Abstract
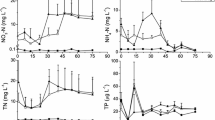
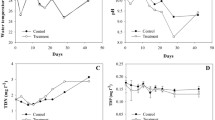
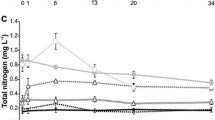
Since it was commercially introduced in 1974, glyphosate has been one of the most commonly used herbicides in agriculture worldwide, and there is growing concern about its adverse effects on the environment. Assuming that glyphosate may increase the organic turbidity of water bodies, we evaluated the effect of a single application of 2.4 ± 0.1 mg l−1 of glyphosate (technical grade) on freshwater bacterioplankton and phytoplankton (pico, micro, and nanophytoplankton) and on the physical and chemical properties of the water. We used outdoor experimental mesocosms under clear and oligotrophic (phytoplanktonic chlorophyll a = 2.04 μg l−1; turbidity = 2.0 NTU) and organic turbid and eutrophic (phytoplanktonic chlorophyll a = 50.3 μg l−1; turbidity = 16.0 NTU) scenarios. Samplings were conducted at the beginning of the experiment and at 1, 8, 19, and 33 days after glyphosate addition. For both typologies, the herbicide affected the abiotic water properties (with a marked increase in total phosphorus), but it did not affect the structure of micro and nanophytoplankton. In clear waters, glyphosate treatment induced a trend toward higher bacteria and picoeukaryotes abundances, while there was a 2 to 2.5-fold increase in picocyanobacteria number. In turbid waters, without picoeukaryotes at the beginning of the experiment, glyphosate decreased bacteria abundance but increased the number of picocyanobacteria, suggesting a direct favorable effect. Moreover, our results show that the impact of the herbicide was observed in microorganisms from both oligo and eutrophic conditions, indicating that the impact would be independent of the trophic status of the water body.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allende L, Tell G, Zagarese H, Torremorell A, Pérez G, Bustingorry J, Escaray R, Izaguirre I (2009) Phytoplankton and primary production in clear-vegetated, inorganic-turbid, and algal-turbid shallow lakes from the pampa plain (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 624:45–60
American Public Health Association (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewaters, 21st edn. Centennial Edition. APHA, American Water Works Association, Water Environmental Federation, Washington, DC
Amrhein N, Deus B, Gehrke P, Steinrucken HC (1980) The site of inhibition of the shikimate pathway by ghyphosate. II. Interference of glyphosate with chorismate formation in vivo and in vitro. Plant Physiol 66:830–834
Anagnostidis K, Komárek J (1988) Modern approach to the classification system of cyanophytes. 3. Oscillatoriales. Arch Hydrobiol Suppl 80:327–472
Arunakumara K, Walpola BC, Yoon M-H (2013) Metabolism and degradation of glyphosate in aquatic cyanobacteria: a review. Afr J Microbiol Res 7:4084–4090
Austin AP, Harris GE, Lucey WP (1991) Impact of an organophosphate herbicide (glyphosate) on periphyton communities developed in experimental streams. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 47:29–35
Bengtsson G, Lars-Anders H, Montenegro K (2004) Reduced grazing rates in Daphnia pulex caused by contaminants: implications for trophic cascades. Environ Toxicol Chem 23(11):2641–2648
Bonnineau C, Gallardo Sague I, Urrea G, Guasch H (2012) Light history modulates antioxidant and photosynthetic responses of biofilms to both natural (light) and chemical (herbicides) stressors. Ecotoxicology 21:1208–1224
Bourrelly P (1970) Les algues d'eau douce. III. N. Boubée, Paris
Bourrelly P (1972) Les algues d'eau douce. I. N. Boubée, Paris
Bourrelly P (1981) Les algues d'eau douce. II. N. Boubée, Paris
Callieri C (2007) Picophytoplankton in freshwater ecosystems: the importance of small-sized phototrophs. Fresh Rev 1:1–28
CASAFE (2013) Cámara de Sanidad, y Fertilizantes. Informe de Mercado Argentino de Productos Fitosanitarios. Buenos Aires, Argentina
CCM International (2011) Outlook for China glyphosate industry 2012–2016
Chan K-Y, Leung SC (1986) Effects of paraquat and glyphosate on growth, respiration, and enzyme activity of aquatic bacteria. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 36:52–59
Dukatz F, Ferrari R, Canziani G (2006) Evaluación de sistemas lacunares bonaerenses mediante imágenes Landsat TM. Biol Acuát 22:95–101
Duke SO, Powles SB (2008) Glyphosate: a once-in-a century herbicide. Pest Manag Sci 64:319–25
Duke SO, Baerson SR, Rimando AM (2003) Herbicides: glyphosate. In: Plimmer JR, Gammon DW, Ragsdale NN (eds) Encyclopedia of agrochemicals. Wiley, New York
Feng JC, Thompson DG, Reynolds P (1990) Fate of glyphosate in a Canadian forest watershed. 1. Aquatic residues and off-target deposit assessment. J Agric Food Chem 38:1110–1118
Forlani G, Pavan M, Gramek M, Kafarski P, Lipok J (2008) Biochemical bases for a widespread tolerance of cyanobacteria to the phosphonate herbicide glyphosate. Plant Cell Physiol 49:443–456
Goldsborough LG, Beck AE (1989) Rapid dissipation of glyphosate in small forest ponds. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:537–544
Goldsborough LG, Brown DJ (1988) Dissipation of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water and sediments of boreal forest ponds. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1139–1147
Hove-Jensen B, Zechel DL, Jochimsen B (2014) Utilization of glyphosate as phosphate source: biochemistry and genetics of bacterial carbon-phosphorus lyase. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 78:176–197
Hurley JP (1988) Analysis of aquatic pigments by high performance liquid chromatography. J Analyt Purif 3:12–16
Ilikchyan IN, Michael R, McKay L, Zehr JP, Dyhrman ST, Bullerjahn GS (2009) Detection and expression of the phosphonate transporter gene phnD in marine and freshwater picocyanobacteria. Environ Microbiol 11:1314–1324
Ilikchyan IN, Michael R, McKay L, Kotovaya OA, Condon R, Bullerjahn GS (2010) Seasonal expression of the picocyanobacterial phosphonate transporter gene phnD in the Sargasso Sea. Front Microbiol 1:135
Jacob GS, Garbow JR, Hallas LE, Kimack NM, Kishore GM, Schaffer J (1988) Metabolism of glyphosate in Pseudomonas sp. strain LBr. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2953–2958
Jakubowska N, Szeląg-Wasielewska E (2015) Toxic picoplanktonic cyanobacteria—review. Mar Drugs 13:1497–1518
Jürgens K, Arndt H, Zimmermann H (1997) Impact of metazoan and protozoan grazers on bacterial biomass distribution in microcosm experiments. Aquat Microb Ecol 12:131–138
Khoury GA, Gehris TC, Tribe L, Torres Sánchez RM, dos Afonso Santos M (2010) Glyphosate adsorption on montmorillonite: an experimental and theoretical study of surface complexes. Appl Clay Sci 50:167–175
Komárek J, Anagnostidis K (1986) Modern approach to the classification systm of cyanophytes. 2. Chroococcales. Arch Hydrobiol Suppl 73:157–226
Lajmanovich RC, Peltzer PM, Cabagna MC, Attademo AM, Junges CM (2011) Toxicity of four herbicide formulations with glyphosate on Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae) tadpoles: B-esterases and glutathione S-transferase inhibitors. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:681–9
Laurion I, Lami A, Sommaruga R (2002) Distribution of mycosporine-like amino acids and photoprotective carotenoids among freshwater phytoplankton assemblages. Aquat Microb Ecol 26:283–294
McAuliffe KS, Hallas LE, Kulpa CF (1990) Glyphosate degradation by Agrobacterium radibacter isolated from activated sludge. J Ind Microbiol 6:219–221
Mann RM, Bidwell JR (1999) The toxicity of glyphosate formulations to four species of Southwestern Australian frogs. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:193–199
Mantoura RFC, Llewellyn CA (1983) The rapid determination of algal chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments and their breakdown products in natural waters by reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 151:297–314
Mbanaso FU, Coupe SJ, Charlesworth SM, Nnadi EO (2013) Laboratory-based experiments to investigate the impact of glyphosate-containing herbicide on pollution attenuation and biodegradation in a model pervious paving system. Chemosphere 90:737–746
Mercurio P, Flores F, Mueller JF, Carter S, Negri AP (2014) Glyphosate persistence in seawater. Mar Pollut Bull 85:385–390
Millenium Ecosystem Assessment (2000) Fresh Water. Chapter 7. United Nations Emvironment Programme. http://www.unep.org/maweb/en/Condition.aspx
Monaghan RM, Wilcock RJ, Smith LC, Tikkisetty B, Thorrold BS, Costall D (2007) Linkages between land management activities and water quality in an intensively farmed catchment in southern New Zealand. Agric Ecosyst Environ 118:211–222
Obojska AB, Lejczak B, Kubrak M (1999) Degradation of phosphates by streptomycete isolates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:872–876
Peck LS (2011) Organisms and responses to environmental change. Mar Gen 4:237–243
Pengue WA (2005) Transgenic crops in Argentina: the ecological and social debt. Bull Sc Technol Society 25:314–322
Pérez GL, Torremorell A, Mugni H, Rodríguez P, do Nascimento M, Allende L, Bustingorry J, Escaray R, Ferraro M, Izaguirre I, Pizarro H, Bonetto C, Morris DP, Zagarese H (2007) Effects of the herbicide Roundup® on freshwater microbial communities: a mesocosm study. Ecol Appl 17:2310–2322
Pérez G, Vera MS, Miranda L (2011) Effects of herbicide glyphosate and glyphosate-based formulations on aquatic ecosystems. In: Kortekamp A (Ed) Herbicides and environment. ISBN: 978-953-307-476-4, InTech, open access publisher
Peruzzo PJ, Porta AA, Ronco AE (2008) Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ Pollut 156:61–66
Pesce S, Batisson I, Bardot C, Fajon C, Portelli C, Montuelle B, Bohatier J (2009) Response of spring and summer riverine microbial communities following glyphosate exposure. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 72:1905–1912
Pesce S, Bouchez A, Montuelle B (2011) Effects of organic herbicides on phototrophic microbial communities in freshwater ecosystems. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 214:87–124
Pessagno RC, Torres Sánchez RM, dos Afonso Santos M (2008) Glyphosate behavior at soil and mineral water interfaces. Environ Pollut 153:53–59
Pipke R, Schulz A, Amrhein N (1987) Uptake of glyphosate by an Arthrobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:974–978
Porter KC, Feig YS (1980) The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol Oceanogr 25:943–948
Quirós R, Rosso JJ, Rennella A, Sosnovsky A, Boveri M (2002) Análisis del estado trófico de las lagunas pampeanas (Argentina). Interciencia 27:58–591
Relyea RA (2005) The impact of insecticides and herbicides on the biodiversity and productivity of aquatic communities. Ecol Appl 15:618–627
Roisch U, Lingens F (1980) Mechanism of action of glyphosate. Effect on growth and on the enzymes of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Hoppe-Seylers Zeitschrift fur Physiologische Chemie 361:1049–1058
Sáenz ME, Di Marzio WD, Alberdi JL, Tortorelli MC (1997) Effects of technical grade and a commercial formulation of glyphosate on algal population growth. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:638–644
Saxton MA, Morrow EA, Bourbonniere RA, Wilhelm SW (2011) Glyphosate influence on phytoplankton community structure in Lake Erie. J Great Lakes Res 37:683–690
Scheffer M, Meijer ML, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol Evol 8:275–279
Schulz A, Krtiper A, Amrhein N (1985) Differential sensitivity of bacterial 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthases to the herbicide glyphosate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 28:297–301
Simonsen R (1979) The diatom system. Ideas Phylogeny Bacillaria 2:9–71
Utermöhl M (1958) Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Methodik. MIH Verh Int Ver Limnol 9:1–38
Vendrell E, Gomez De Barreda Ferraz D, Sabater C, Carrasco JM (2009) Effect of glyphosate on growth of four freshwater species of phytoplankton: a microplate bioassay. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:538–542
Venrick EL (1978) How many cells to count? In: Sournia A (ed) Phytoplankton manual. UNESCO, Paris, pp 167–180
Vera MS, Lagomarsino L, Sylvester M, Pérez G, Rodríguez P, Mugni H, Sinistro R, Ferraro M, Bonetto C, Zagarese H, Pizarro H (2010) New evidences of Roundup® (glyphosate formulation) impact on the periphyton and the water quality of freshwater ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 19:710–721
Vera MS, Di Fiori E, Lagomarsino L, Sinistro R, Escaray R, Iummato MM, Juárez A, Ríos de Molina MC, Tell G, Pizarro H (2012) Direct and indirect effects of the glyphosate formulation Glifosato Atanor® on freshwater microbial communities. Ecotoxicology 21:1805–1816
Vera MS, Juarez A, Pizarro HN (2014) Comparative effects of technical-grade and a commercial formulation of glyphosate on the pigment content of periphytic algae. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93:399–404
Vereecken H (2005) Mobility and leaching of glyphosate: a review. Pest Manag Sci 61:1139–1151
Yadav SS, Giri S, Singha U, Boro F, Giri A (2013) Toxic and genotoxic effects of Roundup on tadpoles of the Indian skittering frog (Euflictis cyanophlyctis) in the presence and absence of predator stress. Aquat Toxicol 132–133:1–8
Zaranyika MF, Nyandoro GM (1993) Degradation of glyphosate in the aquatic environment: an enzymatic kinetic model that takes into account microbial degradation of both free and colloidal (or sediment) particle adsorbed glyphosate. J Agric Food Chem 41:838–884
Zhu Y, Zhang FC, Tong W (1999) Determination of glyphosate by ion chromatography. J Chromatogr A 850:297–301
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT 2010 0908) and Universidad de Buenos Aires (UBACyT 20020130100248BA). Thanks are due to Lic Natalia Aprigliano for field assistance and two anonymous reviewers that improved the work with their suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pizarro, H., Vera, M.S., Vinocur, A. et al. Glyphosate input modifies microbial community structure in clear and turbid freshwater systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 5143–5153 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5748-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5748-0