Abstract
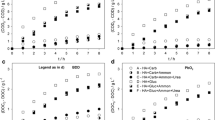
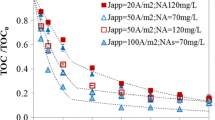
In this work, the electrochemical oxidation of synthetic urine by anodic oxidation using boron-doped diamond as anode and stainless steel as cathode was investigated. Results show that complete depletion of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total organic carbon (TOC) can be attained regardless of the current density applied in the range 20–100 mA cm−2. Oxalic and oxamic acids, and, in lower concentrations, creatol and guanidine were identified as the main intermediates. Chloride ions play a very important role as mediators and contribute not only to obtain a high efficiency in the removal of the organics but also to obtain an efficient removal of nitrogen by the transformation of the various raw nitrogen species into gaseous nitrogen through chloramine formation. The main drawback of the technology is the formation of chlorates and perchlorates as final chlorine products. The increase of current density from 20 to 60 mA cm−2 led to an increase in the rate of COD and TOC removals although the process becomes less efficient in terms of energy consumption (removals of COD and TOC after applying 18 Ah dm−3 were 93.94 and 94.94 %, respectively, at 20 mA cm−2 and 89.17 and 86.72 %, respectively, at 60 mA cm−2). The most efficient conditions are low current densities and high temperature reaching total mineralization at an applied charge as low as 20 kAh m−3. This result confirmed that the electrolysis using diamond anodes is a very interesting technology for the treatment of urine.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed B, Limem E, Abdel-Wahab A, Nasr B (2011) Photo-Fenton treatment of actual agro-industrial wastewaters. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:6673–6680
Antoniou MG, Nambiar U, Dionysiou DD (2009) Investigation of the photocatalytic degradation pathway of the urine metabolite, creatinine: the effect of pH. Water Res 43:3956–3963
Bensalah N, Bedoui A, Chellam S, Abdel-Wahab A (2013) Electro-Fenton treatment of photographic processing wastewater. Clean Soil Air Water 41:635–644
Bergmann MEH, Koparal AS, Iourtchouk T (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes, formation of halogenate and perhalogenate species: a critical review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:348–390
Blum D, Feachem RG (1983) Measuring the impact of water-supply and sanitation investments on diarrheal diseases—problems of methodology. Int J Epidemiol 12:357–365
Brillas E, Boye B, Sires I, Garrido JA, Rodriguez RM, Arias C, Cabot PL, Comninellis C (2004) Electrochemical destruction of chlorophenoxy herbicides by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochim Acta 49:4487–4496
Brillas E, Sires I, Oturan MA (2009) Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem Rev 109:6570–6631
Calza P, Pelizzetti E, Minero C (2005) The fate of organic nitrogen in photocatalysis: an overview. J Appl Electrochem 35:665–673
Canizares P, Lobato J, Paz R, Rodrigo MA, Saez C (2005) Electrochemical oxidation of phenolic wastes with boron-doped diamond anodes. Water Res 39:2687–2703
Canizares P, Saez C, Lobato J, Paz R, Rodrigo MA (2007) Effect of the operating conditions on the oxidation mechanisms in conductive-diamond electrolyses. J Electrochem Soc 154:E37–E44
Canizares P, Saez C, Martinez F, Rodrigo MA (2008) The role of the characteristics of p-Si BDD anodes on the efficiency of wastewater electro-oxidation processes. Electrochem Solid State Lett 11:E15–E19
Cano A, Canizares P, Barrera-Diaz C, Saez C, Rodrigo MA (2012) Use of conductive-diamond electrochemical-oxidation for the disinfection of several actual treated wastewaters. Chem Eng J 211:463–469
Cotillas S, Llanos J, Canizares P, Mateo S, Rodrigo MA (2013) Optimization of an integrated electrodisinfection/electrocoagulation process with Al bipolar electrodes for urban wastewater reclamation. Water Res 47:1741–1750
Dirany A, Sires I, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2010) Electrochemical abatement of the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole from water. Chemosphere 81:594–602
Elahmadi MF, Bensalah N, Gadri A (2009) Treatment of aqueous wastes contaminated with Congo Red dye by electrochemical oxidation and ozonation processes. J Hazard Mater 168:1163–1169
Faouzi M, Canizares P, Gadri A, Lobato J, Nasr B, Paz R, Rodrigo MA, Saez C (2006) Advanced oxidation processes for the treatment of wastes polluted with azoic dyes. Electrochim Acta 52:325–331
Feng L, van Hullebusch ED, Rodrigo MA, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2013) Removal of residual anti-inflammatory and analgesic pharmaceuticals from aqueous systems by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. A review. Chem Eng J 228:944–964
Greer MA, Goodman G, Pleus RC, Greer SE (2002) Health effects assessment for environmental perchlorate contamination: the dose response for inhibition of thyroidal radioiodine uptake in humans. Environ Health Perspect 110:927–937
Guinea E, Arias C, Cabot PL, Garrido JA, Rodriguez RM, Centellas F, Brillas E (2008) Mineralization of salicylic acid in acidic aqueous medium by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using platinum and boron-doped diamond as anode and cathodically generated hydrogen peroxide. Water Res 42:499–511
Guinea E, Brillas E, Centellas F, Canizares P, Rodrigo MA, Saez C (2009a) Oxidation of enrofloxacin with conductive-diamond electrochemical oxidation, ozonation and Fenton oxidation. A comparison. Water Res 43:2131–2138
Guinea E, Centellas F, Brillas E, Canizares P, Saez C, Rodrigo MA (2009b) Electrocatalytic properties of diamond in the oxidation of a persistent pollutant. Appl Catal B Environ 89:645–650
Haidar M, Dirany A, Sires I, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2013) Electrochemical degradation of the antibiotic sulfachloropyridazine by hydroxyl radicals generated at a BDD anode. Chemosphere 91:1304–1309
Hanjra MA, Blackwell J, Carr G, Zhang F, Jackson TM (2012) Wastewater irrigation and environmental health: implications for water governance and public policy. Int J Hyg Environ Health 215:255–269
Heinonen-Tanski H, Sjoblom A, Fabritius H, Karinen P (2007) Pure human urine is a good fertiliser for cucumbers. Bioresour Technol 98:214–217
Höglund C, Ashbolt N, Stenström TA, Svensson L (2002) Viral persistence in source-separated human urine. Adv Environ Res 6:265–275
Lacasa E, Canizares P, Llanos J, Rodrigo MA (2011a) Removal of nitrates by electrolysis in non-chloride media: effect of the anode material. Sep Purif Technol 80:592–599
Lacasa E, Canizares P, Saez C, Fernandez FJ, Rodrigo MA (2011b) Electrochemical phosphates removal using iron and aluminium electrodes. Chem Eng J 172:137–143
Lacasa E, Canizares P, Llanos J, Rodrigo MA (2012a) Effect of the cathode material on the removal of nitrates by electrolysis in non-chloride media. J Hazard Mater 213:478–484
Lacasa E, Llanos J, Canizares P, Rodrigo MA (2012b) Electrochemical denitrification with chlorides using DSA and BDD anodes. Chem Eng J 184:66–71
Lacasa E, Tsolaki E, Sbokou Z, Andres Rodrigo M, Mantzavinos D, Diamadopoulos E (2013) Electrochemical disinfection of simulated ballast water on conductive diamond electrodes. Chem Eng J 223:516–523
Marselli B, Garcia-Gomez J, Michaud PA, Rodrigo MA, Comninellis C (2003) Electrogeneration of hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 150:D79–D83
Martinez-Huitle CA, Ferro S (2006) Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: direct and indirect processes. Chem Soc Rev 35:1324–1340
Martinez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B Environ 87:105–145
Michaud PA, Mahe E, Haenni W, Perret A, Comninellis C (2000) Preparation of peroxodisulfuric acid using boron-doped diamond thin film electrodes. Electrochem Solid State Lett 3:77–79
Oturan N, Hamza M, Ammar S, Abdelhedi R, Oturan MA (2011) Oxidation/mineralization of 2-nitrophenol in aqueous medium by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using Pt/carbon-felt and BDD/carbon-felt cells. J Electroanal Chem 661:66–71
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2005) Application of diamond electrodes to electrochemical processes. Electrochim Acta 51:191–199
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2007) Electrocatalytic materials for the electrochemical oxidation of synthetic dyes. Appl Catal B Environ 75:95–101
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2008) Removal of colour and COD from wastewater containing acid blue 22 by electrochemical oxidation. J Hazard Mater 153:83–88
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2009) Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem Rev 109:6541–6569
Polcaro AM, Mascia M, Palmas S, Vacca A (2004) Electrochemical degradation of diuron and dichloroaniline at BDD electrode. Electrochim Acta 49:649–656
Polcaro AM, Vacca A, Mascia M, Palmas S (2005) Oxidation at boron doped diamond electrodes: an effective method to mineralise triazines. Electrochim Acta 50:1841–1847
Polcaro AM, Vacca A, Mascia M, Palmas S (2007) Electrokinetic removal of 2,6-dichlorophenol and diuron from kaolinite and humic acid–clay system. J Hazard Mater 148:505–512
Randazzo S, Scialdone O, Brillas E, Sires I (2011) Comparative electrochemical treatments of two chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons. Time course of the main reaction by-products. J Hazard Mater 192:1555–1564
Raut AS, Cunningham GB, Parker CB, Klem EJD, Stoner BR, Deshusses MA, Glass JT (2013) Electrochemical disinfection of human urine for water-free and additive-free toilets using boron-doped diamond electrodes, ECS Transactions, pp. 1–11
Reyter D, Belanger D, Roue L (2010) Nitrate removal by a paired electrolysis on copper and Ti/IrO2 coupled electrodes—influence of the anode/cathode surface area ratio. Water Res 44:1918–1926
Sanchez-Carretero A, Saez C, Canizares P, Rodrigo MA (2011) Electrochemical production of perchlorates using conductive diamond electrolyses. Chem Eng J 166:710–714
Serrano K, Michaud PA, Comninellis C, Savall A (2002) Electrochemical preparation of peroxodisulfuric acid using boron doped diamond thin film electrodes. Electrochim Acta 48:431–436
Shuval H, Lampert Y, Fattal B (1997) Development of a risk assessment approach for evaluating wastewater reuse standards for agriculture. Water Sci Technol 35:15–20
Sires I, Garrido JA, Rodriguez RM, Cabot PI, Centellas F, Arias C, Brillas E (2006) Electrochemical degradation of paracetamol from water by catalytic action of Fe2+, Cu2+, and UVA light on electrogenerated hydrogen peroxide. J Electrochem Soc 153:D1–D9
Sires I, Brillas E, Cerisola G, Panizza M (2008) Comparative depollution of mecoprop aqueous solutions by electrochemical incineration using BDD and PbO2 as high oxidation power anodes. J Electroanal Chem 613:151–159
Svorc L, Stankovic DM, Kalcher K (2014) Boron-doped diamond electrochemical sensor for sensitive determination of nicotine in tobacco products and anti-smoking pharmaceuticals. Diam Relat Mater 42:1–7
Vinneras B, Palmquist H, Balmer P, Jonsson H (2006) The characteristics of household wastewater and biodegradable solid waste—a proposal for new Swedish design values. Urban Water J 3:3–11
Vlyssides AG, Karlis PK, Rori N, Zorpas AA (2002) Electrochemical treatment in relation to pH of domestic wastewater using Ti/Pt electrodes. J Hazard Mater 95:215–226
Zhou M, Sarkka H, Sillanpaa M (2011) A comparative experimental study on methyl orange degradation by electrochemical oxidation on BDD and MMO electrodes. Sep Purif Technol 78:290–297
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge University of Gabes (Tunisia) for providing partial financial support to accomplish this research work. This work was also supported by the Spanish government through project CTM2013-45612-R. Financial support of the Spanish government and EU through project FEDER 2007–2013 PP201010 (Planta Piloto de Estación de Estación de Regeneración de Aguas Depuradas) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dbira, S., Bensalah, N., Bedoui, A. et al. Treatment of synthetic urine by electrochemical oxidation using conductive-diamond anodes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 6176–6184 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3831-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3831-6