Abstract
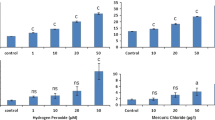
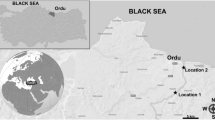
Mercury (Hg) is one of the major aquatic contaminants even though emissions have been reduced over the years. Despite the relative abundance of investigations carried out on Hg toxicity, there is a scarcity of studies on its DNA damaging effects in fish under realistic exposure conditions. This study assessed the Hg genotoxicity in Golden grey mullets (Liza aurata) at Laranjo basin, a particularly contaminated area of Ria de Aveiro (Portugal) well known for its Hg contamination gradient. (1) Fish were seasonally caught at Laranjo basin and at a reference site (S. Jacinto), and (2) animals from the reference site were transplanted and caged (at bottom and surface), for 3 days, in two different locations within Laranjo basin. Using the comet assay, blood was analyzed for genetic damage and apoptotic cell frequency. The seasonal survey showed greater DNA damage in the Hg-contaminated area for all sampling seasons excluding winter. The temporal variation pattern of DNA lesions was: summer ≈ autumn > winter > spring. Fish caged at Laranjo also exhibited greater DNA damage than those caged at the reference site, highlighting the importance of gill uptake on the toxicity of this metal. No increased susceptibility to apoptosis was detected in either wild or caged fish, indicating that mercury damages DNA of blood cells by a nonapoptotic mechanism. Both L. aurata and the comet assay proved to be sensitive and suitable for genotoxicity biomonitoring in mercury-contaminated coastal systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arabi M (2004) Analyses of impact of metal ion contamination on carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) gill cell suspensions. Biol Trace Elem Res 100(3):229–246. doi:10.1385/BTER:100:3:229
Arabi M, Alaeddini MA (2005) Metal-ion-mediated oxidative stress in the gill homogenate of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)—antioxidant potential of manganese, selenium, and albumin. Biol Trace Elem Res 108(1–3):155–168. doi:10.1385/BTER:108:1-3:155
Ayllon F, Garcia-Vazquez E (2000) Induction of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in European minnow Phoxinus phoxinus and mollie Poecilia latipinna: an assessment of the fish micronucleus test. Mutat Res 467:177–186
Belpaeme K, Cooreman K, Kirsch-Volders M (1998) Development and validation of the in vivo alkaline comet assay for detecting genomic damage in marine flatfish. Mutat Res 415:167–184
Ben-Ozer EY, Rosenspire AJ, McCabe MJ Jr, Worth RG, Kindzelskii AL, Warra NS, Petty HR (2000) Mercuric chloride damages cellular DNA by a non-apoptotic mechanism. Mutat Res 470:19–27
Biesinger KE, Anderson LE, Eaton JG (1982) Chronic effects of inorganic and organic mercury on Daphnia magna: toxicity, accumulation, and loss. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 11:769–774. doi:10.1007/BF01059166
Blasco J, Rubio JA, Forja J, Gomez-Parra A, Establier R (1998) Heavy metals in some fishes of the Mugilidae family from salt-ponds of Cadiz bay, SW Spain. Ecotoxicol Environ Restoration 1(2):71–77
Boening DW (2000) Ecological effects, transport, and fate of mercury: a general review. Chemosphere 40:1335–1351. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00283-0
Buschini A, Carboni P, Martino A, Poli P, Rossi C (2003) Effects of temperature on baseline and genotoxicant-induced DNA damage in haemocytes of Dreissena polymorpha. Mutat Res 537:81–92
Coelho JP, Pereira ME, Duarte A, Pardal MA (2005) Macroalgae response to a mercury contamination gradient in a temperate coastal lagoon (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 65:492–500. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2005.06.020
Collins AR, Dobson VL, Duinska M, Kennedy G, Stetina R (1997) The comet assay: what can it really tell us? Mutat Res 375:183–193. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(97)00013-4
Coughlan BM, Hartl MGJ, O’Reilly SJ, Sheehan D, Morthersill C, van Pelt F, O’Halloran J, O’Brien NM (2002) Detecting genotoxicity using the Comet assay following chronic exposure of Manila clam Tapes semidecussatus to polluted estuarine sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 44:1359–1365. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00254-0
Davis JA, Yee D, Collins JN, Schwarzbach SE, Luoma SN (2003) Potential for increased mercury accumulation in the estuary food web. In: Brown LR (ed) Issues in San Francisco estuary tidal wetlands restoration. San Francisco Estuary and Watershed Science 1(1):article 4
De Flora S, Bennicelli C, Bagnasco M (1994) Genotoxicity of mercury compounds. A review. Mutat Res 317:57–79
Duez P, Dehon G, Kumps A, Dubois J (2003) Statistics of the comet assay: a key to discriminate between genotoxic effects. Mutagenesis 2(18):159–166. doi:10.1093/mutage/18.2.159
Guilherme S, Valega M, Pereira ME, Santos MA, Pacheco M (2008a) Erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities in wild and caged fish (Liza aurata) along an environmental mercury contamination gradient. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70(3):411–421. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.08.016
Guilherme S, Válega M, Pereira ME, Santos MA, Pacheco M (2008b) Antioxidant and biotransformation responses in Liza aurata under environmental mercury exposure—relationship with mercury accumulation and implications for public health. Mar Pollut Bull 56(5):845–859. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.02.003
Helma C, Uhl M (2000) A public domain image-analysis program for the single-cell gel-electrophoresis (comet) assay. Mutat Res 466:9–15
Kim I-Y, Hyun C-K (2006) Comparative evaluation of the alkaline comet assay with the micronucleus test for genotoxicity monitoring using aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64(3):288–297. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.05.019
Klobucar GIV, Pavlica M, Erben R, Papes D (2003) Application of the micronucleus and comet assays to mussel Dreissena polymorpha haemocytes for genotoxicity monitoring of freshwater environments. Aquat Toxicol 64:15–23. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(03)00009-2
Koppen G (1999) Single cell gel electrophoresis/comet assay for plants—a tool to assess DNA integrity. Mol. Ph.D. thesis. Vlaamse Instelling voor Technologisch Onderzoek (VITO), Belgium
Koppen G, Verschaeve L (1996) The alkaline comet test on plant cells: a new genotoxicity test for DNA strand breaks in Vicia faba root cells. Mutat Res 360:193–200
Kraemer LD, Campbell PGC, Hare L (2005) Dynamics of Cd, Cu and Zn accumulation in organs and sub-cellular fractions in field transplanted juvenile yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Environ Pollut 138:324–337. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.03.006
Lee RF, Steinert S (2003) Use of the single cell gel electrophoresis/comet assay for detecting DNA damage in aquatic (marine and freshwater) animals (Review). Mutat Res 544:43–64. doi:10.1016/S1383-5742(03)00017-6
Meintieres S, Nesslany F, Pallardy M, Marzin D (2003) Detection of ghost cells in the standard alkaline comet assay is not a good measure of apoptosiss. Environ Mol Mutagen 41:260–269. doi:10.1002/em.10156
Mitchelmore CL, Chipman JK (1998) Detection of DNA strand breaks in brown trout (Salmo trutta) hepatocytes and blood cells using the single cell gel electrophoresis (comet) assay. Aquat Toxicol 41:161–182. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(97)00064-7
Mitchelmore CL, Birmelim C, Livingstone DR, Chipman JK (1998) Detection of DNA strand breaks in isolated mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) digestive gland cells using the comet assay. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 41:51–58. doi:10.1006/eesa.1998.1666
Nacci DE, Cayula S, Jackim E (1996) Detection of DNA damage in individual cells from marine organisms using the single cell gel assay. Aquat Toxicol 35(3–4):197–210. doi:10.1016/0166-445X(96)00016-1
Nepomuceno JC, Ferrari I, Spano MA, Centeno AJ (1997) Detection of micronuclei in peripheral erythrocytes of Cyprinus carpio exposed to metallic mercury. Environ Mol Mutagen 30:293–297. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(1997)30:3<293::AID-EM7>3.0.CO;2-M
Pacheco M, Santos MA, Teles M, Oliveira M, Rebelo JE, Pombo L (2005) Biotransformation and genotoxic biomarkers in mullet species (Liza sp.) from a contaminated coastal lagoon (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Environ Monit Assess 107:133–153. doi:10.1007/s10661-005-5308-z
Pereira ME, Duarte AC, Millward GE, Abreu SN, Reis MC (1997) Distribution of mercury and other heavy metals in the Ria de Aveiro. Quimica Analitica 16(S1):S31–S35
Pereira ME, Duarte AC, Millward G, Vale C, Abreu SN (1998) Tidal export of particulate mercury from the most contaminated area of Aveiro’s Lagoon, Portugal. Sci Total Environ 213:157–163. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00087-4
Perry DM, Weis JS, Weis P (1988) Cytogenetic effects of methylmercury in embryos of the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 17(5):569–574. doi:10.1007/BF01055824
Ramalhosa E, Monterroso P, Abreu S, Pereira E, Vale C, Duarte A (2001) Storage and export of mercury from a contaminated bay (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Wetlands Ecol Manage 9:311–316. doi:10.1023/A:1011864702531
Rank J, Jensen K (2003) Comet assay on gill cells and hemocytes from the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54:323–329. doi:10.1016/S0147-6513(02)00006-4
Rank J, Lehtonen KK, Strand J, Laursen M (2007) DNA damage, acetylcholinesterase activity and lysosomal stability in native and transplanted mussels (Mytilus edulis) in areas close to coastal chemical dumping sites in Denmark. Aquat Toxicol 84(1):50–61. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.05.013
Salagovic J, Maes A, Van Gorp U, Verschaeve L, Kalina I (1997) The cell cycle positions influence DNA migration as measured with the alkaline comet assay in stimulated human lymphocytes. Folia Biol 43(2):79–82
Singh NP (2000) Microgels for estimation of DNA strand breaks, DNA protein crosslinks and apoptosis. Mutat Res 455:111–127. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(00)00075-0
Singh NP, McCoy T, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–192. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Speit G, Hartmann A (2004) The comet assay—a sensitive test for the detection of DNA damage repair. Methods Mol Biol 291:85–96
Steinert SA, Streib-Montee R, Leather JM, Chadwick DB (1998) DNA damage in mussels at sites in San Diego Bay. Mutat Res 399(1):65–85. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(97)00267-4
Sumathi M, Kalaiselvi K, Palanivel M, Rajaguru P (2001) Genotoxicity of textile dye effluent on fish (Cyprinus carpio) measured using the comet assay. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 66(3):407–414. doi:10.1007/s00128-001-0020-3
Tice RR, Agurel E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartman A, Kobayashi H, Rojas E, Ryu J-C, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(2000)35:3<206::AID-EM8>3.0.CO;2-J
Venier P, Maron S, Canova S (1997) Detection of micronuclei in gill cells and haemocytes of mussels exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Mutat Res 390:33–44
Weis P, Weis JS (1977) Methylmercury teratogenesis in the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Teratology 16(3):317–325. doi:10.1002/tera.1420160311
Wiener JG, Krabbenhoft DP, Heinz GH, Scheuhammer AM (2002) Ecotoxicology of mercury. In: Hoffman DJ, Rattner BA, Burton GA Jr, Cairns J Jr (eds) Handbook of ecotoxicology, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 409–463
Acknowledgment
The authors are very thankful for the technical assistance of Mr. Aldiro Pereira.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, C.S.A., Guilherme, S.I.A.G., Barroso, C.M.M. et al. Evaluation of DNA Damage Induced by Environmental Exposure to Mercury in Liza aurata Using the Comet Assay. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58, 112–122 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9330-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9330-y