Abstract
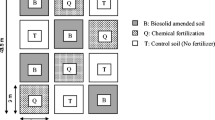
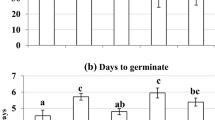
The achievement of environmentally sound and economically feasible disposal strategies for biosolids is a major issue in the wastewater treatment industry around the world, including Swaziland. Currently, an iron ore mine site, which is located within a wildlife sanctuary, is being considered as a suitable place where controlled disposal of biosolids may be practiced. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the effects of urban biosolids on iron mine soils with regard to plant metal content and ecotoxicological effects on earthworms. This was done through chemical analysis of plants grown in biosolid-amended mine soil. Earthworm behaviour, reproduction and bioaccumulation tests were also conducted on biosolid-amended mine soil. According to the results obtained, the use of biosolids led to creation of soil conditions that were generally favourable to earthworms. However, plants were found to have accumulated Zn up to 346 mg kg−1 (in shoots) and 462 mg kg−1 (in roots). This was more than double the normal Zn content of plants. It was concluded that while biosolids can be beneficial to mine soils and earthworms, they can also lead to elevated metal content in plant tissues, which might be a concern to plant-dependant wildlife species. Nonetheless, it was not possible to satisfactorily estimate risks to forage quality since animal feeding tests with hyperaccumulator plants have not been reported. Quite possibly, there may be no cause for alarm since the uptake of metals from soil is greater in plants grown in pots in the greenhouse than from the same soil in the field since pot studies fail to mimic field conditions where the soil is heterogeneous and where the root system possesses a complex topology. It was thought that further field trials might assist in arriving at more satisfactory conclusions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal J, Sherameti I, Varma A (2011) Detoxification of heavy metals: state of art. In: Sherameti I, Varma A (Eds.).) Detoxification of Heavy Metals, Soil Biology 30, DOI 10.1007/978–3–642-21408-0_1. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 1–34
Ahmadpour P, Soleimani M, Ahmadpour F, Abdu A (2014) Evaluation of copper bioaccumulation and translocation in Jatropha curcas grown in a contaminated soil. International Journal of Phytoremediation 16(5):454–468
Alvarenga P, Palma P, de Varennes A, Cunha-Queda A (2012) A contribution towards the risk assessment of soils from the São Domingos mine (Portugal): chemical, microbial and ecotoxicological indicators. Environ Pollut 161:50–56
Bai Y, Chen W, Chang AC, Page A (2010) Uptake of metals by food plants grown on soils 10 years after biosolids application. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part B 45:531–539
Borden RK, Black R (2011) Biosolids application and long term noxious weed dominance in the western United States. Restor Ecol 19(5):639–647
Boyer S, Wratten SD (2010) The potential of earthworms to restore ecosystem services after opencast mining a review. Basic and Applied Ecology 11:196–203
Bradl HB, Kimb C, Kramarc U, Stiiben D (2005) Interactions of heavy metals. In: Bradl HB (ed) Heavy metals in the environment. Elsevier, UK, pp. 28–148
Brown S, Chaney R, Sprenger M, Compton H (2002) Assessing impact to wildlife at biosolids-remediated sites. Biocycle 43(8):50–58
Brown S, Henry C, Chaney R, Compton H, DeVolder P (2003) Using municipal biosolids in combination with other residuals to restore metal contaminated mining areas. Plant Soil 249:203–215
Buch AC, Brown GG, Niva C, Sautter KD, Sousa JP (2013) Toxicity of three pesticides commonly used in Brazil to Pontoscolex corethrurus (Müller, 1857) and Eisenia andrei (Bouché, 1972. Appl Soil Ecol 69:32–38
Cele EN, Maboeta M (2016a) A greenhouse trial to investigate the ameliorative properties of biosolids and plants on physicochemical conditions of iron ore tailings: implications for an iron ore mine site remediation. J Environ Manag 165:167–174
Cele EN, Maboeta M (2016b) Response of soil enzyme activities to synergistic effects of biosolids and plants in iron ore mine soils. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (In Press)
Chaney RL, Broadhurst CL, Centofanti T (2010) Phytoremediation of soil trace elements. In: Hooda PE (ed) Trace elements in soils. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, UK, pp. 311–352
Chen W, Chang AC, Wu L, Page AL, Koo B (2010) Trace elements in biosolids-amended soils. In: Hooda PE (ed) Trace elements in soils. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, UK, pp. 113–129
Cheraghi M, Lorestani B, Khorasani N, Yousefi N, Karami M (2011) Findings on the phytoextraction and phytostabilization of soils contaminated with heavy metals. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:1133–1141
Cherfi A, Achour M, Cherfi M, Otmania S, Morsli A (2015) Health risk assessment of heavy metals through consumption of vegetables irrigated with reclaimed urban wastewater in Algeria. Process Saf Environ Prot 98:245–252
Clothier BE, Green SR, Robinson BH, Thayalakumaran T, Scotter DR, Vogeler I, Mills TM, Deurer M, van der Velde M, Granel T (2008) Contaminants in the rootzone: bioavailability, uptake and transport, and their implications for remediation. In: Naidu R (ed) Chemical bioavailability in terrestrial environments. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 633–655
Correa RS, White RE, Weatherley AJ (2006) Risk of nitrate leaching from two soils amended with biosolids. Water Resources 33(4):453–462
Dai J, Becquer T, Rouiller JH, Reversat G, Bernhard-Reversat F, Nahmani J, Lavelle P (2004) Heavy metal accumulation by two earthworm species and its relationship to total and DTPA-extractable metals in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 36:91–98
Deepesh V, Verma VK, Suma K, Ajay S, Gnanavelu A, Madhusudanan M (2014) Evaluation of an organic soil amendment generated from municipal solid waste seeded with activated sewage sludge. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management. doi:10.1007/s10163-014-0329-8
Demuynck S, Grumiaux F, Mottier V, Schikorski D, Lemière S, Lelprêtre A (2007) Cd/Zn exposure interactions on metallothionein response in Eisenia fetida (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Comp Biochem Physiol 145:658–668
Dongmei L, Changqun D (2008) Restoration potential of pioneer plants growing on lead-zinc mine tailings in Lanping, Southwest China. J Environ Sci 20:1202–1209
Du Y, He M, Xu M, Yan Z, Zhou Y, Guo G, et al. (2014) Interactive effects between earthworms and maize plants on the accumulation and toxicity of soil cadmium. Soil Biol Biochem 72:193–202
Egan M (2013) Biosolids management strategies: an evaluation of energy production as an alternative to land application. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:4299–4310
Epstein, E (2003) Land application of sewage sludge and biosolids. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Field, A (2009) Discovering statistics using SPSS, 3rd edn. Sage Publications London.
Forsberg LS, Ledin S (2006) Effects of sewage sludge on pH and plant availability of metals in oxidising sulphide mine tailings. Sci Total Environ 358:21–35
Fytili D, Zabanitou A (2008) Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 12:116–140
Hagmann DF, Goodey MN, Mathieu C, Evans J, Aronsonc MFJ, Gallagher F, Krumins JA (2015) Effect of metal contamination on microbial enzymatic activity in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 91:291–297
Hillman JP, Hill J, Morgan JE, Wilkinson JM (2003) Recycling of sewage sludge to grassland: a review of the legislation to control of the localization and accumulation of potential toxic metals in grazing systems. Grass Forage Sci 58:101–111
Hu Y, Nan Z, Su J, Wang N (2013) Heavy metal accumulation by poplar in calcareous soil with various degrees of multi-metal contamination: implications for phytoextraction and phytostabilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7194–9203
Hund-Rinke K, Lindemann M, Simon M (2005) Experiences with novel approaches in earthworm testing alternatives. Journal of Soils & Sediments 5(4):233–239
Janssen RPT, Posthuma L, Hollander HAD, Van Veen RPM, Pejnenburg W (1997) Equilibrium partitioning of heavy metals in Dutch field soils. II: prediction of metal accumulation in earthworms. Environ Toxicol Chem 16(12):2479–2488
Jepkoech JK, Simiyu GM, Aruseyi M (2013) Selected heavy metals in water and sediments and their bioconcentrations in plant (Polygonum pulchrum) in Sosiani River, Uasin Gishu County, Kenya. J Environ Prot 4:796–802
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton.
Kobeticova K, Hofman J, Holoubek I (2010) Ecotoxicity of wastes in avoidance tests with Enchytraeus albidus, Enchytraeus crypticus and Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta. Waste Manag 30:558–564
Langdon CJ, Hodson ME, Arnold RE, Black S (2005) Survival, Pb-uptake and behaviour of three species of earthworm in Pb treated soils determined using an OECD-style toxicity test and a soil avoidance test. Environ Pollut 138:368–375
Laturnus F, von Arnold K, Grøn C (2007) Organic contaminants from sewage sludge applied to agricultural soils: false alarm regarding possible problems for food safety. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14(1):53–60
Li J, Zhou X, Yan J, Li H, He J (2015) Effects of regenerating vegetation on soil enzyme activity and microbial structure in reclaimed soils on a surface coal mine site. Appl Soil Ecol 87:56–62
Loureiro S, Soares AM, Nogueira A (2005) Terrestrial avoidance behaviour tests as screening tool to assess soil contamination. Environ Pollut 138:121–131
Lukkari T, Aatsinki M, Vaisanen A, Haimi J (2005) Toxicity of copper and zinc assessed with three different earthworm tests. Appl Soil Ecol 30:133–146
Ma Y, Dickinson NM, Wong MH (2002) Toxicity of Pb/Zn mine tailings to the earthworm Pheretima and the effects of burrowing on metal availability. Biol Fertil Soils 36:79–86
Ma SC, Zhang H, Ma ST, Wang R, Wang GX, Shao Y, et al. (2015) Effects of mine wastewater irrigation on activities of soil enzymes and physiological properties, heavy metal uptake and grain yield in winter wheat. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:483–490
Madejon E, Doronila AI, Madejon P, Baker JM, Woodrow IE (2012) Biosolids, mycorrhizal fungi and eucalypts for phytostabilization of arsenical sulphidic mine tailings. Agroforest Systems 84:389–399
Maiti SH (2007) Bioreclamation of coalmine overburden dumps, with special emphasis on micronutrients and heavy metals accumulation in tree species. Environ Monit Assess 125:111–122
Maiti SK, Saxena NC (1998) Biological reclamation of coalmine spoils without topsoil: an amendment study with domestic raw sewage and grass-legume mixture. Int J Surf Min Reclam Environ 12(2):87–90
McBride MB (2003) Toxic metals in sewage sludge-amended soils: has promotion of beneficial use discounted the risks? Adv Environ Res 8:5–19
Meeinkuirt W, Pokethitiyook P, Kruatrachue M, Tanhan P, Chaiyarat R (2012) Phytostabilization of Pb-contaminated mine tailings by various tree species in a pot and field trial experiments. International Journal of Phytoremediation 14:925–938
Miller RO (1998) High-temperature oxidation: dry ashing. In: Kalra, YP (Ed.) Handbook of reference methods for plant analysis, Boca Raton: CRC Press, pp 53–56.
Moreno-Penaranda R, Lloret F, Alcaniz JM (2004) Effects of sewage sludge on plant community composition in restored limestone quarries. Restor Ecol 12(2):290–296
National Research Council (2005) Mineral tolerance of animals, 2nd edn. National Academies Press, Washington USA.
Novo LAB, Covelo EF, González L (2013) Phytoremediation of amended copper mine tailings with Brassica juncea. Int J Min Reclam Environ 27(3):215–226
OECD (2004) Guidelines for the testing of chemicals: earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei). Paris, France International.
Perez-de-Mora A, Burgos P, Cabrera F, Madejon E (2007) In situ amendment and revegetation reduce trace element leaching in a contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 185:209–222
Phipps T, Tank SL, Wirtz J, Brewer L, Coyner A, Ortego LS, Fairbrother A (2002) Essentiality of nickel and homeostatic mechanisms for its regulation in terrestrial organisms. Environ Rev 10:209–261
Pritchard DL, Penney N, McLaughlin MJ, Rigby H, Schwarz K (2010) Land application of sewage sludge (biosolids) in Australia: risks to the environment and food crops. Water Science & Technology 62(1):48–57
Reinecke SA, Reinecke AJ (2004) The comet assay as biomarker of heavy metal genotoxicity in earthworms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:208–215
Reinecke AJ, Maboeta MS, Vermeulen LA, Reinecke SA (2002) Assessment of lead nitrate and mancozeb toxicity in earthworms using the avoidance response. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 68:779–786
Renoux AY, Rocheleau S, Sarrazin M, Sunahara GI, Blais JF (2007) Assessment of a sewage sludge treatment on cadmium, copper and zinc bioavailability in barley, ryegrass and earthworms. Environ Pollut 145:41–50
Rigueiro-Rodriguez A, Mosquera-Losada MR, Ferreiro-Dominguez N (2012) Pasture and soil zinc evolution in forest and agriculture soils of Northwest Spain three years after fertilisation with sewage sludge. Agric Ecosyst Environ 150:111–120
Ruiz E, Rodríguez L, Alonso-Azcárate J (2009) Effects of earthworms on metal uptake of heavy metals from polluted mine soils by different crop plants. Chemosphere 75:1035–1041
Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Weeks JM, Hopkin SP (1998) Toxicity of nickel to the earthworm and the applicability of the neutral red retention assay. Ecotoxicology 7:291–295
Seleiman MF, Santanen A, Stoddard FL, Makela P (2012) Feedstock quality and growth of bioenergy crops fertilized with sewage sludge. Chemosphere 89:1211–1217
Shi Y, Shi Y, Wang X, Lu Y, Yan S (2007) Comparative effects of lindane and deltamethrin on mortality, growth, and cellulase activity in earthworms (Eisenia fetida. Pestic Biochem Physiol 89:31–38
Sizmur T, Palumbo-Roe B, Hodson ME (2011) Impact of earthworms on trace element solubility in contaminated mine soils amended with green waste compost. Environ Pollut 159:1852–1860
Smith BA, Egeler P, Gilberg D, Hendershot W, Stephenson GL (2010) Uptake and elimination of cadmium and zinc by Eisenia andrei during exposure to low concentrations in artificial soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 59:264–273
Suthar S, Singh S (2008) Bioconcentrations of metals (Fe, Cu, Zn, Pb) in earthworms (Eisenia fetida), inoculated in municipal sewage sludge: do earthworms pose a possible risk of terrestrial food chain contamination? Environmental Toxicology DOI 10.1002/tox.
Swaziland Environmental Authority (2011) Ngwenya Environmental Impact Assessment and Comprehensive Mitigation Plan. Mbabane, Swaziland: Government Printer.
Verdugo C, Sanchez P, Santibanez C, Urrestarazu P, Bustamante E, Silva Y, et al. (2011) Efficacy of lime, biosolids, and mycorrhizal for the phytostabilization of sulfidic copper tailings in Chile: a greenhouse experiment. International Journal of Phytoremediation 13:107–125
Waterhouse BR, Boyer S, Adair KL, Wratten SD (2014) Using municipal biosolids in ecological restoration: what is good for plants and soil may not be good for endemic earthworms. Ecol Eng 70:414–421
White PJ, Greenwood DJ (2013) Properties and management of cationic elements for crop growth. In: Gregory PJ, Nortcliff S (eds) Soil conditions and plant growth. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, UK, pp. 160–194
Wyszkowska J, Borowik A, Kucharski M, Kucharski J (2013) Effects of cadmium, copper and zinc on plants, soil microorganisms and soil enzymes. J Elem:769–796. doi:10.5601/jelem.2013.18.4.455
Yeardley RB, Lazorchak JM, Gast LC (1996) The potential of an earthworm avoidance test for evaluation of hazardous waste sites. Environ Toxicol Chem 15(9):1532–1537
Yilmaz DD, Temizgul A (2012) Effects of municipal sewage sludge doses on the chlorophyll contents and heavy metal concentration of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris var. saccharifera). Bioremediation Journal 16(3):131–140
Acknowledgments
This publication is part of Ph.D. studies conducted at North-West University (NWU) in South Africa. Authors are grateful to the Swaziland Water Services and the Unit for Environmental Sciences and Management at NWU for financial assistance during the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cele, E.N., Maboeta, M. Amelioration of iron mine soils with biosolids: Effects on plant tissue metal content and earthworms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 23005–23016 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7504-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7504-5