Abstract
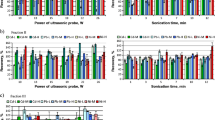
Ultrasonic probe sonication (UPS) and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) were used for rapid single extraction of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn from soils polluted by former mining activities (Mónica Mine, Bustarviejo, NW Madrid, Spain), using 0.01 mol L−1 calcium chloride (CaCl2), 0.43 mol L−1 acetic acid (CH3COOH), and 0.05 mol L−1 ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) at pH 7 as extracting agents. The optimum extraction conditions by UPS consisted of an extraction time of 2 min for both CaCl2 and EDTA extractions and 15 min for CH3COOH extraction, at 30% ultrasound (US) amplitude, whereas in the case of MAE, they consisted of 5 min at 50 °C for both CaCl2 and EDTA extractions and 15 min at 120 °C for CH3COOH extraction. Extractable concentrations were determined by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). The proposed methods were compared with a reduced version of the corresponding single extraction procedures proposed by the Standards, Measurements and Testing Programme (SM&T). The results obtained showed a great variability on extraction percentages, depending on the metal, the total concentration level and the soil sample, reaching high values in some areas. However, the correlation analysis showed that total concentration is the most relevant factor for element extractability in these soil samples. From the results obtained, the application of the accelerated extraction procedures, such as MAE and UPS, could be considered a useful approach to evaluate rapidly the extractability of the metals studied.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano DC (2001) Trace elements in the terrestrial environment. Biogeochemistry, bioavailability and risks of metals, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Alvarenga PM, Araújo MF, Silva JAL (2004) Elemental uptake and root-leaves transfer in Cistus ladanifer L. growing in a contaminated pyrite mining area (Aljustrel-Portugal). Water Air Soil Poll 152:81–96. doi:10.1023/B:WATE.0000015333.24165.5e
Antosiewicz DM, Escudĕ-Duran C, Wierzbowska E, Skłodowska A (2008) Indigenous plant species with the potential for the phytoremediation of arsenic and metals contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Poll 193:197–210. doi:10.1007/s11270-008-9683-2
Anawar HM, García-Sánchez A, Santa Regina I (2008) Evaluation of various chemical extraction methods to estimate plant-available arsenic in mine soils. Chemosphere 70:1459–1467. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.058
Arain MB, Kazi TG, Jamali MK, Jalbani N, Afridi HI, Baig JA (2008) Speciation of heavy metals in sediment by conventional, ultrasound and microwave assisted single extraction methods: a comparison with modified sequential extraction procedure. J Hazard Mater 154:998–1006. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.004
De la Calle I, Cabaleiro N, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2013) Ultrasound-assisted single extraction tests for rapid assessment of metal extractability from soils by total reflection X-ray fluorescence. J Hazard Mater 260:202–209. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.05.021
Fedotov PS, Kördel W, Miró M, Peijnenburg WJGM, Wennrich R, Huang PM (2012) Extraction and fractionation methods for exposure assessment of trace metals, metalloids, and hazardous organic compounds in terrestrial environments. Crit Rev Env Sci Tech 42:1117–1171. doi:10.1080/10643389.2011.556544
García-Casillas D, García-Salgado S, Quijano MA (2014) Accuracy evaluation of ultrasound probe sonication and microwave-assisted extraction systems for rapid single extraction of metals in soils. Anal Methods 6:8403–8412. doi:10.1039/c4ay01788a
García-Salgado S, García-Casillas D, Quijano-Nieto MA, Bonilla-Simón MM (2012) Arsenic and heavy metal uptake and accumulation in native plant species from soils polluted by mining activities. Water Air Soil Poll 223:559–572. doi:10.1007/s11270-011-0882-x
Houba VJG, Temminghoff EJM, Gaikhorst GA, Van Vark W (2000) Soil analysis procedures using 0.01 M calcium chloride as extraction reagent. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:1299–1396. doi:10.1080/00103620009370514
Jamali MK, Kazi TG, Arain MB, Afridi HI, Jalbani N, Kandhro GA, Shah AQ, Baig JA (2009) Speciation of heavy metals in untreated sewage sludge by using microwave assisted sequential extraction procedure. J Hazard Mater 163:1157–1164. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.071
Jung MC (2008) Contamination by Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn in mine wastes from abandoned metal mines classified as mineralization types in Korea. Environ Geochem Health 30:205–217. doi:10.1007/s10653-007-9109-x
Kabata-Pendias A (2004) Soil-plant transfer of trace elements—an environmental issue. Geoderma 122:143–149. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.01.004
Kazi TG, Jamali MK, Siddiqui A, Kazi GH, Arain MB, Afridi HI (2006) An ultrasonic assisted extraction method to release heavy metals from untreated sewage sludge samples. Chemosphere 63:411–420. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.08.056
Krasnodębska-Ostręga B, Kaczorowska M, Golimowski J (2006) Ultrasound-assisted extraction for the evaluation of element mobility in bottom sediment collected at mining and smelting Pb–Zn ores area in Poland. Microchim Acta 154:39–43. doi:10.1007/s00604-006-0497-x
Lesniewska B, Swierad E, Lukowski A, Wiater J, Godlewska-Zylkiewicz B (2014) Ultrasound assisted extraction for determination of mobile fractions of copper in soil. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig 65:67–74
Li JS, Xue Q, Wang P, Zhang TT (2015) Enhanced washing for Cr(VI) removal from contaminated soil using EDTA and microwave radiation. Environ Earth Sci 74:2167–2172. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4206-0
Li Q, Zhou J, Chen B, Huang B, Zeng X, Zhan J, Pan X (2014) Toxic metal contamination and distribution in soils and plants of a typical metallurgical industrial area in southwest of China. Environ Earth Sci 72:2101–2109. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3118-8
Meers E, Du Laing G, Unamuno V, Ruttens A, Vangronsveld J, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2007) Comparison of cadmium extractability from soils by commonly used single extraction protocols. Geoderma 141:247–259. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.06.002
Menzies NW, Donn MJ, Kopittke PM (2007) Evaluation of extractants for estimation of the phytoavailable trace metals in soils. Environ Pollut 145:121–130. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.03.021
Moreno-Jiménez E, Peñalosa JM, Manzano R, Carpena-Ruíz RO, Gamarra R, Esteban E (2009) Heavy metals distribution in soils surrounding and abandoned mine in MW Madrid (Spain) and their transference to wild flora. J Hazard Mater 162:854–859. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.109
ORD 2770/2006 MAD (2006) Orden 2770/2006, de 11 de agosto, Consejería de Medio Ambiente y Ordenación del Territorio, Comunidad de Madrid, B.O.C.M. Núm. 204, Lunes 28 de agosto de 2006. pp. 29–30. http://www.madrid.org/wleg_pub/secure/normativas/contenidoNormativa.jsf;jsessionid=2476FF62F75913A96D8363E290B07118.p0313335?opcion=VerHtml&nmnorma=4097&cdestado=P#no-back-button
Pérez Cid B, de Jesús GM, Fernández Gómez E (2002) Comparison of single extraction procedures, using either conventional shaking or microwave heating, and the Tessier sequential extraction method for the fractionation of heavy metals from environmental samples. Analyst 127:681–688. doi:10.1039/b110943j
Pueyo M, López-Sánchez JF, Rauret G (2004) Assessment of CaCl2, NaNO3 and NH4NO3 extraction procedures for the study of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn extractability in contaminated soils. Anal Chim Acta 504:217–226. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2003.10.047
Pueyo M, Sahuquillo A, Rigol A, López-Sánchez JF, Rauret G (2005) A new quality control soil material for monitoring trace metals in accidentally polluted areas. Anal Chim Acta 533:41–49. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2004.10.078
Quevauviller Ph, Rauret G, Griepink B (1993) Single and sequential extraction in sediments and soils. Int J Environ Anal Chem 51:231–235. doi:10.1080/03067319308027629
Quevauviller P, Rauret G, Rubio R, López-Sánchez JF, Ure A, Bacon J, Muntau H (1997) Certified reference materials for the quality control of EDTA- and acetic acid-extractable contents of trace elements in sewage sludge amended soils (CRMs 483 and 484). Fresenius J Anal Chem 357:611–618. doi:10.1007/s002160050222
Quevauviller Ph (2002) Operationally-defined extraction procedures for soil and sediment analysis. Part 3: new CRMs for trace-element extractable contents. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 21:774–785. doi:10.1016/S0165-9936(02)01105-6
Rao CRM, Sahuquillo A, Lopez Sanchez JF (2008) A review of the different methods applied in environmental geochemistry for single and sequential extraction of trace elements in soils and related materials. Water Air Soil Poll 189:291–333. doi:10.1007/s11270-007-9564-0
Relić D, Đorđević D, Sakan S, Anđelković I, Pantelić A, Stanković R, Popović A (2013) Conventional, microwave, and ultrasound sequential extractions for the fractionation of metals in sediments within the Petrochemical Industry, Serbia. Environ Monit Assess 185:7627–7645. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3124-4
Remeteiová D, Ružičková S, Rusnák R (2008) Ultrasound-assisted extraction in the fractionation analysis of gravitation dust sediments. Microchim Acta 163:257–261. doi:10.1007/s00604-008-0005-6
Sahuquillo A, Rigol A, Rauret G (2003) Overview of the use of leaching/extraction tests for risk assessment of trace metals in contaminated soils and sediments. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 22:152–159. doi:10.1016/S0165-9936(03)00303-0
Takeda A, Tsukada H, Takaku Y, Hisamatsu S, Inaba J, Nanzyo M (2006) Extractability of major and trace elements from agricultural soils using chemical extraction methods: application for phytoavailability assessment. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 52:406–417. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0765.2006.00066.x
Tessier A, Campbell P, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851. doi:10.1021/ac50043a017
Wang WS, Shan WQ, Wen B, Zhang SZ (2003) Relationship between the extractable metals from soils and metals taken up by maize roots and shoots. Chemosphere 53:523–530. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00518-6
Wang JM, Jiang JG, Li D, Li TR, Li KM, Tian SC (2015) Removal of Pb and Zn from contaminated soil by different washing methods: the influence of reagents and ultrasound. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:20084–20091. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-5219-7
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (Project CTM2007-66432) and Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (Project GI115815203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Salgado, S., Quijano, M.Á. Rapid metal extractability tests from polluted mining soils by ultrasound probe sonication and microwave-assisted extraction systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 24567–24577 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7999-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7999-9