Abstract
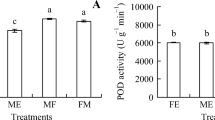
Different ecotypes of crop hybridization can produce heterosis effects and have wide applications in plant breeding. In this study, seedlings of cadmium (Cd) hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum were collected from two different climate–ecology regions of the western Sichuan Basin, China, to carry out reciprocal hybridizing and to study the Cd accumulation characteristics of F1 hybrids of S. nigrum. In the two pot experiments (high and low soil Cd concentration), the biomass and Cd extraction of reciprocal hybridizing F1 hybrids were higher than those of the parents, but the Cd content in different organs was lower than those of the parents. These results indicate that the biomass and Cd extraction of F1 hybrids show over-parent heterosis, and the Cd content shows hybrid weakness. In the field experiment, the variety of the biomass, Cd content, and Cd extraction of reciprocal hybridizing F1 hybrids were the same as the pot experiments, and the Cd extraction by shoots of reciprocal hybridizing F1 hybrids increased by 17.20 and 23.08 %, relative to the two higher parents. Therefore, the reciprocal hybridizing S. nigrum of different climate–ecology regions could be efficiently used to improve the phytoremediation ability of S. nigrum to Cd-contaminated soil.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Akhter Z, Shamsuddin AKM, Rohman MM, Shalim UM, Mohi-Ud-din M, Alam AKMM (2003) Studies on heterosis for yield and yield components in wheat. J Biol Sci 3:892–897
Caunii A, Negrea A, Pentea M, Samfira I, Motoc M, Butnariu M (2015) Mobility of heavy metals from soil in the two species of the aromatic plants. Rev Chim (Bucharest) 66:382–386
Chen TB, Fan ZL, Lei M, Huang ZC, Wei ZY (2002) Arsenic uptake by hyperaccumulator Peteris vittata L.: effect of phosphorus and its significance. Chin Sci Bull 47:1156–1159
Cheng SH, Zhuang JY, Fan YY, Du JH, Cao LY (2007) Progress in research and development on hybrid rice: a super-domesticate in China. Ann Bot 100:959–966
Datta R, Sarkar D (2004) Effective integration of soil chemistry and plant molecular biology in phytoremediation of metals. Environ Geosci 11:53–63
Dey SS, Sharma K, Dey RB, Kumar GMS, Singh D, Kumar R, Parkash C (2015) Inter specific hybridization (Brassica carinata × Brassica oleracea) for introgression of black rot resistance genes into Indian cauliflower (B. oleracea var. botrytis L.). Euphytica 204:149–162
Ichitani K, Taura S, Tezuka T, Okiyama Y, Kuboyama T (2011) Chromosomal location of HWA1 and HWA2, complementary hybrid weakness genes in rice. Rice 4:29–38
Leng Y, Hong DL (2004) Quality characters of hybrid rice grain derived from different ecological types and their genetic analysis in Japonica rice (Oryza sativa). Chin J Rice Sci 18:29–33
Li M, Wang GX, Wei XP (2006) Ecotypes of Glycyrrhiza uralensis in different habitats. Acta Botan Boreali-Occiden Sin 26:368–376
Lin LJ, Liao MA, Mei LY, Liu J, Cheng J, Luo L, Liu Y (2014a) Two ecotypes of hyperaccumulator and accumulator affect cadmium accumulation in cherry seedling by intercropping. Environ Prog Sustainable Energy 33:1251–1257
Lin LJ, Liao MA, Ren YJ, Luo L, Zhang X, Yang DY, He J (2014b) Effects of mulching tolerant plant straw on soil surface on growth and cadmium accumulation of Galinsoga parviflora. PLoS One 9:e114957
Lin LJ, Liu QH, Shi J, Sun JL, Liao MA, Mei LY (2014c) Intercropping different varieties of radish can increase cadmium accumulation in radish. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:1950–1955
Lin LJ, Shi J, Liu QH, Liao MA, Mei LY (2014d) Cadmium accumulation characteristics of the winter farmland weeds Cardamine hirsuta Linn. and Gnaphalium affine D. Don. Environ Monit Assess 186:4051–4056
Liu GS (1996) Soil physical and chemical analysis & description of soil profiles. Standards Press of China, Beijing
Maestri E, Marmiroli M, Visioli G, Marmiroli N (2010) Metal tolerance and hyperaccumulation: costs and trade-offs between traits and environment. Environ Exp Bot 68:1–13
Marques APGC, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2009) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils: phytoremediation as a potentially promising clean-up technology. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 39:622–654
Peng SL, Du WB, Li ZA (2004) A review of heavy metal accumulation and tolerance by plants of different ecotype. J Jishou Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 25:19–26
Prasad PVV, Boote KJ, Allen LH Jr, Sheehy JE, Thomas JMG (2006) Species, ecotype and cultivar differences in spikelet fertility and harvest index of rice in response to high temperature stress. Field Crop Res 95:398–411
Shang CS, Shi B, Cheng SH (1992) Studies on early maturity and high yield in the hybrid progenies of soybean of different ecological types. Acta Agric Boreali-Sinica 7:46–51
Tai PD, Guo SH, Song YF, Sun TH, Li PJ, Jiang S (2000) Comparison of physiological characteristics of different ecotype plants. Chin J Appl Ecol 1:53–56
Wei SH, Zhou QX, Wang X, Zhang KS, Guo GL, Ma Lena QY (2005) A newly-discovered Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. Chin Sci Bull 50:33–38
Wei HS, Clark G, Doronila AI, Jin J, Monsant AC (2013) Cd hyperaccumulative characteristics of Australia ecotype Solanum nigrum L. and its implication in screening hyperaccumulator. Int J Phytoremediation 15:199–205
Whiting SN, Leake JR, McGrath SP, Baker AJ (2001) Hyperaccumulation of Zn by Thlaspi carulescens can ameliorate Zn toxicity in the rhizosphere of cocropped Thlaspi arvense. Environ Sci Technol 35:3237–3241
Yan XH, Hu SJ (2012) Effects of natural hybridization on plant species survival and evolution. J Chongqing Norm Univ (Nat Sci) 29:84–88
Yu CL, Liu B, Xu X (2011) Effect of DA-6 on enhanced remediation efficiency of Solanum nigrum L. in serious cadmium polluted soil. Sci Agric Sin 44:3485–3490
Zhang YX, Yu F, Zhang YY, Song XQ (2008) Uptake, translocation and accumulation of cadmium in plant. Chin J Eco-Agric 16:1317–1321
Zhao HY, Lin LJ, Yan QL, Yang YX, Zhu XM, Shao JR (2011) Effects of EDTA and DTPA on lead and zinc accumulation of ryegrass. J Environ Prot 2:932–939
Zhu XM, Yang WY, Shao JR, Chen XH (2004) The research on milling quality variations of high-quality rice in different ecological regions of Sichuan. Seed 23:3–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Lijin Lin, Jing He and Xun Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., He, J., Wang, X. et al. Cadmium accumulation characteristics of F1 hybrids by reciprocal hybridizing of Solanum nigrum in two climate–ecology regions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 18842–18849 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7089-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7089-z