Abstract
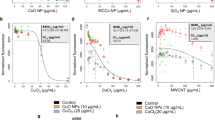
Quantum dots (QDs) are engineered semiconductor nanocrystals with promising application in biomedicine, which have potential toxic effect on biomacromolecules by direct interaction and indirect impact in the body. In this work, the effect of N-acetyl-l-cysteine-capped CdTe quantum dots with fluorescence emission peak at 612 nm (QDs-612) on copper–zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu/ZnSOD) at molecular and cellular level was investigated using isothermal titration calorimetry, spectroscopic techniques, cell counting kit-8, and total SOD assay. The hydrophobic interaction between Cu/ZnSOD and QDs-612 caused static fluorescence quenching of the protein, which was spontaneous with binding constant calculated to be 3.28 × 105 L mol−1. The microenvironment of tyrosine residues, skeleton, and secondary structure of Cu/ZnSOD were changed with adding QDs-612. The molecular Cu/ZnSOD activity was inhibited at different concentrations of QDs-612 as well as the intracellular Cu/ZnSOD activity after 2-h exposure. Compared with the cell viability of hepatocytes and nephrocytes (decreased markedly of the initial level) with higher concentrations of QDs-612 in the absence of vitamin C, the cell viability of these two primary cells increased in the presence of vitamin C, indicating the oxidative damage induced by QDs-612. Therefore, the inhibition of Cu/ZnSOD activity in these two primary cells may be caused by the oxidative damage of massive ROS or direct interaction with QDs-612. This work establishes a new approach to investigate the biological toxicity of CdTe QDs to biomacromolecule from both molecular and cellular perspectives and obtains experimental evidence to thoroughly study the toxicity of CdTe QDs in vivo.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QDs:
-
Quantum dots
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- ROS:
-
Reactivated oxygen species
- Cu/ZnSOD:
-
Copper–zinc superoxide dismutase
- MnSOD:
-
Manganese superoxide dismutase
- ECSOD:
-
Extracellular superoxide dismutase
- ITC:
-
Isothermal titration calorimetry
- CCK-8:
-
Cell counting kit-8
- QDs-612:
-
N-acetyl-l-cysteine-capped CdTe quantum dots with fluorescence emission peak at 612 nm
- NAC:
-
N-acetyl-l-cysteine
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Tyr:
-
Tyrosine
- Trp:
-
Tryptophan
- PB:
-
Phosphate buffer
- CD:
-
Circular dichroism
- WST-1:
-
2-(4-Iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2,4-disulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, disodium salt
References
Aseervatham GSB, Sivasudha T, Jeyadevi R, Ananth DA (2013) Environmental factors and unhealthy lifestyle influence oxidative stress in humans-an overview. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:4356–4369
Branco RJ, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ (2006) Molecular dynamics simulations of the enzyme Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase. J Phys Chem B 110:16754–16762
Bruchez MJ, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281:2013--2016
Cao J, Wei Y, Cheng Y (2013) Study on the binding interaction between perfluoroalkyl acids and DNA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8355–8363
Cao Z, Liu R, Dong Z, Yang X, Chen Y (2015) The effect of sarafloacin on Cu/ZnSOD structure and activity. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 136:601–606
Chan WC, Nie S (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281:2016–2018
Chen H, Zhang Z, Cai D, Zhang S, Zhang B, Tang J, Wu Z (2011) A hydrogen peroxide sensor based on Ag nanoparticles electrodeposited on natural nano-structure attapulgite modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 86:266–270
Chen J, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Zi Y, Qian Y, Gao H, Lin S (2012) Binding of triclosan to human serum albumin: insight into the molecular toxicity of emerging contaminant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2528–2536
Choi AO, Cho SJ, Desbarats J, Lovrić J, Maysinger D (2007) Quantum dot-induced cell death involves Fas upregulation and lipid peroxidation in human neuroblastoma cells. J Nanobiotechnol 5:1
Choi AO, Brown SE, Szyf M, Maysinger D (2008) Quantum dot-induced epigenetic and genotoxic changes in human breast cancer cells. J Mol Med 86:291–302
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Lunec J (2003) Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J 17:1195–1214
Dong Z, Liu LH, Han B, Pincheira R, Zhang JT (2004) Role of eIF3 p170 in controlling synthesis of ribonucleotide reductase M2 and cell growth. Oncogene 23:3790–3801
Gauthier TD, Shane EC, Guerin WF, Seitz WR, Grant CL (1986) Fluorescence quenching method for determining equilibrium constants for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons binding to dissolved humic materials. Environ Sci Technol 20:1162–1166
Goth L (1991) A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin Chim Acta 196:143–151
Hardman R (2006) A toxicologic review of quantum dots: toxicity depends on physicochemical and environmental factors. Environ Health Perspect 114:165–172
Hauck TS, Anderson RE, Fischer HC, Newbigging S, Chan WC (2010) In vivo quantum-dot toxicity assessment. Small 6:138–144
Juarez JC, Betancourt O, Pirie-Shepherd SR, Guan X, Price ML, Shaw DE, Mazar AP, Doñate F (2006) Copper binding by tetrathiomolybdate attenuates angiogenesis and tumor cell proliferation through the inhibition of superoxide dismutase 1. Clin Cancer Res 12:4974–4982
Jurczuk M, Brzóska MM, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J, Gałażyn-Sidorczuk M, Kulikowska-Karpińska E (2004) Antioxidant enzymes activity and lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney of rats exposed to cadmium and ethanol. Food Chem Toxicol 42:429–438
Kalt W, Forney CF, Martin A, Prior RL (1999) Antioxidant capacity, vitamin C, phenolics, and anthocyanins after fresh storage of small fruits. J Agric Food Chem 47:4638–4644
Kehrer JP (2000) The Haber–Weiss reaction and mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicology 149:43–50
Khan SN, Islam B, Yennamalli R, Sultan A, Subbarao N, Khan AU (2008) Interaction of mitoxantrone with human serum albumin: spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies. Eur J Pharm Sci 35:371–382
Kim SY, Kwon OJ, Park J-W (2001) Inactivation of catalase and superoxide dismutase by singlet oxygen derived from photoactivated dye. Biochimie 83:437–444
Klajnert B, Bryszewska M (2002) Fluorescence studies on PAMAM dendrimers interactions with bovine serum albumin. Bioelectrochemistry 55:33–35
Lackowicz JR (1983) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Plenum Press, New York
Liu Y, Chen M, Jiang L, Song L (2014) New insight into molecular interaction of heavy metal pollutant-cadmium (II) with human serum albumin. Environl Sci Pollut Res 21:6994–7005
Liu R, Yang J, Sun C, Li L, Wu X, Li Z, Qi C (2003) Study of the interaction of nucleic acids with acridine orange-CTMAB and determination of nucleic acids at nanogram levels based on the enhancement of resonance light scattering. Chem Phys Lett 376:108–115
Lu J-Q, Jin F, Sun T-Q, Zhou X-W (2007) Multi-spectroscopic study on interaction of bovine serum albumin with lomefloxacin-copper (II) complex. Int J Biol Macromol 40:299–304
Lu Z, Li M, Bao H, Qiao Y, Toh Y, Yang X (2008) Mechanism of antimicrobial activity of CdTe quantum dots. Langmuir 24:5445–5452
Métivier R, Bourven I, Labanowski J, Guibaud G (2013) Interaction of erythromycin ethylsuccinate and acetaminophen with protein fraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from various bacterial aggregates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7275–7285
Mátyus L, Szöllősi J, Jenei A (2006) Steady-state fluorescence quenching applications for studying protein structure and dynamics. J Photochem Photobio B 83:223–236
Ma L, Ze Y, Liu J, Liu H, Liu C, Li Z, Zhao J, Yan J, Duan Y, Xie Y (2009) Direct evidence for interaction between nano-anatase and superoxide dismutase from rat erythrocytes. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 73:330–335
Miao L, St Clair DK (2009) Regulation of superoxide dismutase genes: implications in disease. Free Radic Biol Med 47:344–356
Miller J (1979) Recent advances in molecular luminescence analysis. Proc Anal Div Chem Soc 16:203–208
Papadopoulou A, Green RJ, Frazier RA (2005) Interaction of flavonoids with bovine serum albumin: a fluorescence quenching study. J Agric Food Chem 53:158–163
Perry J, Shin D, Getzoff E, Tainer J (2010) The structural biochemistry of the superoxide dismutases. Biochimi Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 1804:245–262
Petroselli G, Dántola ML, Cabrerizo FM, Lorente C, Braun AM, Oliveros E, Thomas AH (2009) Quenching of the fluorescence of aromatic pterins by deoxynucleotides. J Phys Chem A 113:1794–1799
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB (2010) Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic Biol Med 49:1603–1616
Ross PD, Subramanian S (1981) Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 20:3096–3102
Ross PD, Rekharsky MV (1996) Thermodynamics of hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interactions in cyclodextrin complexes. Biophys J 71:2144–2154
Schininà M, Barra D, Simmaco M, Bossa F, Rotilio G (1985) Primary structure of porcine Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase. FEBS Lett 186:267–270
Seidel CA, Schulz A, Sauer MH (1996) Nucleobase-specific quenching of fluorescent dyes. 1. Nucleobase one-electron redox potentials and their correlation with static and dynamic quenching efficiencies. J Phys Chem 100:5541–5553
Shen X-C, Liou X-Y, Ye L-P, Liang H, Wang Z-Y (2007) Spectroscopic studies on the interaction between human hemoglobin and CdS quantum dots. J Colloid Interface Sci 311:400–406
Singh S, Nalwa HS (2007) Nanotechnology and health safety toxicity and risk assessments of nanostructured materials on human health. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:3048–3070
Singh BR, Singh BN, Khan W, Singh HB, Naqvi AH (2012) ROS-mediated apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer LNCaP cells induced by biosurfactant stabilized CdS quantum dots. Biomaterials 33:5753–5767
Sun H, Cui E, Tan Z, Liu R (2014a) Effects of N-acetyl-l-cysteine-capped cdte quantum dots on bovine serum albumin and bovine hemoglobin: isothermal titration calorimetry and spectroscopic investigations. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 28:549–557
Sun H, Yang B, Cui E, Liu R (2014b) Spectroscopic investigations on the effect of N-acetyl-l-cysteine-capped CdTe quantum dots on catalase. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 132:692–699
Tatsuya I, Shingo M, Yoshihito I, Futoshi O, Shinjiro T, Yoshihiko T, Yoshitaka I, Junichi F (2005) Accelerated impairment of spermatogenic cells in sod1-knockout mice under heat stress. Free Radic Res 39:697–705
Turnbull WB, Daranas AH (2003) On the value of c: can low affinity systems be studied by isothermal titration calorimetry? J Am Chem Soc 125:14859–14866
Waisberg M, Joseph P, Hale B, Beyersmann D (2003) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 192:95–117
Ware WR (1962) Oxygen quenching of fluorescence in solution: an experimental study of the diffusion process. J Phys Chem 66:455–458
Wu T, Wu Q, Guan S, Su H, Cai Z (2007) Binding of the environmental pollutant naphthol to bovine serum albumin. Biomacromolecules 8:1899–1906
Xiao J, Bai Y, Wang Y, Chen J, Wei X (2010) Systematic investigation of the influence of CdTe QDs size on the toxic interaction with human serum albumin by fluorescence quenching method. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 76:93–97
Yang B, Liu R, Hao X, Wu Y, Du J (2012) The interactions of glutathione-capped CdTe quantum dots with trypsin. Biol Trace Elem Res 146:396–401
Yin H, Ai S, Shi W, Zhu L (2009) A novel hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on horseradish peroxidase immobilized on gold nanoparticles-silk fibroin modified glassy carbon electrode and direct electrochemistry of horseradish peroxidase. Sensor Actuators B Chem 137:747–753
Yu WW, Qu L, Guo W, Peng X (2003) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater 15:2854–2860
Zhao L, Liu R, Zhao X, Yang B, Gao C, Hao X, Wu Y (2009) New strategy for the evalution of CdTe quantum dot toxicity targeted to bovine serum albumin. Sci Total Environ 407:5019–5023
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by NSFC (20875055, 21277081, 21477067), the Cultivation Fund of the Key Scientific and Technical Innovation Project, Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education and Ministry of Education of China (708058, 20130131110016). Independent innovation program of Jinan (201202083), Science and Technology Development Plan of Shandong Province (2014GSF117027) and Independent innovation foundation of Shandong University natural science projects (2012DX002) are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas Braunbeck
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM. 1
Fig. S1The structure-based alignment of porcine Cu/ZnSOD and mouse Cu/ZnSOD. Fig. S2: The structure and functional regions of mouse Cu/ZnSOD. Fig. S3: Time-resolved fluorescence decay curves of Cu/ZnSOD in the absence and presence of QDs-612. Fig. S4: CAT activity of primary hepatocytes (a and c) and primary nephrocytes (b and d) after 2 h exposure with different concentrations of QDs-612. (DOCX 293 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Cui, E. & Liu, R. Molecular mechanism of copper–zinc superoxide dismutase activity change exposed to N-acetyl-l-cysteine-capped CdTe quantum dots-induced oxidative damage in mouse primary hepatocytes and nephrocytes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 18267–18277 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5035-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5035-0