Abstract
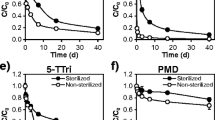
Cyflumetofen is a novel benzoyl acetonitrile acaricide without cross-resistance to existing acaricides. In the present study, for the first time, the environmental behaviors of cyflumetofen and the formation of its main metabolites, 2-(trifluoromethyl) benzoic acid (B-1) and 2-(trifluoromethyl) benzamide (B-3), in the four types of soil (black soil, sierozem, krasnozem, and fluvo-aquic soil) and three types of water/sediment systems (Northeast Lake, Hunan paddy field, and Beijng Shangzhuang reservoir) under aerobic and anaerobic conditions were investigated. The degradation dynamics of cyflumetofen followed first-order kinetics. Under aerobic environment, the half-lives of cyflumetofen in black soil, sierozem, krasnozem and fluvo-aquic soil were 11.2, 10.3, 12.4, and 11.4 days. Under water anaerobic conditions, the half-lives were 13.1, 10.8, 13.9, and 12.8 days. The effects of different conditions and soil types on the half-lives of cyflumetofen were studied using a one-way ANOVA test with post hoc comparison (Tukey’s test). It was shown that the differences in black soil, krasnozem, and fluvo-aquic soil were extremely significant difference (p < 0.05) under aerobic and water anaerobic conditions. And there is a strong correlation between half-life and pH. Under aerobic environment, the half-lives of cyflumetofen in Northeast Lake, Hunan paddy field, and Beijng Shangzhuang reservoir were 15.4, 16.9, and 15.1 days. Under anaerobic conditions, they were 16.5, 17.3, and 16.1 days. Analyzing the differences of the half-lives under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, the difference only in Shangzhuang reservoir was extremely significant difference (p < 0.05). In soils, cyflumetofen degraded metabolites B-1 and B-3, from the first day 0.24 % B-1 was generated, while, only very low levels of B-3 generated at the same time. As time increased, B-3 gradually increased, cyflumetofen reduced gradually. Until 100 days, there were about 3.5 % B-1 and B-3 in the soils. In the water/sediment systems, from the first day, it degraded into B-1 in the sediment, and in the water mainly degraded into B-3.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias-Estévez M, López-Periago E, Martínez-Carballo E, Simal-Gándara J, Mejuto J-C, García-Río L (2008) The mobility and degradation of pesticides in soils and the pollution of groundwater resources. Agric Ecosyst Environ 123:247–260
Authority EFS (2012) Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance cyflumetofen EFSA Journal (1), 77
Babić S, Horvat AJ, Pavlović DM, Kaštelan-Macan M (2007) Determination of pK a values of active pharmaceutical ingredients. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 26:1043–1061
Bermúdez-Couso A, Fernández-Calviño D, Pateiro-Moure M, Nóvoa-Muñoz JC, Simal-Gándara J, Arias-Estévez M (2011) Adsorption and desorption kinetics of carbofuran in acid soils. J Hazard Mater 190:159–167
Beulke S, Dubus IG, Brown CD, Gottesbüren B (2000) Simulation of pesticide persistence in the field on the basis of laboratory data—a review. J Environ Qual 29:1371–1379
Clausen L, Fabricius I (2001) Atrazine, isoproturon, mecoprop, 2, 4-D, and bentazone adsorption onto iron oxides. J Environ Qual 30:858–869
Dalvie MA, Africa A, London L (2009) Change in the quantity and acute toxicity of pesticides sold in south African crop sectors, 1994–1999. Environ Int 35:683–687
Everett CJ, Matheson EM (2010) Biomarkers of pesticide exposure and diabetes in the 1999–2004 National Health and nutrition examination survey. Environ Int 36:398–401
Fenner K, Canonica S, Wackett LP, Elsner M (2013) Evaluating pesticide degradation in the environment: blind spots and emerging opportunities. Science 341:752–758
Gavrilescu M (2005) Fate of pesticides in the environment and its bioremediation. Engineering in Life Sciences 5:497–526
Getenga Z, Madadi V, Wandiga S (2004) Studies on biodegradation of 2, 4-D and metribuzin in soil under controlled conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 72:504–513
Hayashi N, Sasama Y, Takahashi N, Ikemi N (2013) Cyflumetofen, a novel acaricide—its mode of action and selectivity. Pest Manag Sci 69:1080–1084
He M, Jia C, Zhao E, Chen L, Yu P, Jing J, Zheng Y (2015): Concentrations and dissipation of difenoconazole and fluxapyroxad residues in apples and soil, determined by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–9
Houot S, Topp E, Yassir A, Soulas G (2000) Dependence of accelerated degradation of atrazine on soil pH in French and Canadian soils. Soil Biol Biochem 32:615–625
Koch R, Burkness E, Hutchison W, Rabaey T (2005) Efficacy of systemic insecticide seed treatments for protection of early-growth-stage snap beans from bean leaf beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) foliar feeding. Crop Prot 24:734–742
Li M, Liu X, Dong F, Xu J, Qin D, Zheng Y (2012) Determination of cyflumetofen residue in water, soil, and fruits by modified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe method coupled to gas chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 35:2743–2749
Li M, Liu X, Dong F, Xu J, Kong Z, Li Y, Zheng Y (2013) Simultaneous determination of cyflumetofen and its main metabolite residues in samples of plant and animal origin using multi-walled carbon nanotubes in dispersive solid-phase extraction and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1300:95–103
Löffler D, Römbke J, Meller M, Ternes TA (2005) Environmental fate of pharmaceuticals in water/sediment systems. Environmental Science & Technology 39:5209–5218
Marcic D (2012) Acaricides in modern management of plant-feeding mites. J Pest Sci 85:395–408
McKinlay R, Plant J, Bell J, Voulvoulis N (2008) Endocrine disrupting pesticides: implications for risk assessment. Environ Int 34:168–183
MS Dı́az-C, MJL d A, Barcelo D (2003) Environmental behavior and analysis of veterinary and human drugs in soils, sediments and sludge. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 22:340–351
OECD. Test 308: Aerobic and anaerobic transformation in aquatic sediment systems. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, 2002
Ogram A, Jessup R, Ou LT, Rao P (1985) Effects of sorption on biological degradation rates of (2, 4-dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid in soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:582–587
Park J-H, Zhao X, Voice TC (2001) Biodegradation of non-desorbable naphthalene in soils. Environmental science & technology 35:2734–2740
Park J-H, Zhao X, Voice TC (2002) Development of a kinetic basis for bioavailability of sorbed naphthalene in soil slurries. Water Res 36:1620–1628
Pimentel D (1995) Amounts of pesticides reaching target pests: environmental impacts and ethics. J Agric Environ Ethics 8:17–29
Pimentel D, Levitan L (1986) Pesticides: amounts applied and amounts reaching pests. Bioscience 36:86–91
Salvia M-V, Experton J, Geandel C, Cren-Olivé C, Vulliet E (2014) Fate of pharmaceutical compounds and steroid hormones in soil: study of transfer and degradation in soil columns. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:10525–10535
Seiber JN, Kleinschmidt LA (2011) Contributions of pesticide residue chemistry to improving food and environmental safety: past and present accomplishments and future challenges. J Agric Food Chem 59:7536–7543
Takahashi N, Nakagawa H, Sasama Y, Ikemi N (2012) Development of a new acaricide, cyflumetofen. J Pestic Sci 37:263–264
Vidali M (2001) Bioremediation. An overview. Pure Appl Chem 73:1163–1172
Wang L, Zhao P, Zhang F, Li Y, Du F, Pan C (2012) Dissipation and residue behavior of emamectin benzoate on apple and cabbage field application. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:260–264
Xuan-xiang H, Mei-hong S, Wen-ying H, Yan-jun W, Han-yun K, Shuai-feng Z, Bureau JA, Protection HP (2014) Residue dynamics and safely applying technology of cyflumetofen in strawberry. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis 6:029
Yoshida T, Ikemi N, Takeuchi Y, Ebino K, Kojima S, Chiba Y, Nakashima N, Kawakatsu H, Saka M, Harada T (2012) A repeated dose 90-day oral toxicity study of cyflumetofen, a novel acaricide, in rats. J Toxicol Sci 37:91–104
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371970 and 31272070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester heath
Pingping Wang and Minmin Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Li, M., Liu, X. et al. Degradation of cyflumetofen and formation of its main metabolites in soils and water/sediment systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 23114–23122 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7523-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7523-2