Abstract
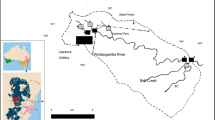
Effects of acid mine drainage (AMD) were investigated in surface waters (Laranjinha River and Ribeirão das Pedras stream) and groundwaters from a coal mining area sampled in two different seasons at Figueira city, Paraná State, Brazil. The spatial data distribution indicated that the acid effluents favor the chemical elements leaching and transport from the tailings pile into the superficial water bodies or aquifers, modifying their quality. The acid groundwaters in both sampling periods (dry: pH 2.94–6.04; rainy: pH 3.25–6.63) were probably due to the AMD generation and infiltration, after the oxidation of sulfide minerals. Such acid effluents cause an increase of the solubilization rate of metals, mainly iron and aluminum, contributing to both groundwater and surface water contamination. Sulfate in high levels is a result of waters’ pollution due to AMD. In some cases, high sulfate and low iron contents, associated with less acidic pH values, could indicate that AMD, previously generated, is nowadays being neutralized. The chemistry of the waters affected by AMD is controlled by the pH, sulfide minerals’ oxidation, oxygen, iron content, and microbial activity. It is also influenced by seasonal variations that allow the occurrence of dissolution processes and the concentration of some chemical elements. Under the perspective of the waters’ quality evaluation, the parameters such as conductivity, dissolved sodium, and sulfate concentrations acted as AMD indicators of groundwaters and surface waters affected by acid effluents.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. J Clean Prod 14:1139–1145. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.09.006
Al-Hashimi A, Evans GJ, Cox B (1996) Aspects of the permanent storage of uranium tailings. Water Air Soil Pollut 88:83–92. doi:10.1007/BF00157414
ANEEL (Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica) (2011) A Situação da Produção de Carvão Mineral no Estado do Paraná em Relação a Nota Técnica 034/2011. Tech. Rep, ANEEL, Brasília
Arnold T, Zorn T, Zänker H, Bernhard G, Nitsche H (1988) Sorption of U(VI) onto phyllite: experiments and modeling. Chem Geol 151:129–141. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(00)00151-0
Baik MH, Hyun SP, Hahn PS (2003) Surface and bulk sorption of uranium (VI) onto granite rock. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 256:11–18. doi:10.1023/A:1023331521718
Benner SG, Gould WD, Blowes DW (2000) Microbial populations associated with the generation and treatment of acid mine drainage. Chem Geol 169:435–448
Berghorn GH, Hunzeker GR (2001) Passive treatment alternatives for remediating abandoned mine drainage. Remediat J 11:111–127. doi:10.1002/rem.1007
Bizzi LA, Schobbenhaus C, Vidotti RM, Gonçalves JH (2003) Geologia, Tectônica e recursos Minerais do Brasil: texto, mapas e SIG. CPRM, Brasília
Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Jambor JL, Weisener CG, Paktunc D, Gould WD, Johnson DB (2014) The geochemistry of acid mine drainage. Reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences. Treatise Geochem 11:131–190. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-095975-7.00905-0
Bonotto DM (1996) Comportamento hidrogeoquímico do 222Rn e isótopos de urânio 238 U e 234 U sob condições controladas de laboratório e em sistemas naturais. Post PhD Thesis, UNESP, Rio Claro
Campaner VP, Luiz-Silva W (2009) Processos físico-químicos em drenagem ácida de mina em mineração de carvão no sul do Brasil. Quim Nov. 32:146–152. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422009000100028
Campaner VP, Luiz-Silva W, Machado W (2014) Geochemistry of acid mine drainage from a coal mining area and processes controlling metal attenuation in stream waters, southern Brazil. An Acad Bras Ciênc 86:539–554. doi:10.1590/0001-37652014113712
Candeias C, Ávila PF, Silva EF, Ferreira A, Salgueiro AR, Teixeira JP (2014) Acid mine drainage from the Panasqueira mine and its influence on Zêzere river (Central Portugal). J Afr Earth Sci 99:705–712. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2013.10.006
Caraballo MA, Macías F, Nieto JM, Ayora C (2016) Long term fluctuations of groundwater mine pollution in a sulfide mining district with dry Mediterranean climate: implications for water resources management and remediation. Sci Total Environ 539:427–435. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.156
Carrero S, Pérez-López R, Fernandez-Martinez A, Cruz-Hernández P, Agnieszka CA, Ayora C, Poulain A (2015) The potential role of aluminium hydroxysulphates in the removal of contaminants in acid mine drainage. Chem Geol 417:414–423. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.10.020
Chen T, Bo Y, Lei C, Xiao X (2014) Pollution control and metal resource recovery for acid mine drainage. Hydrometallurgy 147–148:112–119. doi:10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.04.024
CONAMA (Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente) (2005) Rule 357 published in 17th Mar 2005. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/res/res05/res35705.pdf
CONAMA (Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente) (2011) Rule 430 published in 13th May 2011. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/res/res11/propresol_lanceflue_30e31mar11.pdf
Cravotta CA (2008) Dissolved metals and associated constituents in abandoned coal-mine discharges, Pennsylvania, USA. Part 2: geochemical controls on constituent concentrations. Appl Geochem 23:203–226
Equeenuddin SM, Tripathy S, Sahoo PK, Panigrahi MK (2010) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of acid mine drainage and water pollution at Makum coalfield, India. J Geochem Explor 105:75–82. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.04.006
Francis AJ (1990) Microbial dissolution and stabilization of toxic metals and radionuclides in mixed wastes. Experientia 46:840–851. doi:10.1007/BF01935535
Fungaro DA, Izidoro JC (2006) Remediação da drenagem ácida de mina usando zeólitas sintetizadas a partir de cinzas leves de carvão. Quim Nov. 29:735–740. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422006000400019
Geldenhuis S, Bell FG (1998) Acid mine drainage at a coal mine in the eastern Transvaal, South Africa. Environ Geol 34:234–242. doi:10.1007/s002540050275
Genty T, Bussiere B, Potvin R, Benzaazoua M, Zagury GJ (2012) Dissolution of calcitic marble and dolomitic rock in high iron concentrated acid mine drainage: application to anoxic limestone drains. Environ Earth Sci 66:2387–2401. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1464-3
Gray NF (1996) Field assessment of acid mine drainage contamination in surface and ground water. Environ Geol 27:358–361. doi:10.1007/BF00766705
Gunsinger MR, Ptacek CJ, Blowes DW, Jambor JL (2006) Evaluation of long-term sulfide oxidation processes within pyrrhotite-rich tailings, Lynn Lake, Manitoba. J Contam Hydrol 83:149–170. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2005.10.013
Krebs ASJ, Alexandre NZ (1998) Situação atual dos recursos hídricos da bacia carbonífera, face às atividades de lavra, beneficiamento e uso do carvão mineral e de outras atividades antrópicas. Proceedings of IX Congresso Brasileiro de Águas Subterrâneas, Bahia, pp 60–65
Küsel K (2003) Microbial cycling of iron and sulfur in acid coal mining lake sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut 3:67–90. doi:10.1023/A:1022103419928
Liao J, Wen Z, Ru X, Chen J, Wu H, Wei C (2016) Distribution and migration of heavy metals in soil and crops affected by acid mine drainage: public health implications in Guangdong Province, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 124:460–469. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.11.023
Licht OAB (2001) Atlas geoquímico do Paraná. Mineropar, Curitiba
Lee MH, Choi CS, Cho YH, Lee CW, Shin HS (2001) Concentrations and activity ratios of uranium isotopes en the groundwater os the Okchum Belt in Korea. J Environ Radioact 55:105–116. doi:10.1016/S0265-931X(01)00014-5
Lottermoser B (2010) Mine wastes: characterization, treatment and environmental impacts, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-12419-8
Malmstro ME, Berglund S, Jarsjo J (2008) Combined effects of spatially variable flow and mineralogy on the attenuation of acid mine drainage in groundwater. Appl Geochem 23:1419–1436. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.12.029
MINEROPAR (Minerais do Paraná) (2001) Diagnóstico preliminar dos impactos ambientais da mineração no Paraná. Mineropar, Curitiba
Molson J, Aubertin M, Bussière B (2012) Reactive transport modelling of acid mine drainage within discretely fractured porous media: plume evolution from a surface source zone. Environ Model Softw 38:259–270. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2012.06.010
Nordstrom DK, Alpers CN (1999) Geochemistry of acid mine waters. In: Plumlee GS, Logsdon M (eds) Society & Economic Geologists 6 A 133–160
Nordstrom DK (2009) Acid rock drainage and climate change. J Geochem Explor 100:97–104. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2008.08.002
Nordstrom DK, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ (2015) Hydrogeochemistry and microbiology of mine drainage: an update. Appl Geochem 57:3–16. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.02.008
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Trans Am Geophys Union 25. doi:10.1029/TR025i006p00914
Qureshi A, Maurice C, Öhlander B (2016) Potential of coal mine waste rock for generating acid mine drainage. J Geochem Explor 160:44–54. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.10.014
Schneider RL, Muhlmann H, Tommasi E, Medeiros RA, Daemon RA, Nogueira AA (1974) Revisão estratigráfica da Bacia do Paraná. Proceedings of XXVIII Congresso Brasileiro de Geologia, Porto Alegre, pp 41–65
SEMA (Secretaria de Estado do Meio Ambiente e Recursos Hídricos do Paraná) (2010) Bacias Hidrográficas do Paraná. SEMA, Curitiba
Shim MJ, Choi BY, Lee G, Hwang YH, Yang J, O’Loughlin EJ, Kwon MJ (2015) Water quality changes in acid mine drainage streams in Gangneung, Korea, 10 years after treatment with limestone. J Geochem Explor 159:234–242. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.015
Shuqair MSS (2002) Estudo da contaminação do solo e água subterrânea por elementos tóxicos originados dos rejeitos das minas de carvão de Figueira no Estado do Paraná. PhD Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo
Silva LFO, Wollenschlager M, Oliveira MLS (2011) A preliminary study of coal mining drainage and environmental health in the Santa Catarina region, Brazil. Environ Geochem Health 33:55–65. doi:10.1007/s10653-010-9322-x
Silva LFO, Vallejuelo SFO, Martinez-Arkarazo I, Castro K, Oliveira MLS, Sampaio CH, Brum IAS, Leão FB, Taffarel SR, Madariaga JM (2013) Study of environmental pollution and mineralogical characterization of sediment rivers from Brazilian coal mining acid drainage. Sci Total Environ 447:169–178. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.013
Simate GS, Ndlovu S (2014) Acid mine drainage: challenges and opportunities. J Environ Chem Eng 2:1785–1803. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2014.07.021
Sun J, Tang C, Wu P, Strosnider WHJ, Han Z (2013) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of streams with and without acid mine drainage impacts: a paired catchment study in karst geology, SW China. J Hydrol 504:115–124. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.09.029
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1994) Technical document acid mine drainage prediction. Washington, 48 p. http://water.epa.gov/polwaste/nps/upload/amd.pdf
Wolkersdorfer C (2008) Water management at abandoned flooded underground mines. Fundam Tracer Tests Model Water Treat. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-77331-3
Younger PL, Banwart SA, Hedin RS (2002) Mine water: hydrology, pollution, remediation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. doi:10.1007/978-94-010-0610-1
Zacharias AA, Assine ML (2005) Modelo de preenchimento de vales incisos por associações de fáceis estuarinas, Formação Rio Bonito no Norte do Estado do Paraná. Rev Bras Geosci 35:573–583
Acknowledgments
CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technologic Development) in Brazil is thanked for financial support of this investigation. Three anonymous reviewers are greatly thanked for helpful comments that improved the readability of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galhardi, J.A., Bonotto, D.M. Hydrogeochemical features of surface water and groundwater contaminated with acid mine drainage (AMD) in coal mining areas: a case study in southern Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 18911–18927 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7077-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7077-3