Abstract
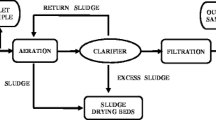
Several parameters of the method, solid-phase extraction (SPE)–ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC)–tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), were optimized to investigate the presence and partitioning of 18 antibiotics (including sulfonamides, tetracyclines, quinolones, macrolides, and β-lactams) during various processing stages at two typical pharmaceutical wastewater treatment plants (PWWTPs) in northern China. Oxytetracycline (OTC), chlortetracycline (CTC), and tetracycline (TC) were all detected in each stage of both PWWTPs. Antibiotics were largely removed through biological units of both PWWTPs, with removal efficiencies of 62.0 to 78.3 %. Mass balance analyses indicated that degradation (44.8–53.7 % for PWWTP1 and 40.1–59.6 % for PWWTP2) was the major mechanism responsible for the removal of tetracyclines, whereas the contribution of sorption by sludge (12.6–20.0 % for PWWTP1 and 18.7–33.5 % for PWWTP2) was less significant for the investigated pharmaceuticals. Although there was significant removal of tetracyclines through PWWTPs, large amounts of tetracyclines were still discharged through the effluent (up to 32.0 ± 6.0 mg L−1) and dewatered sludge (up to 5,481.1 ± 123.0 mg kg−1), which increased the risk of selecting for antibiotic resistance in the receiving water and soil environments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batt AL, Bruce IB, Aga DS (2006) Evaluating the vulnerability of surface waters to antibiotic contamination from varying wastewater treatment plant discharges. Environ Pollut 142(2):295–302
Batt AL, Kim S, Aga DS (2007) Comparison of the occurrence of antibiotics in four full-scale wastewater treatment plants with varying designs and operations. Chemosphere 68(3):428–435
Brown KD, Kulis J, Thomson B, Chapman TH, Mawhinney DB (2006) Occurrence of antibiotics in hospital, residential, and dairy effluent, municipal wastewater, and the Rio Grande in New Mexico. Sci Total Environ 366(2):772–783
Campagnolo ER, Johnson KR, Karpati A, Rubin CS, Kolpin DW, Meyer MT, Esteban JE, Currier RW, Smith K, Thu KM, McGeehin M (2002) Antimicrobial residues in animal waste and water resources proximal to large-scale swine and poultry feeding operations. Sci Total Environ 299:89–95
Chang XS, Meyer MT, LiuXY ZQ, Chen H, Chen JA, Qiu ZQ, Yang L, Cao J, Shu WQ (2010) Determination of antibiotics in sewage from hospitals, nursery and slaughter house, wastewater treatment plant and source water in Chongqing region of Three Gorge Reservoir in China. Environ Pollut 158:1444–1450
Christian T, Schneider RJ, Farber HA, Skutlarek D, Meyer MT, Goldbach HE (2003) Determination of antibiotic residues in manure, soil, and surface waters. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 31:36–44
de Souza SML, de Vasconcelos EC, Dziedzic M, de Oliveira CMR (2009) Environmental risk assessment of antibiotics: an intensive care unit analysis. Chemosphere 77(7):962–967
Deblonde T, Cossu-Leguille C, Hartemann P (2011) Emerging pollutants in wastewater: a review of the literature. Int J Hyg Environ Health 214:442–448
Duong HA, Pham NH, Nguyen HT, Hoang TT, Pham HV, Pham VC, Berg M, Giger W, Alder AC (2008) Occurrence, fate and antibiotic resistance of fluoroquinolone antibacterials in hospital wastewaters in Hanoi, Vietnam. Chemosphere 72(6):968–973
Gao LH, Shi YL, Li WH, Niu HY (2012a) Occurrence of antibiotics in eight sewage treatment plants in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 86(6):665–671
Gao P, Ding YJ, Li H, Xagoraraki I (2012b) Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in a municipal wastewater treatment plant: mass balance and removal processes. Chemosphere 88:17–24
Gatica J, Cytryn E (2013) Impact of treated wastewater irrigation on antibiotic resistance in the soil microbiome. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(6):3529–3538
Glassmeyer ST, Furlong ET, Kolpin DW, Cahill JD, Zaugg SD, Werner SL, Meyer MT, Kryak DD (2005) Transport of chemical and microbial compounds from known wastewater discharges: potential for use as indicators of human fecal contamination. Environ Sci Technol 39:5157–5169
Göbel A, McArdell CS, Joss A, Siegrist H, Giger W (2007) Fate of sulfonamides, macrolides, and trimethoprim in different wastewater treatment technologies. Sci Total Environ 372:361–371
Gómez MJ, Martinez Bueno MJ, Lacorte S, Fernández-Alba AR, Agüera A (2007) Pilot survey monitoring pharmaceuticals and related compounds in a sewage treatment plant located on the Mediterranean coast. Chemosphere 66(6):993–1002
Gu C, Karthikeyan KG (2008) Sorption of the antibiotic tetracycline to humic-mineral complexes. J Environ Qual 37:704–711
Guerra P, Kim M, Shah A, Alaee M, Smyth SA (2014) Occurrence and fate of antibiotic, analgesic/anti-inflammatory, and antifungal compounds in five wastewater treatment processes. Sci Total Environ 473–474:235–243
Gulkowska A, Leung HW, So MK, Taniyasu S, Yamashita N, Yeung LW, Richardson BJ, Lei AP, Giesy JP, Lam PK (2008) Removal of antibiotics from wastewater by sewage treatment facilities in Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China. Water Res 42:39–403
Hou J, Wan W, Mao D, Wang C, Mu Q, Qin S, Luo Y (2015) Occurrence and distribution of sulfonamides, tetracyclines, quinolones, macrolides, and nitrofurans in livestock manure and amended soils of Northern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(6):4545–4554
Jia A, WanY XY, Hu JY (2012) Occurrence and fate of quinolone and fluoroquinolone antibiotics in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Water Res 46(2):387–394
Jiang HY, Zhang DD, Xiao SC, Geng CN, Zhang X (2013) Occurrence and sources of antibiotics and their metabolites in river water, WWTPs, and swine wastewater in Jiulongjiang River basin, south China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(12):9075–9083
Jones O, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2007) The occurrence and removal of selected pharmaceutical compounds in a sewage treatment works utilising activated sludge treatment. Environ Pollut 145(3):738–744
Karthikeyan KG, Meyer MT (2006) Occurrence of antibiotics in wastewater treatment facilities in Wisconsin, USA. Sci Total Environ 361(1–3):196–207
Kim S, Eichhorn P, Jensen JN, Weber AS, Aga DS (2005) Removal of antibiotics in wastewater: effect of hydraulic and solid retention times on the fate of tetracycline in the activated sludge process. Eniviron Sci Technol 39(15):5816–5823
Kim Y, Jung J, Kim M, Park J, Boxall ABA, Choi K (2008) Prioritizing veterinary pharmaceuticals for aquatic environment in Korea. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26:167–176
Kummerer K (2003) Significance of antibiotics in the environment. J Antimicrob Chemother 52:5–7
Kümmerer K (2009) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—a review—part I. Chemosphere 75(4):417–434
Le-Minh N, Khan SJ, Drewes JE, Stuetz RM (2010) Fate of antibiotics during municipal water recycling treatment processes. Water Res 44(15):4295–4323
Li B, Zhang T (2010) Biodegradation and adsorption of antibiotics in the activated sludge process. Eniviron Sci Technol 44(9):3468–3473
Li D, Yang M, Hu J, Ren L, Zhang Y, Chang H, Li K (2008a) Determination and fate of oxytetracycline and related compounds in oxyteracycline production wastewater and the receiving river. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:80–86
Li D, Yang M, Hu JY, Zhang Y, Chang H, Jin F (2008b) Determination of penicillin G and its degradation products in a penicillin production wastewater treatment plant and the receiving river. Water Res 42(1):307–317
Li WH, Shi YL, Gao LH, Liu JM, Cai YQ (2013) Occurrence, distribution and potential affecting factors of antibiotics in sewage sludge of wastewater treatment plants in China. Sci Total Environ 445:306–313
Lin AY, Yu T, Lin C (2008) Pharmaceutical contamination in residential, industrial, and agricultural waste streams: risk to aqueous environments in Taiwan. Chemosphere 74(1):131–141
Lindberg R, Jarnheimer PR, Olsen B, Johansson M, Tysklind M (2004) Determination of antibiotic substances in hospital sewage water using solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and group analogue internal standards. Chemosphere 57(10):1479–1488
Lindberg RH, Wennberg P, Johansson MI, Tysklind M, Andersson BAV (2005) Screening of human antibiotic substances and determination of weekly mass flows in five sewage treatment plants in Sweden. Environ Sci Technol 39(10):342–3429
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang Y, Zhang H, Alvarez PJ (2011) Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45(5):1827–1833
Ma JW, Yu L, Frear C, Zhao QB, Li XJ, Chen SL (2012) Kinetics of psychrophilic anaerobic sequencing batch reactor treating flushed dairy manure. Bioresour Technol 131:6–12
Miao XS, Bishav F, Chen M, Metcalfe CD (2004) Occurrence of antimicrobials in the final effluents of wastewater treatment plants in Canada. Environ Sci Technol 38:3533–3541
Monteiro SC, Boxall ABA (2010) Occurrence and fate of human pharmaceuticals in the environment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 202:53–154
Mutiyar PK, Mittal AK (2014) Risk assessment of antibiotic residues in different water matrices in India: key issues and challenges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(12):7723–7736
Phillips I, Casewell M, Cox T, Groot BD, Friis C, Jones R, Nightingale C, Preston R, Waddell J (2004) Does the use of antibiotics in food animals pose a risk to human health? A critical review of published data. J Antimicrob Chemother 53(1):28–52
Sanderson H, Johnson DJ, Reitsma T, Brain RA, Wilson CJ, Solomon KR (2004) Ranking and prioritization of environmental risks of pharmaceuticals in surface waters. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 39:158–183
Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall ABA (2006) Global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 65(5):725–759
Singh M, Srivastava RK (2011) Sequencing batch reactor technology for biological wastewater treatment: a review. Asia Pac Chem Eng 6(1):3–13
Sipma J, Osuna B, Collado N, Monclus H, Ferrero G, Comas J, Rodriguez-Roda I (2010) Comparison of removal of pharmaceuticals in MBR and activated sludge systems. Desalination 250:653–659
Spongberg AL, Witter JD (2008) Pharmaceutical compounds in the wastewater process stream in Northwest Ohio. Sci Total Environ 397(1):148–157
Thiele-Bruhn S (2003) Pharmaceutical antibiotics compounds in soils—a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 166:145–167
Wang M, Tang JC (2010) Research of antibiotics pollution in soil environments and its ecological toxicity. J Agro Environ Sci 29:261–266
Watkinson AJ, Murby EJ, Costanzo SD (2007) Removal of antibiotics in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment: implications for environmental discharge and wastewater recycling. Water Res 41(18):4164–4176
Xu WH, Zhang G, Li XD, Zou SC (2007) Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res 41(19):4526–4534
Yang X, Flowers RC, Weinberg HS, Singer PC (2011) Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in an advanced wastewater reclamation plant. Water Res 45:5218–5228
Yu DJ, Yi XL, Ma YF, Yin B, Zhou HL, Li J, Huang YF (2009) Effects of administration mode of antibiotics on antibiotic residuce of Enterococcus faecalis inaquatic ecosystems. Chempshere 76(7):915–920
Zhou LJ, Ying GG, Liu S, Zhao JL, Yang B, Chen ZF, Lai HJ (2013) Occurrence and fate of eleven classes of antibiotics in two typical wastewater treatment plants in South China. Sci Total Environ 452:365–376
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the State Environmental Protection commonweal project (201309031), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 21277075, 31270542, and 31470440).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Jie Hou and Chong Wang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, J., Wang, C., Mao, D. et al. The occurrence and fate of tetracyclines in two pharmaceutical wastewater treatment plants of Northern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 1722–1731 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5431-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5431-5