Lucena GL, Silva AG, Honório LMC, Santos VD (2015) Avaliação da Capacidade de Adsorção da Quitosana Quaternizada na Remoção de Íons Cu2+ e Cr3+. Rev. Virtual Quim 7(6):2166–2179, ISSN: 1984–6835. https://doi.org/10.5935/1984–6835.20150128
Mallasen M, Barros HP, Yamashita EY (2008) Produção de peixes em tanques-rede e a qualidade da água. Revista Tecnologia & Inovação Agropecuária 1(1):47–51. Avaliable in: http://www.apta.sp.gov.br/publicacoes/T&IA/T&IAv1n1/Revista_Apta_Artigo_Qualidade_de_Agua.pdf
Martins CIM, Edinga EH, Verdegema MCJ, Heinsbroeka LTN, Schneiderc O, Blanchetond JP, Roque D’orbcasteld E, Verretha JAJ (2010) New developments in recirculating aquaculture systems in Europe: A perspective on environmental sustainability. Aquacultural Engineering 43(3):83–93, Avaliable in. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2010.09.002
Moro, G. V., Torati, L. S., Luiz, D. B., Matos, F. T., 2013. Monitoramento e manejo da qualidade da água em pisciculturas. In: LIMA, A. F. (Org). Piscicultura de água doce: multiplicando conhecimentos. Brasília, DF: Embrapa, 2013. 440p
Muniz, G. I. B., Masson, M. L., Ellendersen, L. S. N., Alves, H.J., 2015. Patente: Privilégio de Inovação. Número do registro: BR1020150292597: "Uso e obtenção de espuma seca e pó de quitosana e nanoquitosana por processo de secagem pelo método de camada de espuma", Instituição de registro: INPI - Instituto Nacional da Propriedade Industrial. Depósito: 23/11/2015, Brasil, 2015
Muniz, G. I. B.; Ellendersen, L. S. N.; Alves, H. J.; Zadinelo, I.V.; Santos, L. D. dos Milinsk, M. C.; Feroldi, M., 2017. Patente: Privilégio de Inovação. Número do registro: BR1020170138070: "Equipamento - filtro a base de espuma de quitosana e/ou nanoquitosana", Instituição de registro: INPI - Instituto Nacional da Propriedade Industrial. Depósito: 26/06/2017, Brasil, 2017
Nascimento, R.F., Lima, A.C.A., Vidal, C.B., Melo, D.Q., Raulino, G.S.C., 2014. Adsorção: aspectos teóricos e aplicações ambientais. Fortaleza: Imprensa Universitária, 2014. 256 p. ISBN: 978–85–7485-186-0
Pereira FV, Paula EL, Mesquita JP, Lucas AA, Mano V (2014) Bionanocompósitos preparados por incorporação de nanocristais de celulose em Polímeros biodegradáveis por meio de evaporação de solvente, automontagem ou Eletrofiação. Quim. Nova 37(7):1209–1219. https://doi.org/10.5935/0100-4042.20140141
Randall, D. J., Tsui, T. K. N., 2002. Ammonia toxicity in fish. Marine Pollution Bulletin 45, 17–23. Avaliable in: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00227-8
Srinatha A, Pandit JK, Singh S (2008) Ionic cross-linked chitosan beads for extended release of ciprofloxacin: In vitro characterization. Indian J Pharm Sci 70(1):16–21. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.40326
Silva APO, Melo JV, Melo JLS, Pedroza MM (2011) Remoção de íons chumbo (Pb2+) de efluentes sintéticos através de adsorção em vermiculita revestida com quitosana. Revista Liberato, Novo Hamburgo 12(17):01–106. Available in:http://www.liberato.com.br/sites/default/files/arquivos/Revista_SIER/v.%2012%2C%20n.%2017%20%282011%29/3.%20Remo%E7%E3o%20de%20%CDons.pdf
Yanbo W, Wenju Z, Weifen L, Zirong X (2006) Acute toxicity of nitrite on tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) at different external chloride concentrations. Fish Physiol Biochem 32(1):49–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-005-5744-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Highlights
• The use of adsorption is a sustainable alternative for water treatment
• Filters filled with chitosan foam adsorb aquaculture pollutants
• Higher dosages of the chitosan foam resulted in lower adsorption of the pollutants
• The best dosage (% m v−1) of the foam in the adsorption filter was 0.10
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zadinelo, I.V., dos Santos, L.D., Cagol, L. et al. Adsorption of aquaculture pollutants using a sustainable biopolymer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 4361–4370 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0794-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0794-4