Abstract
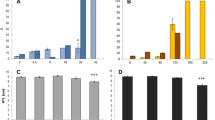
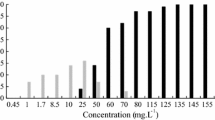
We evaluated the acute lethal and sublethal effects of technical-grade glyphosate (GLY) and the GLY-based commercial formulation Roundup ULTRA MAX® (RU) on two Gosner stages (Gss) 25 and 36 of the South-American Creole frog, Leptodactylus latrans. Bioassays were performed following standardized methods within a wide range of concentrations (0.0007–9.62 mg of acid equivalents per liter—a.e./L—of RU and 3–300 mg/L of GLY). The endpoints evaluated were mortality, swimming activity, growth, development, and the presence of morphologic abnormalities, especially in the mouthparts. No lethal effects were observed on larvae exposed to GLY during either Gs-25 or Gs-36. The concentrations inducing 50 % lethality in RU-exposed larvae at different exposure times and Gss ranged from 3.26 to 9.61 mg a.e./L. Swimming activity was affected by only RU. Effects on growth and development and the induction of morphologic abnormalities—like oral abnormalities and edema—were observed after exposure to either GLY or RU. Gs-25 was the most sensitive stage to both forms of the herbicide. The commercial formulation was much more toxic than the active ingredient on all the endpoints assessed. Effects on growth, development, and the induction of morphologic abnormalities observed in the range of environmental concentrations reported for agroecosystems of Argentina constitute an alert to the potential detrimental effects of the herbicide that could be affecting the fitness and survival of anurans in agroecosystems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostini MG, Kacoliris F, Demetrio P, Natale GS, Bonetto C, Ronco AE (2013) Abnormalities in amphibian populations inhabiting agroecosystems in northeastern Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Dis Aquat Org 104:163–171
Al-Rajab AJ, Hakami OM (2014) Behavior of the non-selective herbicide glyphosate in agricultural soil. Am J Environ Sci 10:94–101
Altig R (2007) Comments on the descriptions and evaluations of tadpole mouthpart anomalies. Herpetol Conserv Biol 2:1–4
Annett R, Habibi HR, Hontela A (2014) Impact of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on the freshwater environment. J Appl Toxicol 34:458–479
Aparicio VC, De Gerónimo E, Marino D, Primost J, Carriquiriborde P, Costa JL (2013) Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere 93:1866–1873
Araújo CVM, Shinn C, Moreira-Santos M, Lopes IG, Espíndola EL, Ribeiro R (2014a) “Copper-driven avoidance and mortality in temperate and tropical tadpoles. Aquat Toxicol 146:70–75
Araújo CVM, Shinn C, Vasconcelos AM, Ribeiro R, Espíndola ELG (2014b) “Preference and avoidance responses by tadpoles: the fungicide pyrimethanil as a habitat disturber. Ecotoxicology 23:851–860
ASTM (2007) ASTM E729-96(2007), Standard guide for conducting acute toxicity tests on test materials with fishes, macroinvertebrates and amphibians. ASTM International, Pennsylvania, USA
Babini MS, Bionda Cde L, Salas NE, Martino AL (2015) Health status of tadpoles and metamorphs of Rhinella arenarum (Anura, Bufonidae) that inhabit agroecosystems and its implications for land use. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 118:118–125
Bantle, J. A., Dumont, J. N., Finch, R. A., Linder, G., and Fort, D. J. (1996). Atlas of abnormalities. A guide for the performance of FETAX. Second ed. Oklahoma State University. Oklahoma, USA.
Benbrook CM (2016) Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environmental Science Europe 28:3–18
Bernal MH, Solomon KR, Carrasquilla G (2009) Toxicity of formulated glyphosate (glyphos) and cosmo-flux to larval Colombian frogs 1. Laboratory acute toxicity. J Toxic Environ Health A 72:961–965
Berril M, Bertram S, Wilson A, Louis S, Brigham D, Stromberg C (1993) Lethal and sublethal impacts of pyrethroid insecticides on amphibian embryos and tadpoles. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:525–539
Berrill M, Coulson D, McGillivray D, Pauli B (1998) Toxicity of endosulfan to aquatic stages of anuran amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1738–1744
Berven KA, Gill DE (1983) Interpreting geographic variation in life-history traits. Am Zool 23:85–97
Bidwell, J. R., and Gorrie, J. R. (1995). “Acute toxicity of a pesticide to selected frog species.” Final Report. Department of Environmental Protection. Perth, Western Australia.
Borggaard OK, Gimsing AL (2008) Fate of glyphosate in soil and the possibility of leaching to ground and surface waters: a review. Pest Manag Sci 64:441–456
Brodeur JC, Svartz G, Perez-Coll CS, Marino DJG, Herkovits J (2009) Comparative susceptibility to atrazine of three developmental stages of Rhinella arenarum and influence on metamorphosis: non-monotonous acceleration of the time to climax and delayed tail resorption. Aquat Toxicol 91:161–170
Broomhall S, Shine R (2003) Effects of the insecticide endosulfan and presence of congeneric tadpoles on Australian treefrog (Litoria freycineti) tadpoles. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:221–226
Brunelli E, Bernabò I, Berg C, Lundstedt-Enkel K, Bonacci A, Tripepi S (2009) Environmentally relevant concentrations of endosulfan impair development, metamorphosis and behaviour in Bufo bufo tadpoles. Aquat Toxicol 91:135–142
CASAFE. (2012). Argentine Plant Protection Products Market. 2012. Chamber of Agricultural Health and Fertilizers. Buenos Aires, Argentina. (in Spanish)
Cauble K, Wagner RS (2005) Sublethal effects of the herbicide glyphosate on amphibian metamorphosis and development. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:429–435
Cei, J. M. (1980). Amphibians of Argentina. Monograph. University of Florence. Firenze, Italy. (in Spanish).
Clements C, Ralph S, Petras M (1997) Genotoxicity of select herbicides in Rana catesbeiana tadpoles using the alkaline single-cell gel DNA electrophoresis (comet) assay. Environ Mol Mutagen 29:277–288
Close B, Banister K, Baumans V, Bernoth E, Bromage N, Bunyan J, Erhardt W, Flecknell P, Gregory N, Hackbarth H (1996) Recommendations for euthanasia of experimental animals: part 1. Lab Anim 30:293–316
Collins JP, Lewis MA (1979) Overwintering tadpoles and breeding season variation in the Rana pipiens complex in Arizona. Southwest Nat 24:371–373
Cooke AS (1981) Tadpoles as indicators of harmful levels of pollution in the field. Environmental Pollution Series A 25:123–133
Costa MJ, Monteiro DA, Oliveira-Neto AL, Rantin FT, Kalinin AL (2008) Oxidative stress biomarkers and heart function in bullfrog tadpoles exposed to Roundup Original®. Ecotoxicology 17:153–163
Coupe RH, Kalkhoff SJ, Capel PD, Gregoire C (2012) Fate and transport of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters of agricultural basins. Pest Manag Sci 68:16–30
Demetrio, P. M. (2012). “Study of biological effects of pesticides used in soybean RR and evaluation of adverse impacts on agro-ecosystems of the Pampas.” PhD Dissertation. National University of La Plata. (in Spanish).
Denoël M, Libon S, Kestemont P, Brasseur C, Focant JF, De Pauw E (2013) Effects of a sublethal pesticide exposure on locomotor behavior: a video-tracking analysis in larval amphibians. Chemosphere 90:945–951
Denver RJ, Crespi EJ (2006) Stress hormones and human developmental plasticity. NeoReviews 7:183–188
Domingo Yagüez, J., Ferreyra, A., Langhi, R., Pausich, G., Pezzola, A., and Coma, C. (2011). Soy Campaign 2010–2011. Buenos Aires, Argentina: National Institute of Agricultural Technology, Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries. (in Spanish).
Duke SO, Powles SB (2008) Glyphosate: a once-in-a-century herbicide. Pest Manag Sci 64:319–325
Edge CB, Thompson DG, Hao C, Houlahan JE (2012) A silviculture application of the glyphosate-based herbicide Vision MAX to wetlands has limited direct effects on amphibian larvae. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:2375–2383
Edginton AN, Sheridan PM, Stephenson GR, Thompson DG, Boermans HJ (2004) Comparative effects of pH and Vision® herbicide on two life stages of four anuran amphibian species. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:815–822
Egea-Serrano A, Relyea RA, Tejedo M, Torralva M (2012) Understanding of the impact of chemicals on amphibians: a meta-analytic review. Ecology and Evolution 2:1382–1397
Feder ME (1983) The relation of air breathing and locomotion to predation on tadpoles, Rana berlandieri, by turtles. Physiol Zool 56:522–531
Finney DJ (1971) Probit Analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England
Fuentes L, Moore LJ, Rodgers JH, Bowerman WW, Yarrow GK, Chao WY (2011) Comparative toxicity of two glyphosate formulations (original formulation of Roundup® and Roundup WeatherMAX®) to six North American larval anurans. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:2756–2761
Gahl MK, Pauli BD, Houlahan JE (2011) Effects of chytrid fungus and a glyphosate-based herbicide on survival and growth of wood frogs (Lithobates sylvaticus. Ecol Appl 21:2521–2529
Giesy, J. P., Dobson, S., and Solomon, K. R. (2000). “Ecotoxicological risk assessment for Roundup® herbicide.” In Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, ed. G. W. Ware. Springer, New York USA. 35–120.
Gosner K (1960) A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 16:183–190
Govindarajulu, P. P. (2008). Literature review of impacts of glyphosate herbicide on amphibians: what risks can the silvicultural use of this herbicide pose for amphibians in B.C.? Wildlife Report No. R-28. B.C. Ministry of Environment. Victoria, BC.
Güngördü A (2013) Comparative toxicity of methidathion and glyphosate on early life stages of three amphibian species: Pelophylax ridibundus, Pseudepidalea viridis, and Xenopus laevis. Aquat Toxicol:140–141
Heyer, R., Langone, J., La Marca, E., Azevedo-Ramos, C., di Tada, I., Baldo, D., Lavilla, E., Scott, N., Aquino, L., and Hardy, J. (2010). Leptodactylus latrans. In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2015-4. www.iucnredlist.org. Accessed on 16 April 2016
Horat P, Semlitsch RD (1994) Effects of predation risk and hunger on the behavior of two species of tadpoles. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 34:393–401
Howe CM, Berrill M, Pauli BD, Helbing CC, Werry K, Veldhoen N (2004) Toxicity of glyphosate-based pesticides to four North American frog species. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1928–1938
Howe G, Gillis R, Mowbray RC (1998) Effect of chemical synergy and larval stage on the toxicity of atrazine and alachlor to amphibian larvae. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:519–525
IUCN (2016). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2016–1. www.iucnredlist.org. Accessed on 7 July 2016.
Jones DK, Hammond JI, Relyea RA (2010) Roundup® and amphibians: the importance of concentration, application time, and stratification. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2016–2025
Jones DK, Hammond JI, Relyea RA (2011) Competitive stress can make the herbicide Roundup® more deadly to larval amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:446–454
Jung RE, Jagoe CH (1995) Effects of low pH and aluminum on body size, swimming performance, and susceptibility to predation of green tree frog (Hyla cinerea) tadpoles. Can J Zool 73:2171–2183
Junges CM, Vidal EE, Attademo AM, Mariani ML, Cardell L, Negro AC, Cassano A, Peltzer PM, Lajmanovich RC, Zalazar CS (2013) Effectiveness evaluation of glyphosate oxidation employing the H2O2/UVC process: toxicity assays with Vibrio fischeri and Rhinella arenarum tadpoles. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B 48:163–170
Lajmanovich RC, Attademo AM, Peltzer PM, Junges CM, Cabagna MC (2011) Toxicity of four herbicide formulations with glyphosate on Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae) tadpoles: B-esterases and glutathione S-transferase inhibitors. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:681–689
Lajmanovich RC, Junges CM, Attademo AM, Peltzer PM, Cabagna-Zenklusen MC, Basso A (2013) Individual and mixture toxicity of commercial formulations containing glyphosate, metsulfuron-methyl, bispyribac-sodium, and picloram on Rhinella arenarum tadpoles. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1–13
Lajmanovich RC, Junges CM, Cabagna-Zenklusen MC, Attademo AM, Peltzer PM, Maglianese M, Marquez VE, Beccaria AJ (2015) Toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis in aqueous suspension on the South American common frog Leptodactylus latrans (Anura: Leptodactylidae) tadpoles. Environ Res 136:205–212
Lajmanovich RC, Sandoval MT, Peltzer PM (2003) Induction of mortality and malformation in Scinax nasicus tadpoles exposed to glyphosate formulations. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:0612–0618
Lanctôt C, Navarro-Martín L, Robertson C, Park B, Jackman P, Pauli BD, Trudeau VL (2014) Effects of glyphosate-based herbicides on survival, development, growth and sex ratios of wood frog (Lithobates sylvaticus) tadpoles. II: agriculturally relevant exposures to Roundup WeatherMax® and Vision® under laboratory conditions. Aquat Toxicol 154:291–303
Lanctôt C, Robertson C, Navarro-Martín L, Edge C, Melvin SD, Houlahan J, Trudeau VL (2013) Effects of the glyphosate-based herbicide Roundup WeatherMax® on metamorphosis of wood frogs (Lithobates sylvaticus) in natural wetlands. Aquat Toxicol:140–141
Lenkowski JR, Sanchez-Bravo G, McLaughlin KA (2010) Low concentrations of atrazine, glyphosate, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, and triadimefon exposures have diverse effects on Xenopus laevis organ morphogenesis. J Environ Sci 22:1305–1308
López S, Aiassa D, Benítez-Leite S, Lajmanovich R, Mañas F, Poletta G, Sánchez N, Simoniello MF, Carrasco AE (2012) Pesticides used in south American GMO-based agriculture: a review of their effects on humans and animal models. In: Advances in molecular toxicology, ed. J. C. Fishbein and J. M. Heilman. Elsevier, Amsterdam The Netherlands, pp. 41–75
Lupi L, Miglioranza KSB, Aparicio VC, Marino D, Bedmar F, Wunderlin DA (2015) Occurrence of glyphosate and AMPA in an agricultural watershed from the southeastern region of Argentina. Sci Total Environ 536:687–694
Mann RM, Bidwell JR (1999) The toxicity of glyphosate and several glyphosate formulations to four species of southwestern Australian frogs. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:193–199
Mc Diarmid RW, Altig R (2000) Tadpoles: the biology of anuran larvae. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, USA
Meyer, M. T., Loftin, K. A., Lee, E. A., Hinshaw, G. H., Dietze, J. E., and Scribner, E. A. (2009). Determination of glyphosate, its degradation product aminomethylphosphonic acid, and glufosinate, In Water by isotope dilution and online solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods. Techniques and Methods 5–A10. U.S. Geological Survey. Virginia, USA.
Moore LJ, Fuentes L, Rodgers JH Jr, Bowerman WW, Yarrow GK, Chao WY, Bridges WC Jr (2012) Relative toxicity of the components of the original formulation of Roundup® to five North American anurans. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:128–133
Morey S, Reznick D (2000) A comparative analysis of plasticity in larval development in three species of spadefoot toads. Ecology 81:1736–1749
Natale, G. S. (2006). “Ecotoxicological analysis of a community of anurans in the Pampa region: effect of Cr (VI) on embryos and larvae of different species of a taxo-community.” PhD Dissertation, National University of La Plata. (in Spanish).
Natale GS, Ammassari LL, Basso NG, Ronco AE (2006) Acute and chronic effects of Cr (VI) on Hypsiboas pulchellus embryos and tadpoles. Dis Aquat Org 72:261–267
Natale GS, Basso NE, Ronco AE (2000) Effect of Cr(VI) on early life stages of three species of Hylid frogs (Amphibia, Anura) from South America. Environ Toxicol 15:509–512
National Research Council of the National Academies (2011) Guide for care and use of laboratory animals, 8th edn. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC, USA
Navarro-Martín L, Lanctôt C, Jackman P, Park BJ, Doe K, Pauli BD, Trudeau VL (2014) Effects of glyphosate-based herbicides on survival, development, growth and sex ratios of wood frogs (Lithobates sylvaticus) tadpoles. I: chronic laboratory exposures to VisionMax®. Aquat Toxicol 154:278–290
Newman MC (2015) Fundamentals of ecotoxicology, The science of pollution. 4th Edition. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis group, Florida USA
Paganelli A, Gnazzo V, Acosta H, López SL, Carrasco AE (2010) Glyphosate-based herbicides produce teratogenic effects on vertebrates by impairing retinoic acid signaling. Chem Res Toxicol 23:1586–1595
Peltzer PM, Lajmanovich RC, Sanchez LC, Attademo AM, Junges CM, Bionda CL, Martino A, Basso A (2011) Morphological abnormalities in amphibian populations. Herpetol Conserv Biol 6:432–442
Peltzer PM, Lajmanovich RC, Attademo AM, Junges CM, Cabagna-Zenklusen MC, Repetti MR, Sigrist ME, Beldoménico H (2013) Effect of exposure to contaminated treefrog (Trachycephalus typhonius) tadpoles. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:G142–G151
Peruzzo PJ, Porta AA, Ronco AE (2008) Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ Pollut 156:61–66
Primost, J. (2013). “Study of environmental levels of glyphosate and AMPA in a model of intensive agriculture area around Urdinarrain, Entre Rios”. Graduate Dissertation, National University of La Plata. (in Spanish)
Puglis HJ, Boone MD (2011) Effects of technical-grade active ingredient vs. commercial formulation of seven pesticides in the presence or absence of UV radiation on survival of green frog tadpoles. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:145–155
Relyea RA (2004) Growth and survival of five amphibian species exposed to combinations of pesticides. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1737–1742
Relyea RA (2012) New effects of Roundup on amphibians: predators reduce herbicide mortality; herbicides induce antipredator morphology. Ecol Appl 22:634–647
Relyea RA, Jones DK (2009) The toxicity of Roundup Original Max® to 13 species of larval amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:2004–2008
Rist L, Semlitsch RD, Hotz H, Reyer H-U (1997) Feeding behaviour, food consumption, and growth efficiency of hemiclonal and parental tadpoles of the Rana esculenta complex. Funct Ecol 11:735–742
Ronco AE, Marino DJG, Abelando M, Almada P, Apartin CD (2016) Water quality of the main tributaries of the Paraná Basin: glyphosate and AMPA in surface water and bottom sediments. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–13
Rowe CL, Hopkins WA, Congdon JD (2001) Integrating individual-based indices of contaminant effects. How multiple sublethal effects may ultimately reduce amphibian recruitment from a contaminated breeding site.” The. Scientific World 1:703–712
Rowe CL, Kinney OM, Fiori AP, Congdon JD (1996) Oral deformities in tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana) associated with coal ash deposition: effects on grazing ability and growth. Freshw Biol 36:723–730
Ruiz de Arcaute C, Salgado Costa C, Demetrio PM, Natale GS, Ronco AE (2012) Influence of existing site contamination on sensitivity of Rhinella fernandezae (Anura, Bufonidae) tadpoles to Lorsban® 48E formulation of chlorpyrifos. Ecotoxicology 21(8):2338–2348
Semlitsch RD (1993) Adaptive genetic variation in growth and development of tadpoles of the hybridogenetic Rana esculenta complex. Evolution 47:1805–1818
Semlitsch RD, Foglia M, Mueller A, Steiner I, Fioramonti E, Fent K (1995) Short_term exposure to triphenyltin affects the swimming and feeding behavior of tadpoles. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1419–1423
Smith DC (1987) Adult recruitment in chorus frogs: effects of size and date at metamorphosis. Ecology 68:344–350
Smith GR (2001) Effects of acute exposure to a commercial formulation of glyphosate on the tadpoles of two species of anurans. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 67:483–488
Smith-Gill SJ, Berven KA (1979) Predicting amphibian metamorphosis. Am Nat 113:563–585
Sparling DW, Fellers GM (2009) Toxicity of two insecticides to California, USA, anurans and its relevance to declining amphibian populations. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1696–1703
Sparling DW, Linder G, Bishop CA, Krest S (2010) Ecotoxicology of amphibians and reptiles, Second edn. Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry Press, Florida USA
Stauffer HP, Semlitsch RD (1993) Effects of visual, chemical and tactile cues of fish on the behavioural responses of tadpoles. Anim Behav 46:355–364
Stebbins RC, Cohen NW (1997) A natural history of amphibians. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey
Tolledo J, Silva ET, Nunes-de-Almeida CHL, Toledo LF (2014) Anomalous tadpoles in a Brazilian oceanic archipelago: implications of oral anomalies on foraging behaviour, food intake and metamorphosis. Herpetol J 24:237–243
U.S. EPA, (1975). Methods for acute toxicity tests with fish, macroinvertebrates, and amphibians. USEPA 660/3–75-009. Ecological Research series, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Washington DC, USA, pp 62.
U.S. E.P.A. (1999). EPA Probit Analysis Program used for calculating LC/EC values. Version 1.5. Ecological Monitoring Research Division, Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. OHIO, USA.
Uthpala AJ, Rupika SR, Ayanthi NN, Priyani HA (2010) Toxicity of agrochemicals to common hourglass tree frog (Polypedates cruciger) in acute and chronic exposure. IJAB Online Issues 12:641–648
Vaira M, Akmentins M, Attademo M, Baldo D, Barrasso DA, Barrionuevo S, Basso N, Blotto B, Cairo S, Cajade R, Céspedez J, Corbalán V, Chilote P, Duré M, Falcione C, Ferraro D, Gutierrez R, Ingaramo Md, Junges C, Lajmanovich R, Lescano JN, Marangoni F, Martinazzo L, Marti R, Moreno L, Natale GS, Perez Iglesias JM, Peltzer P, Quiroga L, Rosset S, Sanabria E, Sanchez L, Schaefer E, Úbeda C, Zaracho V (2012) Categorización del estado de conservación de los anfibios de la República Argentina. Cuadernos de herpetología 26:131–159 in Spanish
Venesky MD, Rossa-Feres DC, Nomura F, Vasconcellos de Andrade G, Leite PT, de Sousa V. TT, Anderson CV, Wassersug RJ (2013) Comparative feeding kinematics of tropical hylid tadpoles. J Exp Biol 216:1928–1937
Venesky MD, Wassersug RJ, Parris MJ (2010a) . “How does a change in labial tooth row number affect feeding kinematics and foraging performance of a Ranid tadpole (Lithobates sphenocephalus)? Biol Bull 218:160–168
Venesky MD, Wassersug RJ, Parris MJ (2010b) “The impact of variation in labial tooth number on the feeding kinematics of tadpoles of southern leopard frog (Lithobates sphenocephalus. Copeia 3:481–486
Williams BK, Semlitsch RD (2010) Larval responses of three Midwestern anurans to chronic, low-dose exposures of four herbicides. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:819–827
Wassersug RJ, Yamashita M (2001) Plasticity and constraints on feeding kinematics in anuran larvae. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 131:183–195
Wilbur HM, Collins JP (1973) Ecological aspects of amphibian metamorphosis. Science 182:1305–1314
Wojtaszek BF, Staznik B, Chartrand DT, Stephenson GR, Thompson DG (2004) Effects of Vision® herbicide on mortality, avoidance response, and growth of amphibian larvae in two forest wetlands. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:832–842
Wood L, Welch AM (2015) Assessment of interactive effects of elevated salinity and three pesticides on life history and behavior of southern toad (Anaxyrus terrestris) tadpoles. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:667–676
Yadav SS, Giri S, Singha U, Boro F, Giri A (2013) Toxic and genotoxic effects of Roundup on tadpoles of the Indian skittering frog (Euflictis cyanophlyctis) in the presence and absence of predator stress. Aquat Toxicol:132–133
Young BE, Stuart SN, Chanson JS, Cox NA, Boucher TM (2004) Disappearing jewels: the status of new world amphibian. Nature Serve, Virgina, USA
Zar JH (2010) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, US
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Damian Marino for chemical analyses. The study was supported by Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica under Grants PICT-2010-0891 and PICT-2014-0919. Dr. Donald F. Haggerty, a retired academic career investigator and native English speaker, edited the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The tadpoles were maintained under laboratory conditions according to the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Research Council 2011).
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bach, N.C., Natale, G.S., Somoza, G.M. et al. Effect on the growth and development and induction of abnormalities by a glyphosate commercial formulation and its active ingredient during two developmental stages of the South-American Creole frog, Leptodactylus latrans . Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 23959–23971 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7631-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7631-z