Abstract
Purpose
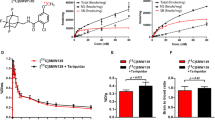
Upregulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) expression in multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions is associated with neuroinflammatory response. This study investigated the correlation between neuroinflammation and S1PR1 expression in the spinal cord of an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) rat model of MS, using the S1PR1 positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer [11C]TZ3321.
Procedures
MicroPET imaging studies of [11C]TZ3321 were performed to measure uptake of [11C]TZ3321 in the spinal cord of EAE rats. Immunohistochemical staining was performed to confirm the overexpression of S1PR1 and other inflammatory biomarkers.
Results
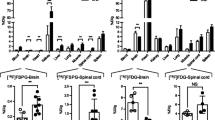
MicroPET imaging demonstrated a 20–30 % increase in [11C]TZ3321 uptake in the lumbar spinal cord of EAE rats versus sham controls at 35–60 min post injection. The increased uptake of [11C]TZ3321 was correlated with the overexpression of S1PR1 in the lumbar spinal cord of EAE rats that was confirmed by immunohistochemical staining. Upregulated S1PR1 expression was associated with glial cell activation and immune cell infiltration.
Conclusions
MicroPET imaging modality with a specific radioligand [11C]TZ3321 is able to assess the expression of S1PR1 in EAE rat lumbar spinal cord. This may provide a new approach to the assessment of neuroinflammatory response in MS and other inflammatory diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3D-OSEM:
-
Three-dimensional ordered subset expectation maximization
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CCL2:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2
- CFA:
-
Complete Freund’s adjuvant
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DAB:
-
3,3-Diaminobenzidine
- EAE:
-
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- GDNF:
-
Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- Iba-1:
-
Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- MBP:
-
Myelin basic protein
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- S1PR1:
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1
- SUV:
-
Standardized uptake value
- TAC:
-
Time–activity curve
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- TSPO:
-
Translocator protein 18 kDa
References
Mahad DH, Trapp BD, Lassmann H (2015) Pathological mechanisms in progressive multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 14:183–193
Ransohoff RM, Hafler DA, Lucchinetti CF (2015) Multiple sclerosis—a quiet revolution. Nat Rev Neurol 11:134–142
Compston A, Confavreux C, Lassmann H et al (2006) McAlpine’s multiple sclerosis, 4th edn. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia
Marsolais D, Rosen H (2009) Chemical modulators of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors as barrier-oriented therapeutic molecules. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:297–307
Kappos L, Radue EW, O’Connor P et al (2010) A placebo-controlled trial of oral fingolimod in relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 362:387–401
Pelletier D, Hafler DA (2012) Fingolimod for multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 366:339–347
Choi JW, Gardell SE, Herr DR et al (2011) FTY720 (fingolimod) efficacy in an animal model of multiple sclerosis requires astrocyte sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:751–756
Galicia-Rosas G, Pikor N, Schwartz JA et al (2012) A sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1-directed agonist reduces central nervous system inflammation in a plasmacytoid dendritic cell-dependent manner. J Immunol 189:3700–3706
Gonzalez-Cabrera PJ, Cahalan SM, Nguyen N et al (2012) S1P1 receptor modulation with cyclical recovery from lymphopenia ameliorates mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Mol Pharmacol 81:166–174
Van Doorn R, Van Horssen J, Verzijl D et al (2010) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 and 3 are upregulated in multiple sclerosis lesions. Glia 58:1465–1476
Garris CS, Wu L, Acharya S et al (2013) Defective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) phosphorylation exacerbates TH17-mediated autoimmune neuroinflammation. Nat Immunol 14:1166–1172
Noda H, Takeuchi H, Mizuno T, Suzumura A (2013) Fingolimod phosphate promotes the neuroprotective effects of microglia. J Neuroimmunol 256:13–18
Samoilova EB, Horton JL, Hilliard B et al (1998) IL-6-deficient mice are resistant to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: roles of IL-6 in the activation and differentiation of autoreactive T cells. J Immunol 161:6480–6486
Izikson L, Klein RS, Charo IF et al (2000) Resistance to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice lacking the CC chemokine receptor (CCR)2. J Exp Med 192:1075–1080
Chiba K, Kataoka H, Seki N et al (2011) Fingolimod (FTY720), sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator, shows superior efficacy as compared with interferon-beta in mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int Immunopharmacol 11:366–372
Maeda Y, Seki N, Kataoka H et al (2015) IL-17-producing Vγ4+ γδ T cells require sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 for their egress from the lymph nodes under homeostatic and inflammatory conditions. J Immunol 195:1408–1416
Seki N, Maeda Y, Kataoka H et al (2013) Role of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis—I. S1P-S1P1 axis induces migration of Th1 and Th17 cells. Pharmacol Pharm 4:628–637
Briard E, Orain D, Beerli C et al (2011) BZM055, an iodinated radiotracer candidate for PET and SPECT imaging of myelin and FTY720 brain distribution. Chemmedchem 6:667–677
Prasad VP, Wagner S, Keul P et al (2014) Synthesis of fluorinated analogues of sphingosine-1-phosphate antagonists as potential radiotracers for molecular imaging using positron emission tomography. Bioorg Med Chem 22:5168–5181
Shaikh RS, Schilson SS, Wagner S et al (2015) Synthesis and evaluation of fluorinated Fingolimod (FTY720) analogues for sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor molecular imaging by positron emission tomography. J Med Chem 58:3471–3484
Jin H, Yang H, Liu H et al (2016) A promising carbon-11 labeled sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 specific PET tracer for imaging vascular injury. J Nucl Cardiol. doi:10.1007/s12350-015-0391-1
Abourbeh G, Theze B, Maroy R et al (2012) Imaging microglial/macrophage activation in spinal cords of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis rats by positron emission tomography using the mitochondrial 18 kDa translocator protein radioligand [18F]DPA-714. J Neurosci 32:5728–5736
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J et al (2007) Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1533–1539
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND et al (1996) Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:834–840
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND et al (1990) Graphical analysis of reversible radioligand binding from time-activity measurements applied to [N-11C-methyl]-(−)-cocaine PET studies in human subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:740–747
Meeson AP, Piddlesden S, Morgan BP, Reynolds R (1994) The distribution of inflammatory demyelinated lesions in the central nervous system of rats with antibody-augmented demyelinating experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Exp Neurol 129:299–310
Constantinescu CS, Farooqi N, O’Brien K, Gran B (2011) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br J Pharmacol 164:1079–1106
Mattner F, Katsifis A, Staykova M et al (2005) Evaluation of a radiolabelled peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand in the central nervous system inflammation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: a possible probe for imaging multiple sclerosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:557–563
Linker RA, Lee DH (2009) Models of autoimmune demyelination in the central nervous system: on the way to translational medicine. Exp Transl Stroke Med 1:5
Kunkel GT, MacEyka M, Milstien S, Spiegel S (2013) Targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer, inflammation and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:688–702
Brinkmann V, Billich A, Baumruker T et al (2010) Fingolimod (FTY720): discovery and development of an oral drug to treat multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:883–897
Chun J, Hartung HP (2010) Mechanism of action of oral fingolimod (FTY720) in multiple sclerosis. Clin Neuropharmacol 33:91–101
Blaho VA, Hla T (2014) An update on the biology of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J Lipid Res 55:1596–1608
Seki N, Kataoka H, Sugahara K et al (2013) Role of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis—II. S1P-S1P1 axis induces pro-inflammatory cytokine production in astrocytes. Pharmacol Pharm 4:638–646
Mehling M, Lindberg R, Raulf F et al (2010) Th17 central memory T cells are reduced by FTY720 in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 75:403–410
Kebir H, Kreymborg K, Ifergan I et al (2007) Human TH17 lymphocytes promote blood–brain barrier disruption and central nervous system inflammation. Nat Med 13:1173–1175
Matusevicius D, Kivisakk P, He B et al (1999) Interleukin-17 mRNA expression in blood and CSF mononuclear cells is augmented in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 5:101–104
de Paula FD, Vlaming ML, Copray SC et al (2014) PET imaging of disease progression and treatment effects in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis rat model. J Nucl Med 55:1330–1335
Colasanti A, Piccini P (2014) PET imaging in multiple sclerosis: focus on the translocator protein. PET and SPECT in neurology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 757–773
Owen DR, Yeo AJ, Gunn RN et al (2012) An 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) polymorphism explains differences in binding affinity of the PET radioligand PBR28. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1–5
Kreisl WC, Fujita M, Fujimura Y et al (2010) Comparison of [C-11]-(R)-PK 11195 and [C-11]PBR28, two radioligands for translocator protein (18 kDa) in human and monkey: implications for positron emission tomographic imaging of this inflammation biomarker. Neuroimage 49:2924–2932
Owen DR, Gunn RN, Rabiner EA et al (2011) Mixed-affinity binding in humans with 18-kDa translocator protein ligands. J Nucl Med 52:24–32
Kreisl WC, Jenko KJ, Hines CS et al (2013) A genetic polymorphism for translocator protein 18 kDa affects both in vitro and in vivo radioligand binding in human brain to this putative biomarker of neuroinflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:53–58
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by DOE-Training in Techniques and Translation: Novel Nuclear Medicine Imaging Agents for Oncology and Neurology, DESC0008432, the Washington University School of Medicine Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology (MIR) Cyclotron Facility Allotment #14-017, and NIH/NINDS, NS075527, and NIH/NIMH, MH092797. We thank Nicole Fettig, Margaret Morris, Amanda Roth, Lori Strong, and Ann Stroncek for their assistance with the microPET imaging studies, Marlene Scott and Bill Coleman in the Elvie L. Taylor Histology Core Facility of Washington University School of Medicine for sample embedding and H&E staining. The authors also like to thank Lynne A. Jones’ assistance in preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 430 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Jin, H., Yue, X. et al. PET Imaging Study of S1PR1 Expression in a Rat Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Mol Imaging Biol 18, 724–732 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-016-0944-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-016-0944-y