Abstract
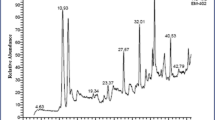
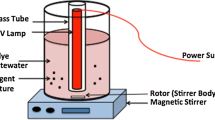
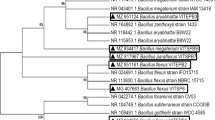
In the present study, the biotechnological potential of the marine-derived fungus Peniophora sp. CBMAI 1063 was investigated in relation to Reactive Black 5 (RB5) dye decolorization and degradation using an integrated statistical design composed of Plackett-Burman design (P&B), central composite design (CCD), and response surface methodology (RSM). RB5 dye was effectively decolorized (94 %) in saline conditions, without any detection of mutagenic compounds, and simultaneously, 57 % of total organic carbon (TOC) was removed in 7 days. The activity of lignin peroxidase (LiP) was not detected during the process. The gene expression of laccase (Lac) and manganese peroxidase (MnP) enzymes produced during the process was evaluated, and results from this experiment coupled with LC-MS analyses revealed that in the early stage of dye decolorization, a higher MnP gene expression and significant enzymatic activity was detected in Peniophora sp. CBMAI 1063 with the formation of p-Base and TAHNDS compounds. This paper reports innovative data related to the textile dye decolorization by the marine-derived basidiomycete Peniophora sp. CBMAI 1063, showing the metabolites formed and enzymatic action throughout the process in saline condition. The strategy used showed to be an efficient statistical approach that provides an attractive solution for the screening and simultaneous optimization of the degradation process.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardi L, Marzona M (2010) Factors affecting the complete mineralization of azo dyes. Biodegradation of azo dyes. Handbook Environ Chem 9:195–210
Bonugli-Santos RC, Durrant LR, Sette LD (2010) Laccase activity and putative laccase genes in marine derived basidiomycetes. Fungal Biol 114:863–872
Bonugli-Santos RC, Durrant LR, Sette LD (2012) The production of ligninolytic enzymes by marine-derived basidiomycetes and their biotechnological potential in the biodegradation of recalcitrant pollutants and the treatment of textile effluents. Water Air Soil Poll 223:2333–2345
Bonugli-Santos RC, Vasconcelos MRS, Passarini MRZ, Vieira GAL, Lopes VCP, Mainardi PH, dos Santos JA, Duarte LA, Otero IVR,Yoshida AMS, Feitosa VA, Pessoa Jr A,Sette LD (2015) Marine-derived fungi: diversity of enzymes and biotechnological applications. Front Microbiol 6:269
Buswell JK, Cai YJ, Chang ST (1995) Effect of nutrient nitrogen on manganese peroxidase and lacase production by Lentinula (Lentinus) edodes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128:81–88
Enayatizamir N, Tabandeh F, Rodríguez-Couto S, Yakhchali B, Alikhani HA, Mohammadi L (2011) Biodegradation pathway and detoxification of the diazo dye Reactive Black 5 by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Bioresource Technol 102:10359–10362
Ghevariya CM, Bhatt JK, Dave BP (2011) Enhanced chrysene degradation by halotolerant Achromobacter xylosoxidans using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technol 102:9668–9674
Giardina P, Palmieri G, Fontanella B, Rivieccio V, Sannia G (2000) Manganese peroxidase isoenzymes produced by Pleurotus ostreatus grown on wood sawdust. Arch Biochem Biophys 376:171–179
Hadibarata T, Adnan LA, Yusoff ARM, Yuniart A, Rubiyatno, Zubir MMFA, Khudhair AB, Teh ZC, Abu Naser M (2013) Microbial decolorization of an azo dye Reactive Black 5 using white-rot fungus Pleurotus eryngii F032. Water Air Soil Poll 224:1595
Heinfling A, Bergbauer M, Szewzyk U (1997) Biodegradation of azo and phthalocyanine dyes by Trametes versicolor and Bjerkandera adusta. Appl Microbiol Biot 48:261–266
Ip AWM, Barford JP, McKay G (2010) Biodegradation of Reactive Black 5 and bioregeneration in upflow fixed bed bioreactors packed with different adsorbents. J Chem Technol Biot 85:658–667
Kaushik P, Malik A (2009) Fungal dye decolourization: recent advances and future potential. Environ Int 35:127–141
Kellner H, Luis P, Buscot F (2007) Diversity of laccase-like multicopperoxidase genes in Morchellaceae: identication of genes potentially involved in extracellular activities related to plant litter decay. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 61:153–163
Khan R, Bhawana P, Fulekar MH (2013) Microbial decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biot 12:75–97
Liu Q, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Zhao A, Chen S, Qian G, Xu ZP (2011) Optimization of fermentative biohydrogen production by response surface methodology using fresh leachate as nutrient supplement. Bioresource Technol 102(2011):8661–8668
Maron DM, Ames BN (1983) Revised methods for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutat Res 113:173–215
Menezes CB, Bonugli-Santos RC, Miqueletto PB, Passarini MRZ, Silva CHD, Justo MR, Leal RR, Fantinatti-Garboggini F, Oliveira VM, Berlinck RG, Sette LD (2010) Microbial diversity associated with algae ascidians and sponges from the north coast of São Paulo state, Brazil. Microbiol Res 165:466–482
Morgenstern I, Klopman S, Hibbett DS (2008) Molecular evolution and diversity of lignin degrading heme peroxidases in the Agaricomycetes. J Mol Evol 66:243–257
Pearce AR, Rizzo DM, Watzin MC, Druschel GK (2013) Unraveling associations between cyanobacteria blooms and in-lake environmental conditions in Missisquoi Bay, Lake Champlain, USA, using a modified self-organizing map. Environ Sci Technol 47:14267–14274
Raghukumar C, D'Souza-Ticlo D, Verma AK (2008) Treatment of colored effluents with lignin-degrading enzymes: an emerging role of marine-derived fungi. Crit Rev Microbiol 34:189–206
Ramsay JA, Nguyen T (2002) Decoloration of textile dyes by Trametes versicolor and its effect on dye toxicity. Biotechnol Lett 24:1757–1761
Rehorek A, Plum A (2006) Online LC-MS-MS process monitoring for optimization of biological treatment of wastewater containing azo dye concentrates. Anal Bioanal Chem 384:1123–1128
Sette LD, Passarini MRZ, Delarmelina C, Salati F, Duarte MCT (2006) Molecular characterization and antimicrobial activity of endophytic fungi from coffee plants. World J Microb Biot 22:1185–1195
Singh AK, Prakash D, Shahi SK (2013) Decolorization of the textile dye (Brown GR) by isolated Aspergillus strain from Meerut region. Int Res J Environ Sci 2:25–29
Solé M, Kellner H, Brock S, Buscot F, Schlosser D (2008) Extracellular laccase activity and transcript levels of putative laccase genes during removal of the xenoestrogen technical nonylphenol by the aquatic hyphomycete Clavariopsis aquatic. FEMS Microbiol Lett 288:47–54
Srinivasan SV, Murthy DVS (2009) Statistical optimization for decolorization of textile dyes using Trametes versicolor. J Hazard Mater 165:909–914
Tang W, Jia R, Zhang DM (2011) Decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes by Schizophyllum sp. F17 in a novel system. Desalination 265:22–27
Tien M, Kirk TK (1984) Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of unique H2O2 requiring oxygenase. P Natl Acad Sci 81:2280–2284
Trincone A (2010) Potential biocatalysts originating from sea environments. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 66:241–256
Usha MS, Sasirekha B, Bela RB, Devi S, Kamalini C, Manasa GA (2006) Optimization of Reactive Black 5 dye and Reactive Red 120 dye degradation. J Chem Pharmaceut Res 3:450–457
Xingzu W, Xiang C, Dezhi S, Hong Q (2008) Biodecolorization and partial mineralization of Reactive Black 5 by a strain of Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J Environ Sci 20:1218–1225
Yang Q, Yang M, Pritsch K, Yediler A, Hagn A, Schloter M, Kettrup A (2003) Decolorization of synthetic dyes and production of manganese-dependent peroxidase by new fungal isolates. Biotechnol Lett 25:709–713
Yingling B, Zhengfang Y (2013) Application of an integrated statistical design for optimization of culture condition for ammonium removal by nitrosomonas europaea. Plos One 8:1–11
Zeng T, Arnold WA (2014) Clustering chlorine reactivity of haloacetic acid precursors in Inland Lakes. Environ Sci Technol 48:139–148
Zeng X, Caia Y, Liaoa X, Zenga X, Li W, Zhangb D (2011) Decolorization of synthetic dyes by crude laccase from a newly isolated Trametes trogii strain cultivated on solid agro-industrial residue. J Hazard Mater 187:517–525
Acknowledgements
R.C Bonugli-Santos was supported by a post-doctoral grant from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo—FAPESP (2009/18399-1), São Paulo, Brazil. The authors wish to thank FAPESP for its financial support (BIOTA-FAPESP grant 2010/50190-2 and FAPESP grant 2013/19486-0) and Roberto G. S. Berlinck for his help in LC-MS data analyses. L.D. Sette thanks CNPq for the Productivity Fellowship (304103/2013-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 185 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonugli-Santos, R.C., Vieira, G.A.L., Collins, C. et al. Enhanced textile dye decolorization by marine-derived basidiomycete Peniophora sp. CBMAI 1063 using integrated statistical design. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 8659–8668 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6053-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6053-2