Abstract
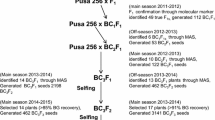
Indian cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis L.; C genome) is highly susceptible to black rot caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Pam.) Dowson. Till now no durable resistance genes have been identified in C genome of Brassica. Two B. carinata genotypes, NPC-9 and HCA-6 were found highly resistant to Xcc race 1 and 4, most prevalent throughout the world. Inter-specific hybridization was attempted for introgression of resistance genes from B. carinata into Indian cauliflower using three different embryo rescue approaches. Reciprocal crosses were made between two B. carinata and 7 lines of Indian cauliflower. Very low rate of success was observed when B. oleracea lines were used as female parents. Among the three different approaches, direct embryo culture was the most successful for development of F1 and BC1 population. Through ovule culture and direct embryo culture 58 F1 hybrids were developed. Success rates for hybrid plant development through ovule culture and direct embryo culture were 1.04 and 11.33 %, respectively. All the F1 hybrids were found to be highly resistant to Xcc race 1 and 4. Eleven NPC-9 based F1 hybrids were used for development of BC1 population through direct embryo culture with a success rate of 30.76 %. Direct embryo culture can be used as an effective tool for introgression of desirable genes across Brassica species. Among 29 BC1 plants, 26 and 25 plants were highly resistant to Xcc race 4 and race 1, respectively. The population developed through inter-specific hybridization would open several avenues to develop durable black rot resistant lines in B. oleracea.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayotte R, Harney PM, Souza Machado V (1987) The transfer of triazine resistance from Brassica napus L. to B. oleracea L. I. Production of F1 hybrids through embryo rescue. Euphytica 36:615–624
Bain DC (1952) Reaction of Brassica seedlings to black rot. Phytopathology 42:497–500
Bothmer R, Gustaffson M, Snogerup S (1995) Brassica sec. Brassica (Brassicaceae) II. Inter- and intra-specific crosses with cultivars of B. oleracea. Genet Resour Crop Evol 42:165–178
Camargo LEA, Williams PH, Osborn TC (1995) Mapping of quantitative loci controlling resistance to Brassica oleracea to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in the field and greenhouse. Phytopathology 85:1296–1300
Chévre AM, Barret P, Eber F, Dupuy P, Brun H, Tanguy X, Renard M (1997) Selection of stable Brassica napus-B.juncea recombinant lines resistant to black leg (Leptosphaeriamaculans). 1. Identification of molecular markers, chromosomal and genomic origin of the introgression. Theor Appl Genet 95:1104–1111
Chiang MS, Chiang BY, Grant WF (1977) Transfer of resistance to race 2 of Plasmodiophora brassicae from Brassica napus to cabbage (B. oleracea var. ‘capitata’). I. Interspecific hybridization between B. napus and B. oleracea var. ‘capitata’. Euphytica 26:319–326
Cook AA, Walker JC, Larson RH (1952) Studies on the disease cycle of black rot of crucifers. Phytopathology 42:162–167
Dickson MD, Hunter JE (1987) Inheritance of resistance in cabbage seedlings to black rot. HortScience 22:108–109
Diederichsen E, Sacristan MD (1994) The use of ovule culture in reciprocal hybridization between B. campestris L. and B. oleracea L. Plant Breeding 113:79–82
Gowers S, Christey MC (1999) Intercrossing Brassica napus and Brassica oleracea to introgress characters from kale to rape. Proceedings of the 10th International Rapeseed Congress, Canberra, Australia
Guo H, Dickson MH, Hunter JE (1991) Brassica napus sources of resistance to black rot in crucifers and inheritance of resistance. HortScience 26:1545–1547
Hansen LN, Earle ED (1995) Transfer of resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris into Brassica oleracea L. by protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 91:1293–1300
Hunter JE, Dickson MH, Ludwig JW (1987) Source of resistance to black rot of cabbage expressed in seedlings and adult plants. Plant Dis 71:263–266
Lu CM, Zhang B, Kakihara F, Kato M (2001) Introgression of genes into cultivated Brassica napus through resynthesis of B. napus via ovule culture and the accompanying change in fatty acid composition. Plant Breed 120:405–410
Meng J, Lu M (1993) Genotype effects of Brassica napus on its reproductive behavior after pollination with B. juncea. Theor Appl Genet 87:238–242
Momotaz A, Kato M, Kakihara F (1998) Production of intergeneric hybrids between Brassica and Sinapis species by means of embryo rescue techniques. Euphytica 103:123–130
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plantarum 15:473–497
Niemann J, Wojciechowski A, Janowicz J (2012) Broadening the variability of quality traits in rapeseed through interspecific hybridization with an application of immature embryo culture. J Biotechnol Comput Biol Nanotechnol 93:109–115
Niemann J, Wojciechowski A, Jedryczka M, Kaczmarek J (2013) Interspecific Hybridization as a Tool for Broadening the Variability of Useful Traits in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). In: F. Branca and A. Tribulato (Eds) Proceedings of the VIth IS on Brassicas and XVIIIth Crucifer Genetics Workshop, Acta Hort, p 1005
Nishiyama I, Sarashima M, Matsuzawa Y (1991) Critical discussion of abortive interspecific crosses in Brassica. Plant Breeding 107:288–302
Saha P, Kalia P, Sonah H, Sharma TR (2014) Molecular mapping of black rot resistance locus Xca1bo on chromosome 3 in Indian cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis L.). Plant Breeding 133:268–274
Taylor JD, Conway J, Roberts SJ, Astley D, Vicente JG (2002) Sources and origin of resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica genomes. Phytopathology 92:105–111
Tonguc M, Griffiths PD (2004) Development of black rot resistant interspecific hybrids between Brassica oleracea L. cultivars and Brassica accession A 19182, using embryo rescue. Euphytica 136:313–318
Tonguc M, Earle ED, Griffiths PD (2003) Segregation distortion of Brassica carinata derived black rot resistance in B. oleracea. Euphytica 134:269–276
Velasco L, Fernandez-Martinez JM (2002) Breeding oilseed crops for improved oil quality. J Crop Production 5:309–344
Vicente JG, Conway J, Roberts SJ, Taylor JD (2001) Identification and origin of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris races and related pathovars. Phytopathology 91:492–499
Vicente JG, Taylor JD, Sharpe AG, Parkin IAP, Lydiate DJ, King GJ (2002) Inheritance of race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica genomes. Phytopathology 92:1134–1141
Weerakoon SR (2011) Producing inter-specific hybrids between Brassica juncea (L.) Czern & Coss and B. oleracea (L.) to synthesize trigenomic (abc) Brassica. J Sci Univ. Kelaniya 6:13–34
Weerakoon SR, Si P, Zili W, Meng J, Yan G (2009) Production and confirmation of hybrids through interspecific crossing between tetraploid B. juncea and diploid B. oleracea towards a hexaploid Brassica population 16th Australian Research Assembly on Brassicas, Ballarat, Victoria
Westman AL, Kresovich S, Dickson MH (1999) Regional variation in Brassica nigra and other weedy crucifers for disease reaction to Alternaria brassicicola and Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Euphytica 106:253–259
Williams PH, Staub T, Sutton JC (1972) Inheritance of resistance in cabbage to black rot. Phytopathology 62:247–252
Wojciechowski A (1985) Interspecific hybrids between Brassica campestris and B. oleracea. I. Effectiveness of crossing. Observations of pollen tube growth. The course of embryogenesis. Genetica Polonica 26(4):423–436
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Dept. of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India for funding the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dey, S.S., Sharma, K., Bhatia Dey, R. et al. Inter specific hybridization (Brassica carinata × Brassica oleracea) for introgression of black rot resistance genes into Indian cauliflower (B. oleracea var. botrytis L.).. Euphytica 204, 149–162 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1352-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1352-0