Abstract
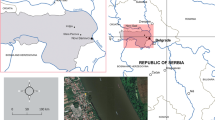
This study examines the use of freshwater bream (Abramis brama) as a sentinel organism for genotoxicity assessment of the Danube River using the comet assay. Sampling of bream was performed during February, April, August, and November in 2014 to assess seasonal variation of DNA damage level as a response to genotoxicity in annual cycle. Additionally, concentrations of fecal coliforms and enterococci were analyzed and they indicated a critical to strong level of fecal pollution on investigated locality during annual cycle. Comet assay was performed on blood, liver, and gill cells of bream. DNA damage level was expressed using tail intensity (TI %), Olive tail moment (OTM), and tail length (TL pix). According to TI and OTM, all three tissues had the highest level of DNA damage in August. The lowest level of DNA damage in liver was measured during February, in blood during November, and in gills during April. According to TL, gills had the highest level of DNA damage in February, and liver cells had the lowest level of damage during April. Multiple correspondence analysis (MCA) showed that DNA damage in blood cells is under the strong influence of variations in NO2, NO3 −, NH4 + levels and also the variation in temperature and oxygen levels. DNA damage in liver cells is highly associated with the variations of Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, and PO4 3− levels. DNA damage in gill cells is strongly affected by the variations of As, Cd, Pb, Cr, and COD (Mn) levels. Freshwater bream is shown to be a potentially good indicator organism in genotoxic potential field studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aborgiba M, Kostić J, Kolarević S, Kračun-Kolarević M, Elbahi S, Knežević-Vukčević J, Lenhardt M, Paunović M, Gačić Z, Vuković-Gačić B (2015) Flooding modifies the genotoxic effects of pollution on a worm, a mussel and two fish species from the Sava River. Sci Total Environ 540:358–367
Akcha F, Hubert FV, Pfhol-Leszkowicz A (2003) Potential value of the comet assay and DNA adduct measurement in dab (Limanda limanda) for assessment of in situ exposure to genotoxic compounds. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 534(1):21–32
Anitha B, Chandra N, Gopinath PM, Durairaj G (2000) Genotoxicity evaluation of heat shock in gold fish (Carassius auratus). Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 469(1):1–8
Ayllon F, Garcia-Vazquez E (2000) Induction of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in European minnow Phoxinus phoxinus and mollie Poecilia latipinna: an assessment of the fish micronucleus test. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 467(2):177–186
Bahlmann A, Lochen T, Schulze T, Kirschner A, Brack W, Schneider RJ, Krauss M (2015) Chemical and immunochemical analysis of anthropogenic markers and organic contaminants. In: Liska I, Wagner F, Deutsch K, Sengl M, Slobodnik J (eds) Joint Danube Survey 3 Final Scientific Report. ICPDR – International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River, Vienna, Austria, pp 277–283
Belpaeme K, Cooreman K, Kirsch-Volders M (1998) Development and validation of the in vivo alkaline comet assay for detecting genomic damage in marine flatfish. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 415(3):167–184
Boettcher M, Grund S, Keiter S, Kosmehl T, Reifferscheid G, Seitz N, Suares Rochaa P, Hollert H, Braunbeck T (2010) Comparison of in vitro and in situ genotoxicity in the Danube River by means of the comet assay and the micronucleus test. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 700(1):11–17
Booth JH (1979) The effects of oxygen supply, epinephrine, and acetylcholine on the distribution of blood flow in trout gills. J Exp Biol 83(1):31–39
Bose RN, Moghaddas S, Gelerinter E (1992) Long-lived chromium (IV) and chromium (V) metabolites in the chromium (VI)-glutathione reaction: NMR, ESR, HPLC, and kinetic characterization. Inorg Chem 31(11):1987–1994
Buschini A, Carboni P, Martino A, Poli P, Rossi C (2003) Effects of temperature on baseline and genotoxicant-induced DNA damage in haemocytes of Dreissena polymorpha. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 537(1):81–92
Buschini A, Martino A, Gustavino B, Monfrinotti M, Poli P, Rossi C, Santoro M, Dörr AJM, Rizzoni M (2004) Comet assay and micronucleus test in circulating erythrocytes of Cyprinus carpio specimens exposed in situ to lake waters treated with disinfectants for potabilization. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 557(2):119–129
Çavaş T, Ergene‐Gözükara S (2005) Micronucleus test in fish cells: a bioassay for in situ monitoring of genotoxic pollution in the marine environment. Environ Mol Mutagen 46(1):64–70
Chen CY, Stemberger RS, Klaue B, Blum JD, Pickhardt PC, Folt CL (2000) Accumulation of heavy metals in food web components across a gradient of lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 45(7):1525–1536
Chovanec A, Hofer R, Schiemer F (2003) Chapter 18 Fish as bioindicators. In: Markert AMB BA, Zechmeister HG (eds) Trace metals and other contaminants in the environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 639–676
Cotelle S, Ferard JF (1999) Comet assay in genetic ecotoxicology: a review. Environ Mol Mutagen 34(4):246–255
De Andrade VM, De Freitas TR, Da Silva J (2004a) Comet assay using mullet (Mugil sp.) and sea catfish (Netuma sp.) erythrocytes for the detection of genotoxic pollutants in aquatic environment. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 560(1):57–67
De Andrade VM, Da Silva J, Da Silva FR, Heuser VD, Dias JF, Yoneama ML, De Freitas TR (2004b) Fish as bioindicators to assess the effects of pollution in two southern Brazilian rivers using the comet assay and micronucleus test. Environ Mol Mutagen 44(5):459–468
de Lemos CT, Rödel PM, Terra NR, Erdtmann B (2001) Evaluation of basal micronucleus frequency and hexavalent chromium effects in fish erythrocytes. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(6):1320–1324
Deutschmann B, Kolarević S, Hollert H, Kaišarević S, Kostić J, Seiler TB, Sipos S, Teodorović I, Vuković-Gačić B (2015) Biomarkers: In-situ detection of genotoxicity of the Danube River in mussels and fish. In: Liska I, Wagner F, Deutsch K, Sengl M, Slobodnik J (eds) Joint Danube Survey 3 Final Scientific Report. ICPDR – International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River, Vienna, Austria, pp 296–303
Dudka S, Miller WP (1999) Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in plants and their transfer to human food chain. J Environ Sci Heal B 34(4):681–708
Farkas A, Salánki J, Varanka I (2000) Heavy metal concentration in fish of Lake Balaton. Lakes and reservoirs. Res and Manag 2000(5):271–279
Farkas A, Salanki J, Specziar A (2002) Relation between growth and the heavy metal concentration in organs of bream Abramis brama L. populating Lake Balaton. Arch Environ Con Tox 43(2):236–243
Farkas A, Salánki J, Specziár A (2003) Age-and size-specific patterns of heavy metals in the organs of freshwater fish Abramis brama L. populating a low-contaminated site. Water Res 37(5):959–964
Frenzilli G, Nigro M, Lyons BP (2009) The comet assay for the evaluation of genotoxic impact in aquatic environments. Mutat Res-Rev Mutat 681(1):80–92
Gardner CJ, Deeming DC, Eady PE (2013) Seasonal movements with shifts in lateral and longitudinal habitat use by common bream, Abramis brama, in a heavily modified lowland river. Fisheries Manag Ecol 20(4):315–325
Gauthier L, Tardy E, Mouchet F, Marty J (2004) Biomonitoring of the genotoxic potential (micronucleus assay) and detoxifying activity (EROD induction) in the River Dadou (France), using the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Sci Total Environ 323(1):47–61
Goodale BC, Walter R, Pelsue SR, Thompson WD, Wise SS, Winn RN, Mitani H, Wise JP (2008) The cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of hexavalent chromium in medaka (Oryzias latipes) cells. Aquat Toxicol 87(1):60–67
Gurr JR, Lin YC, Ho IC, Jan KY, Lee TC (1993) Induction of chromatid breaks and tetraploidy in Chinese hamster ovary cells by treatment with sodium arsenite during the G2 phase. Mutat Res-Genet Tox 319(2):135–142
Hansen BH, Rømma S, Garmo ØA, Olsvik PA, Andersen RA (2006) Antioxidative stress proteins and their gene expression in brown trout (Salmo trutta) from three rivers with different heavy metal levels. Comp Biochem Phys C Toxicol Pharmacol 143(3):263–274
ICPDR, 2002. Water Quality in the Danube River Basin. TNMN Yearbook 2002. http://www.icpdr.org/icpdr-pages/tnmn_yearbooks.htm
Jovičić K, Lenhardt M, Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Ðikanović V, Skorić S, Smederevac-Lalić M, Jaćimović M, Gačić Z, Jarić I, Hegediš A (2014) Assessment of fish stocks and elemental pollution in the Danube, Sava and Kolubara rivers on the territory of the city of Belgrade, Serbia. Acta Zool Bulg 2014(Suppl. 7):179–184
Kirschner AK, Kavka GG, Velimirov B, Mach RL, Sommer R, Farnleitner AH (2009) Microbiological water quality along the Danube River: integrating data from two whole-river surveys and a transnational monitoring network. Water Res 43(15):3673–3684
Kirschner AK, Kavka G, Reischer GH, Sommer R, Blaschke AP, Stevenson M, Vierheilig J, Mach RL, Farnleitner AH (2014) Microbiological water quality of the Danube River: status quo and future perspectives. In: Liska I (ed) The Danube River Basin, Hdb Env Chem, 39th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 439–468
Kleinow KM, Melancon MJ, Lech JJ (1987) Biotransformation and induction: implications for toxicity, bioaccumulation and monitoring of environmental xenobiotics in fish. Environ Health Persp 71:105–119
Kolarević S, Knežević-Vukčević J, Paunović M, Tomović J, Gačić Z, Vuković-Gačić B (2011) The anthropogenic impact on water quality of the river Danube in Serbia: microbiological analysis and genotoxicity monitoring. Arch Biol Sci 63(4):1209–1217
Kolarević S, Knežević-Vukčević J, Paunović M, Vasiljević B, Kračun M, Gačić Z, Vuković-Gačić B (2012) Seasonal variations of microbiological parameters of water quality of the Velika Morava River, Serbia. Arch Biol Sci 64(3):1017–1027
Kolarević S, Knežević-Vukčević J, Paunović M, Kračun M, Vasiljević B, Tomović J, Vuković-Gačić B, Gačić Z (2013) Monitoring of DNA damage in haemocytes of freshwater mussel Sinanodonta woodiana sampled from the Velika Morava River in Serbia with the comet assay. Chemosphere 93(2):243–251
Kolarević S, Kračun-Kolarević M, Kostić J, Slobodnik J, Liška I, Gačić Z, Paunović M, Knežević-Vukčević J, Vuković-Gačić B (2016) Assessment of the genotoxic potential along the Danube River by application of the comet assay on haemocytes of freshwater mussels: the Joint Danube Survey 3. Sci Total Environ 540:377–385
Lee RF, Steinert S (2003) Use of the single cell gel electrophoresis/comet assay for detecting DNA damage in aquatic (marine and freshwater) animals. Mutat Res-Rev Mutat 544(1):43–64
Lenhardt M, Poleksić V, Vuković-Gačić B, Rašković B, Sunjog K, Kolarević S, Jarić I, Gačić Z (2015) Integrated use of different fish related parameters to assess the status of water bodies. Slov Vet Res 52(1):5–13
Liška I, Wagner F, Sengl M, Deutsch K, Slobodník J (2015) Joint Danube Survey 3: a comprehensive analysis of Danube water quality. International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River, Vienna, Austria
Magnuson JJ, Crowder LB, Medvick PA (1979) Temperature as an ecological resource. Am Zool 19(1):331–343
Mitchelmore CL, Chipman JK (1998) DNA strand breakage in aquatic organisms and the potential value of the comet assay in environmental monitoring. Mutat Res-Fund Mol M 399(2):135–147
Nacci DE, Cayula S, Jackim E (1996) Detection of DNA damage in individual cells from marine organisms using the single cell gel assay. Aquat Toxicol 35(3):197–210
Ohe T, Watanabe T, Wakabayashi K (2004) Mutagens in surface waters: a review. Mutat Res-Rev Mutat 567(2):109–149
Osman AG, Abuel-Fadl KY, Kloas W (2012) In situ evaluation of the genotoxic potential of the river Nile: II. Detection of DNA strand-breakage and apoptosis in Oreochromis niloticus niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 747(1):14–21
Pane EF, Haque A, Wood CM (2004) Mechanistic analysis of acute, Ni-induced respiratory toxicity in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): an exclusively branchial phenomenon. Aquat Toxicol 69(1):11–24
Pereira CSA, Guilherme SIAG, Barroso CMM, Verschaeve L, Pacheco MGG, Mendo SALV (2010) Evaluation of DNA damage induced by environmental exposure to mercury in Liza aurata using the comet assay. Arch Environ Con Tox 58(1):112–122
Pruski AM, Dixon DR (2002) Effects of cadmium on nuclear integrity and DNA repair efficiency in the gill cells of Mytilus edulis L. Aquat Toxicol 57(3):127–137
Ramírez OAB, García FP (2005) Genotoxic damage in zebra fish (Danio rerio) by arsenic in waters from Zimapan, Hidalgo, Mexico. Mutagenesis 20(4):291–295
Roberts RD, Johnson MS (1978) Dispersal of heavy metals from abandoned mine workings and their transference through terrestrial food chains. Environ Pollut 16(4):293–310
Salanki J, Katalin V, Berta E (1982) Heavy metals in animals of Lake Balaton. Water Res 16(7):1147–1152
Sanchez-Galan S, Linde AR, Garcia-Vazquez E (1999) Brown trout and European minnow as target species for genotoxicity tests: differential sensitivity to heavy metals. Ecotox Environ Safe 43(3):301–304
Schulz U, Berg R (1987) The migration of ultrasonic‐tagged bream, Abramis brama (L), in Lake Constance (Bodensee‐Untersee). J Fish Biol 31(3):409–414
Shatunovskii MI, Dgebuadze YY, Bobyrev AE, Sokolova EL, Usatîi MA, Crepis OI, Usatîi AM, Cebanu AS (2009) Some regularities of population structure and dynamics variability in bream Abramis brama in water bodies of eastern Europe. J Ichthyol 49(7):503–515
Squier MK, Cohen JJ (2001) Standard quantitative assays for apoptosis. Mol Biotechnol 19(3):305–312
Subotić S, Spasić S, Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Hegediš A, Krpo-Ćetković J, Mićković B, Skorić S, Lenhardt M (2013) Heavy metal and trace element bioaccumulation in target tissues of four edible fish species from the Danube River (Serbia). Ecotox Environ Safe 98:196–202
Sunjog K, Gačić Z, Kolarević S, Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Jarić I, Knežević-Vukčević J, Vuković-Gačić B, Lenhardt M (2012) Heavy metal accumulation and the genotoxicity in barbel (Barbus barbus) as indicators of the Danube River pollution. Sci World J. doi:10.1100/2012/351074
Sunjog K, Kolarević S, Héberger K, Gačić Z, Knežević-Vukčević J, Vuković-Gačić B, Lenhardt M (2013) Comparison of comet assay parameters for estimation of genotoxicity by sum of ranking differences. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(14):4879–4885
Sunjog K, Kolarević S, Kračun-Kolarević M, Gačić Z, Skorić S, Đikanović V, Lenhardt M, Vuković-Gačić B (2014) Variability in DNA damage of chub (Squalius cephalus L.) blood, gill and liver cells during the annual cycle. Environ Toxicol Phar 37(3):967–974
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu J-C, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35(3):206–221
Velimirov B, Milošević N, Kavka GG, Farnleitner AH, Kirschner AK (2011) Development of the bacterial compartment along the Danube River: a continuum despite local influences. Mol Ecol 61(4):955–967
Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Jarić I, Jovanović L, Skorić S, Smederevac-Lalić M, Nikčević M, Lenhardt M (2010) Heavy metal and trace element accumulation in muscle, liver and gills of the Pontic shad (Alosa immaculata Bennet 1835) from the Danube River (Serbia). Microchem J 95(2):341–344
Vuković-Gačić B, Kolarević S, Sunjog K, Tomović J, Knežević-Vukčević J, Paunović M, Gačić Z (2014) Comparative study of the genotoxic response of freshwater mussels Unio tumidus and Unio pictorum to environmental stress. Hydrobiologia 735(1):221–231
White PA, Rasmussen JB (1998) The genotoxic hazards of domestic wastes in surface waters. Mutat Res-Rev Mutat 410(3):223–236
Zhu Y, Wang J, Bai Y, Zhang R (2004) Cadmium, chromium, and copper induce polychromatocyte micronuclei in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). B Environ Contam Tox 72(1):78–86
Acknowledgments
This study was done as a part of the activities within project no. 173045, funded by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Serbia. The authors are especially grateful to Luka Gačić who provided English language improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostić, J., Kolarević, S., Kračun-Kolarević, M. et al. Genotoxicity assessment of the Danube River using tissues of freshwater bream (Abramis brama). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 20783–20795 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7213-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7213-0