Abstract
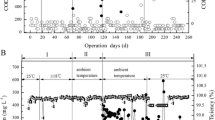
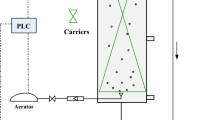
A novel integrated system of anoxic-pure oxygen microbubble-activated sludge reactor-moving bed biofilm reactor was employed in treatment of real coal gasification wastewater. The results showed the integrated system had efficient performance of pollutants removal in short hydraulic retention time. While pure oxygen microbubble with the flow rate of 1.5 L/h and NaHCO3 dosage ratio of 2:1 (amount NaHCO3 to NH4 +-N ratio, mol: mol) were used, the removal efficiencies of COD, total phenols (TPh) and NH4 +-N reached 90, 95, and 95 %, respectively, with the influent loading rates of 3.4 kg COD/(m3 d), 0.81 kg TPh/(m3 d), and 0.28 kg NH4 +-N/(m3 d). With the recycle ratio of 300 %, the concentrations of NO2 −-N and NO3 −-N in effluent decreased to 12 and 59 mg/L, respectively. Meanwhile, pure oxygen microbubble significantly improved the enzymatic activities and affected the effluent organic compositions and reduced the foam expansion. Thus, the novel integrated system with efficient, stable, and economical advantages was suitable for engineering application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Water Works Association and Water Pollution Control Federation, 18th edn
Agarwal A, Ng WJ, Liu Y (2011) Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 84:1175–1180
Boczar BA, Forney LJ, Begley WM, Larson RJ, Federle TW (2001) Characterization and distribution of esterase activity in activated sludge. Water Res 35:4208–4216
Cadoret A, Conrad A, Block J (2002) Availability of low and high molecular weight substrates to extracellular enzymes in whole and dispersed activated sludges. Enzym Microb Technol 31:179–186
Chan YJ, Chong MF, Law CL, Hassell DG (2009) A review on anaerobic–aerobictreatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. Chem Eng J 155:1–18
Chen W, Xu R (2010) Clean coal technology development in China. Energ Policy 38:2123–2130
Calderón K, González-Martínez A, Montero-Puente C, Reboleiro-Rivas P, Poyatos JM, Juárez-Jiménez B, Martínez-Toledo MV, Rodelas B (2012) Bacterial community structure and enzyme activities in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) using pure oxygen as an aeration source. Bioresour Technol 103:87–94
Goel R, Mino T, Satoh H, Matsuo T (1998) Enzyme activities under anaerobic and aerobic conditions in activated sludge sequencing batch reactor. Water Res 32:2081–2088
Gessesse A, Dueholm T, Petersen SB, Nielsen PH (2003) Lipase and protease extraction from activated sludge. Water Res 37:3652–3657
Guisasola A, Petzet S, Baeza JA, Carrera J, Lafuente J (2007) Inorganic carbon limitations on nitrification: experimental assessment and modelling. Water Res 41:277–286
González PS, Ontañon OM, Armendariz AL, Talano MA, Paisio CE, Agostini E (2013) Brassica napus hairy roots and rhizobacteria for phenolic compounds removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1310–1317
Hou BL, Han HJ, Jia SY, Zhuang HF, Zhao Q, Xu P (2014) Effect of alkalinity on nitrite accumulation in treatment of coal chemical industry wastewater using moving bed biofilm reactor. J Environ Sci 26:1014–1022
Jokela JPY, Kettunen RH, Sormunen KM, Rintala JA (2002) Biological nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate: low-cost nitrification in biofilters and laboratory scale in-situ denitrification. Water Res 36:4079–4087
Lee S, Kim M (2013) Fouling characteristics in pure oxygen MBR process according to MLSS concentrations and COD loadings. J Membr Sci 428:323–330
Li HQ, Han HJ, Du MA, Wang W (2011) Removal of phenols, thiocyanate and ammonium from coal gasification wastewater using moving bed biofilm reactor. Bioresour Technol 102:4667–4673
Liwarska-Bizukojc E, Ledakowicz S (2003) Estimation of viable biomass in aerobic biodegradation processes of organic fraction of municipal solid waste (MSW). J Biotechnol 101:165–172
Liu RR, Lu XJ, Tian Q, Yang B, Chen JH (2011) The performance evaluation of hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor for treatment of PVA-containing desizing wastewater. Desalination 271:287–294
Li WG, Su CY, Liu XZ, Zhang L (2014) Influence of the organic loading rate on the performance and the granular sludge characteristics of an EGSB reactor used for treating traditional Chinese medicine wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8167–8175
Molina-Muñoz M, Poyatos JM, Rodelas B, Pozo C, Manzanera M, Hontoria E, Gonzalez-Lopez J (2010) Microbial enzymatic activities in a pilot-scale MBR experimental plant under different working conditions. Bioresour Technol 101:696–704
Ma Q, Qu YY, Shen WL, Zhang ZJ, Wang JW, Liu ZR, Li DX, Li HJ, Zhou JT (2015) Bacterial community compositions of coking wastewater treatment plants in steel industry revealed by Illumina high-throughput sequencing. Bioresour Technol 179:436–443
Rodríguez FA, Reboleiro-Rivas P, González-López J, Hontoria E, Poyatos JM (2012) Comparative study of the use of pure oxygen and air in the nitrification of a MBR system used for wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 121:205–211
Sharma NK, Philip L, Murty Bhallamudi S (2012) Aerobic degradation of phenolics and aromatic hydrocarbons in presence of cyanide. Bioresour Technol 121:263–273
Tokutomi T, Shibayama C, Soda S, Ike M (2010) A novel control method for nitritation: the domination of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria by high concentrations of inorganic carbon in an airlift-fluidized bed reactor. Water Res 44:4195–4203
Terasaka K, Hirabayashi A, Nishino T, Fujioka S, Kobayashi D (2011) Development of microbubble aerator for wastewater treatment using aerobic activated sludge. Chem Eng Sci 66:3172–3179
Vázquez I, Rodríguez J, Marañón E, Castrillón L, Fernández Y (2006) Simultaneous removal of phenol, ammonium and thiocyanate from coke wastewater by aerobic biodegradation. J Hazard Mater 137:1773–1780
Wang JL, Quan XC, Wu LB, Qian Y, Hegemann W (2002) Bioaugmentation as a tool to enhance the removal of refractory compound in coke plant wastewater. Process Biochem 38:777–781
Whiteley CG, Heron P, Pletschke B, Rose PD, Tshivhunge S, Van Jaarsveld FP, Whittington-Jones K (2002) The enzymology of sludge solubilisation utilising sulphate reducing systems: properties of proteases and phosphatases. Enzym Microb Technol 31:419–424
Wang W, Han HJ, Yuan M, Li HQ (2010) Enhanced anaerobic biodegradability of real coal gasification wastewater with methanol addition. J Environ Sci 22:1868–1874
Wang W, Han HJ, Yuan M, Li HQ, Fang F, Wang K (2011) Treatment of coal gasification wastewater by a two-continuous UASB system with step-feed for COD and phenols removal. Bioresour Technol 102:5454–5460
Wang W, Han HJ (2012) Recovery strategies for tackling the impact of phenolic compounds in a UASB reactor treating coal gasification wastewater. Bioresour Technol 103:95–100
Wang ZX, Xu XC, Gong Z, Yang FL (2012) Removal of COD, phenols and ammonium from Lurgi coal gasification wastewater using A2O-MBR system. J Hazard Mater 235–236:78–84
Zhang WH, Wei CH, Yan B, Feng CH, Zhao GB (2013) Identification and removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wastewater treatment processes from coke production plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6418–6432
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the international scientific and technological cooperation program of China (no. 2014DFE90040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, H., Han, H. & Shan, S. Treatment of real coal gasification wastewater using a novel integrated system of anoxic hybrid two stage aerobic processes: performance and the role of pure oxygen microbubble. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 11916–11926 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6393-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6393-y