Abstract
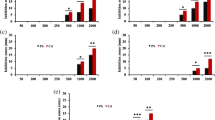
The toxic heavy metal cadmium (Cd) appears as one of the major global threats to human and animal health. Human being and aquatic life are exposed to Cd by breathing, eating, or drinking when industrial effluents released into environment. The study was aimed to identify cadmium-binding Lactobacillus strain to reduce its bioaccessibility in in vitro digestion model. In this context, forty-eight lactobacilli strains isolated and characterized from fermented dairy products and human origin were screened for their Cd biosorption potential using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (FAAS). The present study revealed that Cd biosorption potential of 48 lactobacilli strains ranged from 1.0832 ± 0.012 to 3.562 ± 0.03 mg Cd g−1 of cells from initial 10 mg L−1 cadmium chloride (CdCl2) aqueous solution. Lactobacillus plantarum strain HD 48 demonstrated highest biosorption of 3.562 ± 0.03 mg Cd g−1 of cells. Lactobacilli-Cd complex stability indicated its strong stability as even after three washes with Milli-Q water metal desorption was nonsignificant (p < 0.05) and further studies to delineate the influence of Cd (100 mg L−1 CdCl2) on their growth. Moreover, these strains were able to reduce Cd bioaccessibility in the in vitro digestion model in the range of 24.71 to 41.62 %. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) investigations on Cd bioadsorption also revealed its surface associated bioadsorption phenomenon. These findings depicted that probiotic strain L. plantarum HD 48 was found to be endowed with remarkable Cd biosorption ability as well as reduction in its bioaccessibility. These results suggest that probiotic strain L. plantarum HD 48 has immense potential to sequester Cd from aqueous solution which could be further explored as a potent source to diminish body Cd burden.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Charbonnier L, Mesnil A, Rainbow PS, Wang WX (2008) Bioaccessibility of essential and non-essential metals in commercial shellfish from Western Europe and Asia. Food Chem Toxicol 46(6):2010–2022. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2008.01.041
Arauz ILC, Afton S, Wrobel K, Caruso JA, Corona J, Wrobel K (2008) Study on the protective role of selenium against cadmium toxicity in lactic acid bacteria: an advanced application of ICP-MS. J Hazard Mater 153(3):1157–1164. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.075
Baldwin DR, Marshall WJ (1999) Heavy metal poisoning, and its laboratory investigation. Ann Clin Biochem 36:267–300. doi:10.1177/000456329903600301
Bhakta JN, Ohnishi K, Munekage Y, Iwasaki K, Wei MQ (2012) Characterization of lactic acid bacteria-based probiotics as potential heavy metal sorbents. J Appl Microbiol 112(6):1193–1206. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05284.x
Brahma B, Patra MC, Karri S, Chopra M, Mishra P, De BC, Kumar S, Mahanty S, Thakur K, Poluri KM, Datta TK (2015) Diversity, antimicrobial action and structure-activity relationship of buffalo Cathelicidins. PLoS One 10(12):e0144741. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0144741
Buckler HM, Smith WDF, Rees WDW (1986) Self-poisoning with oral cadmium chloride. Br Med J 292:1559–1560. doi:10.1136/bmj.292.6535.1559
Dorta DJ, Leite S, DeMarco KC, Prado IM, Rodrigues T, Mingatto FE, Uyemura SA, Santos AC, Curti C (2003) A proposed sequence of events for cadmium-induced mitochondrial impairment. J Inorg Biochem 97(3):251–257. doi:10.1016/S0162-0134(03)00314-3
Doyle JJ, Marshall RT, Pfander WH (1975) Effects of cadmium on the growth and uptake of microorganisms. Appl Microbiol 29(4):562–564
El-Helow ER, Sabry SA, Amer RM (2000) Cadmium biosorption by a cadmium resistant strain of Bacillus thuringiensis: regulation and optimization of cell surface affinity for metal cations. Biometals 13(4):273–280. doi:10.1023/A:1009291931258
Faroon O, Ashizawa A, Wright S, Tucker P, Jenkins K, Ingerman L, Rudisill C (2012) Toxicological profile for cadmium. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), Atlanta, GA.
Fazeli M, Hassanzadeh P, Alaei S (2011) Cadmium chloride exhibits a profound toxic effect on bacterial microflora of the mice gastrointestinal tract. Hum Exp Toxicol 30(2):152–159. doi:10.1177/0960327110369821
Godt J, Scheidig F, Grosse-Siestrup C, Esche V, Brandenburg P, Reich A, Groneberg DA (2006) The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. Journal of occupational medicine and toxicology 1(1):1. doi:10.1186/1745-6673-1-22
Gulnaz O, Saygideger S, Kusvuran E (2005) Study of Cu (II) biosorption by dried activated sludge: effect of physico-chemical environment and kinetics study. J Hazard Mater 120(1):193–200. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.01.003
Halttunen T, Salminen S, Tahvonen R (2007) Rapid removal of lead and cadmium from water by specific lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 114:30–35. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.10.040
Halttunen T, Salminen S, Meriluoto RJ, Kalle LT (2008) Reversible surface binding of cadmium and lead by lactic acid and bifidobacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 125:170–175. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.03.041
Ibrahim F, Halttunen T, Tahvonen R, Salminen S (2006) Probiotic bacteria as potential detoxification tools: assessing their heavy metal binding isotherms. Can J Microbiol 52:877–885. doi:10.1139/W06-043
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol 7(2):60–72. doi:10.2478/intox-2014-0009
Jarup L, Alfven T (2004) Low level cadmium exposure, renal and bone effects—the OSCAR study. Biometals 17(5):505–509. doi:10.1023/B:BIOM.0000045729.68774.a1
Kabak B, Ozbey F (2012) Aflatoxin M1 in UHT milk consumed in Turkey and first assessment of its bioaccessibility using an in vitro digestion model. Food Control 28(2):338–344. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.05.029
Kaewsarn P, Yu Q (2001) Cadmium (II) removal from aqueous solutions by pre-treated biomass of marine alga Padina sp. Environ Pollut 112(2):209–213. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00114-7
Kinoshita H, Sohma Y, Ohtake F, Ishida M, Kawai Y, Kitazawa H, Saito T, Kimura K (2013) Biosorption of heavy metals by lactic acid bacteria and identification of mercury binding protein. Res Microbiol 164:701–709. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2013.04.004
Kobayashi E, Suwazono Y (2009) Estimation of benchmark rice cadmium doses as threshold values for abnormal urinary findings with adjustment for consumption of Jinzu River water. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83:102–107. doi:10.1007/s00128-009-9766-9
Liu J, Qu W, Kadiiska MB (2009) Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:209–214. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.01.029
Meriluoto J, Codd GA (2005) Cyanobacterial monitoring and cyanotoxin analysis. Acta Academiae Aboensis 65(1):1–145. doi:10.3390/toxins7062198
Monachese M, Burton JP, Reid G (2012) Bioremediation and tolerance of humans to heavy metals through microbial processes: a potential role for probiotics? Appl Environ Microbiol 78(18):6397–6404. doi:10.1128/AEM.01665-12
Oomen AG, Rompelberg CJ, Bruil MA, Dobbe CJ, Pereboom DP, Sips AJ (2003) Development of an in vitro digestion model for estimating the bioaccessibility of soil contaminants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44(3):0281–0287. doi:10.1007/s00244-002-1278-0
Satarug S, Moore MR (2004) Adverse health effects of chronic exposure to low-level cadmium in foodstuffs and cigarette smoke. Environ Health Perspect 112(10):1099–1103. doi:10.1289/ehp.6751
Satarug S, Garrett SH, Sens MA, Sens DA (2011) Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Ciencia & saude coletiva 16(5):2587–2602. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901234
Serrano-Nino JC, Cavazos-Garduno A, Hernandez-Mendoza A, Applegate B, Ferruzzi MG, San Martin-González MF, García HS (2013) Assessment of probiotic strains ability to reduce the bioaccessibility of aflatoxin M1 in artificially contaminated milk using an in vitro digestive model. Food Control 31(1):202–207. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.09.023
Sharma S, Prasad FM (2010) Accumulation of lead and cadmium in soil and vegetable crops along major highways in Agra (India). Journal of. Chemistry 7(4):1174–1183. doi:10.1155/2010/678589
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2009) Heavy metals in vegetables collected from production and market sites of a tropical urban area of India. Food Chem Toxicol 47(3):583–591. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2008.12.016
Singh A, Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of foodstuffs from the wastewater irrigated site of a dry tropical area of India. Food Chem Toxicol 48(2):611–619. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.11.041
Staessen JA, Thijs L, Fagard R, O'Brien ET, Clement D, de Leeuw PW, Mancia G, Nachev C, Palatini P, Parati G, Tuomilehto J (1999) Predicting cardiovascular risk using conventional vs ambulatory blood pressure in older patients with systolic hypertension. JAMA 282(6):539–546. doi:10.1001/jama.282.6.539
Sun L, Liu G, Yang M, Zhuang Y (2012) Bioaccessibility of cadmium in fresh and cooked Agaricus blazei Murill assessed by in vitro biomimetic digestion system. Food Chem Toxicol 50(5):1729–1733. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.02.044
Tian F, Xiao Y, Li X, Zhai Q, Wang G, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Chen W (2015) Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8246 against copper toxicity in mice. PLoS One 10(11):e0143318. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143318
Topcu A, Bulat T (2010) Removal of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution by Enterococcus faecium strains. J Food Sci 75:T13–T17. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01429.x
Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P, Mahajan R (2009) Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr Neuropharmacol 7(1):65–74. doi:10.2174/157015909787602823
Veglio F, Beolchini F (1997) Removal of metals by biosorption: a review. Hydrometallurgy 44(3):301–316. doi:10.1016/S0304-386X (96)00059-x
Veglio F, Beolchini F, Gasbarro A (1997) Biosorption of toxic metals: an equilibrium study using free cells of Arthrobacter sp. Process Biochem 32(2):99–105. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(96)00047-7
Versantvoort CH, Oomen AG, Van de Kamp E, Rompelberg CJ, Sips AJ (2005) Applicability of an in vitro digestion model in assessing the bioaccessibility of mycotoxins from food. Food Chem Toxicol 43(1):31–40
Vig K, Megharaj M, Sethunathan N, Naidu R (2003) Bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium to microorganisms and their activities in soil: a review. Adv Environ Res 8(1):121–135. doi:10.1016/S1093-0191(02)00135-1
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Ism Ecology. doi:10.5402/2011/402647
Yadav A, Yadav PK, Shukla DN (2013) Investigation of heavy metal status in soil and vegetables grown in urban area of Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh, India. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications 3(9):1–7.
Yang LS, Zhang XW, Li YH, Li HR, Wang Y, Wang WY (2011) Bioaccessibility and risk assessment of cadmium from uncooked rice using an in vitro digestion model. Biol Trace Elem Res 145(1):81–86. doi:10.1007/s12011-011-9159-x
Zhai Q, Wang G, Zhao J, Liu X, Tian F, Zhang H, Chen W (2013) Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8610 against acute cadmium toxicity in mice. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(5):1508–1515. doi:10.1128/AEM.03417-12
Zhai Q, Wang G, Zhao J, Liu X, Narbad A, Chen YQ, Zhang H, Tian F, Chen W (2014) Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8610 against chronic cadmium toxicity in mice: Intestinal sequestration is not the only route of protection. Applied and environmental microbiology. AEM-00762. doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00762-14
Zhai Q, Yin R, Yu L, Wang G, Tian F, Yu R, Zhao J, Liu X, Chen YQ, Zhang H, Chen W (2015) Screening of lactic acid bacteria with potential protective effects against cadmium toxicity. Food Control 54:23–30. doi:10.1039/C4RA12865F
Zhang WL, Du Y, Zhai MM, Shang Q (2014) Cadmium exposure and its health effects: a 19-year follow-up study of a polluted area in China. Sci Total Environ 470:224–228. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.070
Zhuang P, McBride MB, Xia H, Li N, Li Z (2009) Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci Total Environ 407(5):1551–1561. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.061
Zoghi A, Khosravi-Darani K, Sohrabvandi S (2014) Surface binding of toxins and heavy metals by probiotics. Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry 14(1):84–98. doi:10.2174/1389557513666131211105554
Zoumpopoulou G, Foligne B, Christodoulou K, Grangette C, Pot B, Tsakalidou E (2008) Lactobacillus fermentum ACA-DC 179 displays probiotic potential in vitro and protects against trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis and salmonella infection in murine models. Int J Food Microbiol 121(1):18–26. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.10.013
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the Director, ICAR-National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI) Karnal-132001, (Haryana), India. The first author also acknowledges University Grant Commission (UGC) for the financial support in terms of all India fellowship (RGNF-SRF). We greatly acknowledge the help rendered by Mr. Rajkumar for providing AAS facility at ICAR-Central Soil Salinity Research Institute, Karnal-132001, (Haryana) INDIA and Devashish Dewedi for help in designing this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Author contributions
Narendra Kumar: Conceived the work, design the whole experiment and statistical analysis of the experimental data. The manuscript was seriously written by Narendra Kumar. Rohit Panwar was involved in the preparation of media and acid washing of glass wares.
Chand ram and Vijay Kumar: Provided technical suggestions and critically reviewed the manuscript to improve the overall quality of the article. The grammatical and language improvement was also done.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Kumar, V., Panwar, R. et al. Efficacy of indigenous probiotic Lactobacillus strains to reduce cadmium bioaccessibility - An in vitro digestion model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 1241–1250 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7779-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7779-6