Abstract
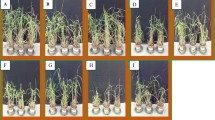
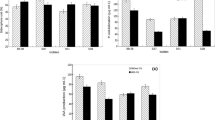
Cadmium-resistant Micrococcus sp. TISTR2221, a plant growth-promoting bacterium, has stimulatory effects on the root lengths of Zea mays L. seedlings under toxic cadmium conditions compared to uninoculated seedlings. The performance of Micrococcus sp. TISTR2221 on promoting growth and cadmium accumulation in Z. mays L. was investigated in a pot experiment. The results indicated that Micrococcus sp. TISTR2221significantly promoted the root length, shoot length, and dry biomass of Z. mays L. transplanted in both uncontaminated and cadmium-contaminated soils. Micrococcus sp. TISTR2221 significantly increased cadmium accumulation in the roots and shoots of Z. mays L. compared to uninoculated plants. At the beginning of the planting period, cadmium accumulated mainly in the shoots. With a prolonged duration of cultivation, cadmium content increased in the roots. As expected, little cadmium was found in maize grains. Soil cadmium was significantly reduced with time, and the highest percentage of cadmium removal was found in the bacterial-inoculated Z. mays L. after transplantation for 6 weeks. We conclude that Micrococcus sp. TISTR2221 is a potent bioaugmenting agent, facilitating cadmium phytoextraction in Z. mays L.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad F, Ahmad I, Khan MS (2008) Screening of free-living rhizospheric bacteria for their multiple plant growth promoting activities. Microbiol Res 163:173–181
Ahmad I, Akhtar MJ, Zahir ZA, Naveed M, Mitter B, Sessitsch A (2014) Cadmium-tolerant bacteria induce metal stress tolerance in cereals. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:11054–11065
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals: concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881
Anjum NA, Umar S, Iqbal M (2014) Assessment of cadmium accumulation, toxicity, and tolerance in Brassicaceae and Fabaceae plants: implications for phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:10286–10293
Barocsi A, Csintalan Z, Kocsanyi L, Dushenkov S, Kuperberg JM, Kucharski R, Richter PI (2003) Optimizing phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil by exploiting plants’ stress adaptation. Int J Phytoremediation 5:13–23
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plant. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34
Chaney RL, Malik M, Lim YM, Brown SL, Brewer EP, Angle JS, Baker AJM (1997) Phytoremediation of soil metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:279–284
Chanprasert M, Prapagdee B, Wongthanate J, Eiamphungporn W (2011) Isolation and screening of IAA-producing rhizobacteria from heavy metal contaminated areas, Proceedings in the 8th KU-KPS conference. Kasetsart University, Bangkok, pp 737–744
Chen YX, He YF, Luo YM, Yu YL, Lin Q, Wong MH (2003) Physiological mechanism of plant roots exposed to cadmium. Chemosphere 50:789–793
Chen ZJ, Sheng XF, He LY, Huang Z, Zhang WH (2013) Effects of root inoculation with bacteria on the growth, Cd uptake and bacterial communities associated with rape grown in Cd-contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 244–245:709–717
Chiu KK, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2005) Enhanced uptake of As, Zn, and Cu by Vetiveria zizanioides and Zea mays using chelating agents. Chemosphere 60:1365–1375
Faust MB, Christians NE (2000) Copper reduces shoot growth and root development of creeping bent grass. Crop Sci 40:498–502
Glick BR (2010) Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 28:367–374
Guo J, Feng R, Ding Y, Wang R (2014) Applying carbon dioxide, plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium and EDTA can enhance the phytoremediation efficiency of ryegrass in a soil polluted with zinc, arsenic, cadmium and lead. J Environ Manag 141:1–8
He LY, Chen ZJ, Ren GD, Zhang YF, Qian M, Sheng XF (2009) Increased cadmium and lead uptake of a cadmium hyperaccumulator tomato by cadmium-resistant bacteria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1343–1348
Jeong S, Moon HS, Nam K, Kim JY, Kim TS (2012) Application of phosphate solubilizing bacteria for enhancing bioavailability and phytoextraction of cadmium (Cd) from polluted soil. Chemosphere 88:204–210
Jiang CY, Sheng XF, Qian M, Wang QY (2008) Isolation and characterization of a heavy metal-resistant Burkholderia sp. from heavy metal-contaminated paddy field soil and its potential in promoting plant growth and heavy metal accumulation in metal-polluted soil. Chemosphere 72:157–164
Khaokaew S, Landrot G (2014) A field-scale study of cadmium phytoremediation in a contaminated agricultural soil at Mae Sot district, Tak province, Thailand: (1) Determination of Cd-hyperaccumulating plants. Chemosphere. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.108
Kumar P, Dushenkov V, Motto H, Raskin I (1995) Phytoextraction: the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soils. Environ Sci Technol 29:1232–1238
Lebeau T, Braud A, Jezequel K (2008) Performance of bioaugmentation-assisted phytoextraction applied to metal contaminated soils: a review. Environ Pollut 153:497–522
Liu DH, Jiang WS, Gao XZ (2003) Effects of cadmium on root growth, cell division and nucleoli in root tip cells of garlic. Biol Plant 47:79–83
Liu J, Qu W, Kadiiska MB (2009) Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:209–214
Liu Z, Ge H, Li C, Zhao Z, Song F, Hu S (2015) Enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil by plant co-cropping associated with PGPR. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:29
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2009) Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacterium Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain Ax10 for the improvement of copper phytoextraction by Brassica juncea. J Environ Manag 90:831–837
Mattina MJI, Lannucci-Berger W, Musante C, White JC (2003) Concurrent plant uptake of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from soil. Environ Pollut 124:375–378
McGrath SP, Cunliffe CH (1985) A simplified method for the extraction of the metals Fe, Zn, Cu, Ni, Cd, Pb, Cr, Co and Mn from soils and sewage sludges. J Sci Food Agric 36:794–798
Meers E, Ruttens A, Hopgood M, Lesage E, Tack FMG (2005) Potential of Brassica rapa, Cannabis sativa, Helianthus annuus and Zea mays for phytoextraction of heavy metals from calcareous dredged sediment derived soils. Chemosphere 61:561–572
Moreira H, Marques APGC, Franco AR, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2014) Phytomanagement of Cd-contaminated soils using maize (Zea mays L.) assisted by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9742–9753
Murakami M, Ae N, Ishikawa S (2007) Phytoextraction of cadmium by rice (Oryza sativa L.), soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.), and maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Pollut 145:96–103
Phaenark C, Pokethitiyook P, Kruatrachue M, Ngernsansaruay C (2009) Cd and Zn accumulation in plants from the Padaeng zinc mine area. Int J Phytoremediation 11:479–495
Pongsakul P, Attajarusit S (1999) Assessment of heavy metal contaminations in soil. Thai J Soils Fertil 21:71–82 (in Thai)
Prapagdee B, Chanprasert M, Mongkolsuk S (2013) Bioaugmentation with cadmium-resistant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria to assist cadmium phytoextraction by Helianthus annuus. Chemosphere 92:659–666
Sanità di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Sheng XF, Sun LN, Huang Z, He LY, Zhang WH, Chen ZJ (2012) Promotion of growth and Cu accumulation of bio-energy crop (Zea mays) by bacteria: implications for energy plant biomass production and phytoremediation. J Environ Manag 103:58–64
Simmons RW, Pongsakul P, Chaney L, Saiyasitpanich D, Klinphoklap S, Nobuntou W (2003) The relative exclusion of zinc and iron from rice grain in relation to rice grain cadmium as compared to soybean: implications for human health. Plant Soil 257:163–170
Simmons RW, Pongsakul P, Saiyasitpanich D, Klinphoklap S (2005) Elevated levels of cadmium and zinc in paddy soils and elevated levels of cadmium in rice grain downstream of a zinc mineralized area in Thailand: implications for public health. Environ Geochem Health 27:501–511
Sun Y, Zhou Q, Wang L, Liu W (2009) Cadmium tolerance and accumulation characteristics of Bidens pilosa L. as a potential Cd-hyperaccumulator. J Hazard Mater 161:808–814
Teixeira C, Almeida MR, da Silva MN, Bordalo AA, Mucha AP (2014) Development of autochthonous microbial consortia for enhanced phytoremediation of salt-marsh sediments contaminated with cadmium. Sci Total Environ 493:757–765
Thawornchaisit U, Polprasert C (2009) Evaluation of phosphate fertilizers for the stabilization of cadmium in highly contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 165:1109–1113
Vangronsveld J, Herzig R, Weyens N, Boulet J, Adriaensen K, Ruttens A, Thewys T, Vassilev A, Meers E, Nehnevajova E, Van der Lelie D, Mench M (2009) Phytoremediation of contaminated soils and groundwater: lessons from the field. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:765–794
Wang M, Zou J, Duan A, Jiang W, Liu D (2007) Cadmium accumulation and its effects on metal uptake in maize (Zea mays L.). Bioresour Technol 98:82–88
Wang Y, Yan A, Dai J, Wang NN, Wu D (2012) Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in Chlorophytum comosum: a popular ornamental plant and potential Cd hyperaccumulator. Environ Monit Assess 184:929–937
Yokota A, Khamna S, Peberdy JF, Lumyong S (2010) Indole-3-acetic acid production by Streptomyces sp. isolated from some Thai medicinal plant rhizosphere soils. Eurasia J Biosci 4:23–32
Yoon J, Cao X, Zhou Q, Ma L (2006) Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci Total Environ 368:456–464
Zhang S, Li T, Huang H, Zou T, Zhang X, Yu H, Zheng Z, Wang Y (2012) Cd accumulation and phytostabilization potential of dominant plants surrounding mining tailings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:3879–3888
Acknowledgments
This research project was supported by the grant from Thailand Research Fund and Mahidol University (grant no. RSA5780026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sangthong, C., Setkit, K. & Prapagdee, B. Improvement of cadmium phytoremediation after soil inoculation with a cadmium-resistant Micrococcus sp.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 756–764 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5318-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5318-5