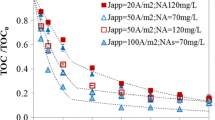
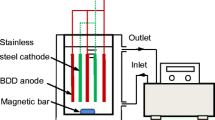
Abstract
Boron-doped diamond (BDD) and Ti/Pt/PbO2 anodes were utilized to perform the electrodegradation of synthetic samples containing humic acid in the presence of different organic and inorganic carbon-containing and nitrogen-containing compounds. The influence of the chloride ion in the degradation process of the different synthetic samples was also assessed. The results showed that the anodic oxidation process can efficiently degrade recalcitrant compounds such as humic acid. The presence of carbonate in solution enhances the nitrogen removal, whereas it hinders the oxidation of the organic compounds. When organic nitrogen is present, it is converted to NH4 +, which in turn is oxidized to nitrate and to volatile nitrogen compounds. Hydroxyl radicals are more prone to oxidize the organic nitrogen than the ammonium nitrogen. The presence of chloride enhances the organic matter and nitrogen removal rates, BDD being the anode material that yields the highest removals.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade LS, Rutuolo LAM, Rocha-Filho RC, Bocchi N, Biaggio S, Iniesta J, García-Garcia V, Montiel V (2007) On the performance of Fe and Fe, F doped Ti–Pt/PbO2 electrodes in the electrooxidation of the Blue Reactive 19 dye in simulated textile wastewater. Chemosphere 66:2035–2043. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.10.028
Anglada A, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2009) Contributions of electrochemical oxidation to waste-water treatment: fundamentals and review of applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:1747–1755. doi:10.1002/jctb.2214
Anglada A, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I, Mantzavinos D, Diamadopoulos E (2011) Boron-doped diamond anodic treatment of landfill leachate: evaluation of operation variables and formation of oxidation by-products. Water Res 45:828–838. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.017
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B Environ 166:603–643. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Canizares P, Rubén P, Sáez C, Rodrigo MA (2009) Costs of the electrochemical oxidation of wastewaters: a comparison with ozonation and Fenton oxidation processes. J Environ Manage 90:410–420. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.10.010
Chen G (2004) Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 38:11–41. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2003.10.006
Chiang LC, Chang JE, Wen TC (1995) Indirect oxidation effect in electrochemical oxidation treatment of landfill leachate. Water Res 29:671–678. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(94)00146-X
Ciríaco L, Anjo C, Correia J, Pacheco MJ, Lopes A (2009) Electrochemical degradation of Ibuprofen on Ti/Pt/PbO2 and Si/BDD electrodes. Electrochim Acta 54:1464–1472. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2008.09.022
Eaton A, Clesceri L, Rice E, Greenberg A, Franson MA (2005) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Fernandes A, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2012) Anodic oxidation of a biologically treated leachate on a boron-doped diamond anode. J Hazard Mater 199–200:82–87. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.074
Fernandes A, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2015) Review on the electrochemical processes for the treatment of sanitary landfill leachates: present and future. Appl Catal B-Environ 176:183–200. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.03.052
Fernandes A, Santos D, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2014) Nitrogen and organic load removal from sanitary landfill leachates by anodic oxidation at Ti/Pt/PbO2, Ti/Pt/SnO2-Sb2O4 and Si/BDD. Appl Catal B Environ 148:288–294. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.10.060
Fernandes A, Santos D, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2016) Electrochemical oxidation of humic acid and sanitary landfill leachate: Influence of anode material, chloride concentration and current density. Sci Total Environ 541:282–291. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.052
Lin H, Niu J, Ding S, Zhang L (2012) Electrochemical degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by Ti/SnO2-Sb, Ti/SnO2-Sb/PbO2 and Ti/SnO2-Sb/MnO2 anodes. Water Res 46:2281–2289. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.053
Lin H, Niu J, Xu J, Huang H, Li D, Yue Z, Feng C (2013a) Highly efficient and mild electrochemical mineralization of long-chain perfluorocarboxylic acids (C9−C10) by Ti/SnO2−Sb−Ce, Ti/SnO2−Sb/Ce−PbO2, and Ti/BDD electrodes. Environ Sci Technol 47:13039–13046. doi:10.1021/es4034414
Lin H, Niu J, Xu J, Li Y, Pan Y (2013b) Electrochemical mineralization of sulfamethoxazole by Ti/SnO2-Sb/Ce-PbO2 anode: Kinetics, reaction pathways, and energy cost evolution. Electrochim Acta 97:167– 174. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.03.019
Liu J, Cao J, Chen H, Zhou D (2015) Adsorptive removal of humic acid from aqueous solution by micro and mesoporous covalent triazine-based framework. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 481:276–282. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.05.021
Mazellier P, Leroy É, De Laat J, Legube B (2003) Degradation of carbendazim by UV/H2O2 investigated by kinetic modelling. Environ Chem Lett 1:68–72. doi:10.1007/s10311-002-0010-7
Niu J, Li Y, Shang E, Xu Z, Liu J (2016) Electrochemical oxidation of perfluorinated compounds in water. Chemosphere 146:526–538. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.115
Panizza M, Martinez-Huitle C (2013) Role of electrode materials for the anodic oxidation of a real landfill leachate—comparison between Ti–Ru–Sn ternary oxide, PbO2 and boron-doped diamond anode. Chemosphere 90:1455–60. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.09.006
Pérez G, Saiz J, Ibãnez R, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2012) Assessment of the formation of inorganic oxidation by-products during the electrocatalytic treatment of ammonium from landfill leachates. Water Res 46:2579–2590. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.015
Sirés I, Brillas E (2012) Remediation of water pollution caused by pharmaceutical residues based on electrochemical separation and degradation technologies: A review. Environ Int 40:212–229. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2011.07.012
Woisetschläger D, Humpl B, Koncar M, Siebenhofer M (2013) Electrochemical oxidation of wastewater—opportunities and drawbacks. Water Sci Technol 65:1173–9. doi:10.2166/wst.2013.366
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support received from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, FCT, for the financing of the FibEnTech Research Unit, project Pest-OE/CTM/UI0195/2014, and for the grant awarded to Annabel Fernandes, SFRH/BPD/103615/2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Variation with time of DIC, relative TDN and nitrite concentration during the electrodegradation experiments performed using (a,c,e) BDD and (b,d,f) Ti/Pt/PbO2 anodes (TIF 20501 kb)
Fig. S2
Variation with time of DIC, relative TDN and nitrite concentration during the electrodegradation experiments performed using (a,c,e) BDD and (b,d,f) Ti/Pt/PbO2 anodes in the presence of chloride initial concentration of 4.5 g L-1 (TIF 20345 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, A., Coelho, J., Ciríaco, L. et al. Electrochemical wastewater treatment: influence of the type of carbon and of nitrogen on the organic load removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 24614–24623 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6851-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6851-6