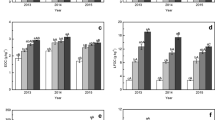
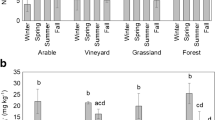
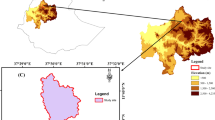
Abstract
The farmland tillage practices changed the soil chemical properties, which also impacted the soil respiration (R s ) process and the soil carbon conservation. Originally, the farmland in northeast China had high soil carbon content, which was decreased in the recent decades due to the tillage practices. To better understand the R s dynamics in different land use types and its relationship with soil carbon loss, soil samples at two layers (0–15 and 15–30 cm) were analyzed for organic carbon (OC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), total carbon (TC), available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), soil particle size distribution, as well as the R s rate. The R s rate of the paddy land was 0.22 (at 0–15 cm) and 3.01 (at 15–30 cm) times of the upland. The average concentrations of OC and clay content in cultivated areas were much lower than in non-cultivated areas. The partial least squares analysis suggested that the TC and TN were significantly related to the R s process in cultivated soils. The upland soil was further used to test soil CO2 emission response at different biochar addition levels during 70-days incubation. The measurement in the limited incubation period demonstrated that the addition of biochar improved the soil C content because it had high concentration of pyrogenic C, which was resistant to mineralization. The analysis showed that biochar addition can promote soil OC by mitigating carbon dioxide (CO2) emission. The biochar addition achieved the best performance for the soil carbon conservation in high-latitude agricultural area due to the originally high carbon content.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla M, Kumar S, Jones M, Burke J, Williams M (2011) Testing DNDC model for simulating soil respiration and assessing the effects of climate change on the CO2 gas flux from Irish agriculture. Glob Planet Chang 78(3–4):106–115
Abdalla M, Osborne B, Lanigan G, Forristal D, Williams M, Smith P, Jones MB (2013) Conservation tillage systems: a review of its consequences for greenhouse gas emissions. Soil Use Manag 29(2):199–209
Almagro M, Querejeta JI, Boix-Fayos C, Martínez-Mena M (2013) Carolina Boix-Fayos and María Martínez-Mena 2013 links between vegetation patterns, soil C and N pools and respiration rate under three different land uses in a dry Mediterranean ecosystem. J Soils Sediments 13:641–653
Arthur ET, Moldrup MP, de Jonge LW (2015) Effects of biochar and manure amendments on water vapor sorption in a sandy loam soil. Geoderma 243–244:175–182
Blevins RL, Thomas GW, Cornelius PL (1977) Influence of no-tillage and nitrogen fertilization on certain soil properties after 5 years of continuous corn. Agron J 69(3):383–386
Bond-Lamberty B, Thomson A (2010) Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record. Nature 464:579–582
Campos CA (2006) Response of soil surface CO2-C flux to land use changes in a tropical cloud forest (Mexico). For Ecol Manag 234:305–312
Chen Y, Tessier S, MacKenzie AF, Laverdiere MR (1995) Nitrous oxide emission from an agricultural soil subjected to different freeze-thaw cycles. Agric Ecosyst Environ 55:123–128
Conforti M, Castrignano A, Robustelli G, Scarciglia F, Stelluti M, Buttafuoco G (2015) Laboratory-based Vis–NIR spectroscopy and partial least square regression with spatially correlated errors for predicting spatial variation of soil organic matter content. Catena 124(1):60–67
Dieckow J, Bayer C, Conceicao PC, Zanatta JA, Martin-neto L, Milori DBM, Salton JC, Macedo MM, Mielniczuk J, Hernanis LC (2009) Land use, tillage, texture and organic matter stock and composition in tropical and subtropical Brazilian soils. Eur J Soil Sci 60:240–249
Dilustro JJ, Collins B, Duncan L, Crawford C (2005) Moisture and soil texture effects on soil CO2 efflux components in southeastern mixed pine forests. For Ecol Manag 204(1):87–97
Drury CF, Reynolds WD, Tan CS, Welacky TW, McLaughlin NB (2006) Emissions of nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide: influence of tillage type and nitrogen placement depth. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:570–581
Foley JA, DeFries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapim FS, Coe MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK, Helkowski JH, Holloway T, Howard EA, Kucharik CJ, Monfreda C, Patz JA, Prentice IC, Ramankutty N, Snyder PK (2005) Global consequences of land use. Science 39(5734):570–574
Gamboa AM, Galicia L (2011) Differential influence of land use/cover change on topsoil carbon and microbial activity in low-latitude temperate forests. Agric Ecosyst Environ 142(3–4):280–290
Gong JR, Wang YH, Liu M, Huang YM, Yan X, Zhang ZY, Zhang W (2014) Effects of land use on soil respiration in the temperate steppe of inner Mongolia, china. Soil Tillage Res 144:20–31
Greonigen K, Qi X, Osenberg W, Luo Y, Hungate B (2014) Faster decomposition under increased atmospheric CO2 limits soil carbon storage. Science 344(6183):508–509
Han GX, Zhou GS, Xu ZZ, Yang Y, Liu JL, Shi KQ (2007) Biotic and abiotic factors controlling the spatial and temporal variation of soil respiration in an agricultural ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 39(2):418–425
Houghton RA, Hackler JL, Lawrence KT (1999) The US carbon budget: contributions from land-use change. Science 285:574–578
Huang HB, Ouyang W, Guo BB, Shi YD, Hao FH (2014) Vertical and horizontal distribution of soil parameters in intensive agricultural zone and effect on diffuse nitrogen pollution. Soil Tillage Res 144:32–40
Jiao W, Ouyang W, Hao FH, Liu B, Wang FL (2014) Geochemical variability of heavy metals in soil after land use conversions in northeast china and its environmental applications. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 16:924–931
Jobbagy EG, Jackson RB (2000) The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol Appl 10(2):423–436
Jones BEH, Haynes RJ, Phillips IR (2011) Influence of organic waste and residue mud additions on chemical, physical and microbial properties of bauxite residue sand. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(2):199–211
Kasimir-Klemedtsson Å, Klemedtsson L, Berglund K, Martikainen P, Silvola J, Oenema O (2007) Greenhouse gas emissions from farmed organic soils: a review. Soil Use Manag 13(s4):245–250
Lehmann J, Gaunt J, Rondon M (2006) Biochar sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems–a review. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Chang 11:403–427
Louis AS, Joanne KH, Susanna R, Vickery LA (2014) Thermodynamic theory explains the temperature optima of soil microbial processes and high Q10 values at low temperatures. Glob Chang Biol 20:3578–3586
Marinozzi M, Coppola L, Monaci E, Karpouzas DG, Papadopoulou E, Menkissoglu-Spiroudi U, Vischetti C (2011) Influence of organic waste and residue mud additions on chemical, physical and microbial properties of bauxite residue sand. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(2):199–211
Moon DH, Park JW, Chang YY, Ok YS, Lee SS, Ahmad M, Koutsospyros A, Park JH, Baek K (2013) Immobilization of lead in contaminated firing range soil using biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(12):8464–8471
Mukherjee A, Lal R, Zimmerman AR (2014) Effects of biochar and other amendments on the physical properties and greenhouse gas emissions of an artificially degraded soil. Sci Total Environ 487(15):26–36
Olson SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circ 939:1–19
Oral HV, Guney M, Kucuker MA, Onay T, Copty NK, Mater B, Yenigun O (2013) The impact of hazelnuts in land-use changes on soil carbon and in situ soil respiration dynamics. J Environ Manag 129:341–349
Ouyang W, Skidmore AK, Hao FH, Tiejun Wang TJ (2010) Soil erosion dynamics response to landscape pattern. Sci Total Environ 408(6):1358–1366
Ouyang W, Huang HB, Hao FH, Guo BB (2013) Synergistic impacts of land-use change and soil property variation on non-point source nitrogen pollution in a freeze-thaw area. J Hydrol 495(12):126–134
Ouyang W, Shan YS, Hao FH, Lin CY (2014) Differences in soil organic carbon dynamics in paddy fields and drylands in northeast china using the CENTURY model. Agric Ecosyst Environ 194:38–47
Pawlett M, Ritz K, Dorey RA, Rocks S, Ramsden J, Harris JA (2013) The impact of zero-valent iron nanoparticles upon soil microbial communities is context dependent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(2):1041–1049
Reicosly DC, Archer DW (2007) Moldboard plow tillage depth and short-term carbon dioxide release. Soil Tillage Res 94(1):109–121
Rustad LE, Huntington TG, Boone RD (2000) Controls on soil respiration: implications for climate change. Biogeochemistry 48:1–6
Simfukwe P, Hill PW, Emmett BA, Jones DL (2011) Soil classification provides a poor indicator of carbon turnover rates in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 43(8):1688–1696
Six J, Ogle SM, Jaybreidt F, Conant RT, Mosier AR, Paustian K (2004) The potential to mitigate global warming with no-tillage management is only realized when practiced in the long term. Glob Chang Biol 10(2):155–160
Smith JL, Collins HP, Bailey VL (2010) The effect of young biochar on soil respiration. Soil Biol Biochem 42(12):2345–2347
Song YY, Song CC, Yang GS, Miao YQ, Wang JY, Guo YD (2012) Fractions and soil enzyme activities after marshland reclamation and restoration in the sanjiang plain in northeast china. J Environ Manag 50(3):418–426
Spokas KA, Reicosky DC (2009) Impacts of sixteen different biochar on soil greenhouse gas production. Anal Environ Sci 3:17–193
Stanford G (1982) Assessment of soil nitrogen availability: nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agron Monogr 22:651–688
Suddick EC, Six J (2013) An estimation of annual nitrous oxide emissions and soil quality following the amendment of high temperature walnut shell biochar and compost to a small scale vegetable crop rotation. Sci Total Environ Vol 465(1):298–307
Withers PJA, Hodgkinson RA (2009) The effect of farming practices on phosphorus transfer to a headwater stream in England. Agric Ecosyst Environ 131(3–4):347–355
Zavalloni C, Alberti G, Biasiol S, Vedove GD, Fornasier F, Liu J, Peressotti A (2011) Microbial mineralization of biochar and wheat straw mixture in soil: a short-term study. Appl Soil Ecol 50(10):45–51
Zhang GL (2010) Changes of soil labile organic carbon in different land uses in sanjiang plain, Heilongjiang province. Chin Geogr Sci 20(2):139–143
Zhao XC, Ouyang W, Hao FH, Lin CY, Wang FL, Han S, Geng XJ (2013) Properties comparison of biochars from corn straw with different pretreatment and sorption behaviour of atrazine. Bioresour Technol 147:338–344
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the assistance of the Bawujiu Farm in Heilongjiang Province. This study was financially supported by the Supporting Program of the “Twelfth Five-year Plan” for Science & Technology Research of China (2012BAD15B05), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41371018), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Conflict of interest
The samplings of the soil were permitted by the local farm. Information obtained from other publication has been cited properly. All contributors to this paper have been listed in the authors and all the authors had read the final version and agreed to the submission. All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Human and animal rights and informed consent
The research did not involve the human participants and animals. The supporters of the study have been clearly listed in the MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, W., Geng, X., Huang, W. et al. Soil respiration characteristics in different land uses and response of soil organic carbon to biochar addition in high-latitude agricultural area. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 2279–2287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5306-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5306-9