Abstract
Purpose
This study developed formulas to predict obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and the Apnea–Hypopnea Index (AHI) in Korean patients with suspected OSA using clinical, anthropometric, and cephalometric variables.
Methods
We evaluated relevant variables in 285 subjects with suspected OSA. These included demographic characteristics, sleep-related symptoms, medical history, clinical scales, anthropometric measurements including facial surface measurements, and cephalometric measurements. All participants underwent full-night laboratory polysomnography. The prediction formula for the probability of OSA was created by logistic regression analysis and confirmed by the bootstrap resampling technique. The formula for predicting the AHI was developed using multiple linear regression analysis.
Results
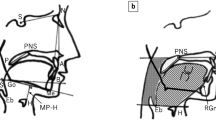
The probability of having OSA was as follows: p = 1 / (1 + exponential (exp)−f), where f = −16.508 + 1.445 × loudness of snoring 4 + 0.485 × loudness of snoring 3 + 0.078 × waist circumference + 0.209 × subnasale-to-stomion distance + 0.183 × thickness of the uvula (UTH) supine + 0.041 × age. The AHI prediction formula was as follows: −112.606 + 3.516 × body mass index + 0.683 × mandibular plane–hyoid supine + 10.915 × loudness of snoring 4 + 6.933 × loudness of snoring 3 + 1.297 × UTH supine + 0.272 × age.
Conclusion
This is the first study to establish formulas to predict OSA and the AHI in Koreans with suspected OSA using cephalometric and other variables. These results will contribute to prioritizing the order in which patients with suspected OSA are referred for polysomnography.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kryger MH, Roth T (2017) Principles and practice of sleep medicine, Sixth edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia
Kim J, In K, You S, Kang K, Shim J, Lee S et al (2004) Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in middle-aged Korean men and women. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170(10):1108–1113
Villaneuva AT, Buchanan PR, Yee BJ, Grunstein RR (2005) Ethnicity and obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med Rev 9(6):419–436
Bouloukaki I, Kapsimalis F, Mermigkis C, Kryger M, Tzanakis N, Panagou P et al (2011) Prediction of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in a large Greek population. Sleep Breath 15(4):657–664
Caffo B, Diener-West M, Punjabi NM, Samet J (2010) A novel approach to prediction of mild obstructive sleep disordered breathing in a population-based sample: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Sleep 33(12):1641–1648
Kang HH, Kang JY, Ha JH, Lee J, Kim SK, Moon HS et al (2014) The associations between anthropometric indices and obstructive sleep apnea in a Korean population. PLoS One 9(12):e114463
Musman S, Passos VM, Silva IB, Barreto SM (2011) Evaluation of a prediction model for sleep apnea in patients submitted to polysomnography. J Bras Pneumol 37(1):75–84
Santaolalla Montoya F, Iriondo Bedialauneta JR, Aguirre Larracoechea U, Martinez Ibarguen A, Sanchez Del Rey A, Sanchez Fernandez JM (2007) The predictive value of clinical and epidemiological parameters in the identification of patients with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA): a clinical prediction algorithm in the evaluation of OSA. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264(6):637–643
Lee RW, Petocz P, Prvan T, Chan AS, Grunstein RR, Cistulli PA (2009) Prediction of obstructive sleep apnea with craniofacial photographic analysis. Sleep 32(1):46–52
Perri RA, Kairaitis K, Cistulli P, Wheatley JR, Amis TC (2014) Surface cephalometric and anthropometric variables in OSA patients: statistical models for the OSA phenotype. Sleep Breath 18(1):39–52
Sutherland K, Lee RW, Petocz P, Chan TO, Ng S, Hui DS et al (2016) Craniofacial phenotyping for prediction of obstructive sleep apnoea in a Chinese population. Respirology 21(6):1118–1125
Li KK, Kushida C, Powell NB, Riley RW, Guilleminault C (2009) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a comparison between Far-East Asian and white men. Laryngoscope 110(10):1689–1693
Kong H-W, Lee H-J, Choi Y-S, Rha J-H, Ha C-K, Hwang DU et al (2004) Clinical predictors of obstructive sleep apnea. J Korean Neurol Assoc 23:324–329
Armalaite J, Lopatiene K (2016) Lateral teleradiography of the head as a diagnostic tool used to predict obstructive sleep apnea. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 45(1):20150085
Hsu PP, Tan AK, Chan YH, Lu PK, Blair RL (2005) Clinical predictors in obstructive sleep apnoea patients with calibrated cephalometric analysis—a new approach. Clin Otolaryngol 30(3):234–241
Kang K, Park KS, Kim JE, Kim SW, Kim YT, Kim JS et al (2013) Usefulness of the Berlin Questionnaire to identify patients at high risk for obstructive sleep apnea: a population-based door-to-door study. Sleep Breath 17(2):803–810
Chung F, Yegneswaran B, Liao P, Chung SA, Vairavanathan S, Islam S et al (2008) STOP questionnaire: a tool to screen patients for obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology 108(5):812–821
Cho YW, Lee JH, Son HK, Lee SH, Shin C, Johns MW (2011) The reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breath 15(3):377–384
Brodsky L, Moore L, Stanievich JF (1987) A comparison of tonsillar size and oropharyngeal dimensions in children with obstructive adenotonsillar hypertrophy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 13(2):149–156
Samsoon GL, Young JR (1987) Difficult tracheal intubation: a retrospective study. Anaesthesia 42(5):487–490
Kim H-A, Cho Y-W, Lee H, Lee J-H, Ahn B-H, Suh Y-S et al (2005) An evaluation of Apnea-Hypopnea Index, sleep questionnaires, oropharyngeal findings and cephalometric parameters in patients with snoring. J Korean Neurol Assoc 23(2):215–221
Seo EW, Lee HK, Han MW, Seo MH, Kim HJ, Song SI (2013) Cephalometric predisposing factors of the snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 35:161–166
Hwang S-H, Park I-S, Nam K-Y, Kim J-B, Cho Y-W, Suh Y-S et al (2008) Cephalometric differences in obstructive sleep apnea between obese and non-obese Korean male patients. Korean J Orthod 38(3):202–213
Iber C, American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Westchester
Grunkemeier GL, Wu Y (2004) Bootstrap resampling methods: something for nothing? Ann Thorac Surg 77(4):1142–1144
Rowley JA, Aboussouan LS, Badr MS (2000) The use of clinical prediction formulas in the evaluation of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 23(7):929–938
Julia-Serda G, Perez-Penate G, Saavedra-Santana P, Ponce-Gonzalez M, Valencia-Gallardo JM, Rodriguez-Delgado R et al (2006) Usefulness of cephalometry in sparing polysomnography of patients with suspected obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 10(4):181–187
Heo JY, Kim JS (2011) Correlation between severity of sleep apnea and upper airway morphology: cephalometry and MD-CT study during awake and sleep states. Acta Otolaryngol 131(1):84–90
Yu X, Fujimoto K, Urushibata K, Matsuzawa Y, Kubo K (2003) Cephalometric analysis in obese and nonobese patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Chest 124(1):212–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) provided the financial support in the form of Basic Science Research Program funding (NRF-2011-0013991, NRF-2013R1A1A2059105). The sponsor had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.T., Park, K.H., Shin, SH. et al. Formula for predicting OSA and the Apnea–Hypopnea Index in Koreans with suspected OSA using clinical, anthropometric, and cephalometric variables. Sleep Breath 21, 885–892 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-017-1506-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-017-1506-5