Abstract
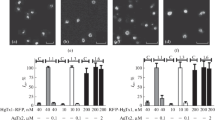
The P2X7 receptor is a frequently studied member of the purinergic receptor family signalling via channel opening and membrane pore formation. Fluorescent imaging is an important molecular method for studying cellular receptor expression and localization. Fusion of receptors to fluorescent proteins might cause major functional changes and requires careful functional evaluation such as has been done for the rat P2X7 receptor. This study examines fusion constructs of the human P2X7 receptor. We assessed surface expression, channel opening with calcium influx, and pore formation using YO-PRO-1 dye uptake in response to BzATP stimulation in transfected cells. We found that tagging at the N-terminal of the human P2X7 receptor with the enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) disturbed channel opening and pore formation despite intact surface expression. A triple hemagglutinin (3HA) fused to the N-terminal also disrupted pore formation but not channel opening showing that even a small tag alters the normal function of the receptor. Together, this suggests that in contrast to what has been observed for the rat P2X7 receptor, the human P2X7 receptor contains N-terminal motifs important for signalling that prevent the construction of a functionally active fusion protein.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morandini AC, Savio LEB, Coutinho-Silva R (2014) The role of P2X7 receptor in infectious inflammatory diseases and the influence of ectonucleotidases. Biom J 37(4):169–177. https://doi.org/10.4103/2319-4170.127803
BJ G, Zhang WY, Bendall LJ et al (2000) Expression of P2X(7) purinoceptors on human lymphocytes and monocytes: evidence for nonfunctional P2X(7) receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C1189–C1197
Sperlagh B, Vizi ES, Wirkner K, Illes P (2006) P2X7 receptors in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 78(6):327–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.03.007
Wang J, Liu S, Nie Y, Wu B, Wu Q, Song M, Tang M, Xiao L, Xu P, Tan X, Zhang L, Li G, Liang S, Zhang C (2015) Activation of P2X7 receptors decreases the proliferation of murine luteal cells. Reprod Fertil Dev 27(8):1262. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD14381
Jiang W, Lv H, Wang H, Wang D, Sun S, Jia Q, Wang P, Song B, Ni L (2015) Activation of the NLRP3/caspase-1 inflammasome in human dental pulp tissue and human dental pulp fibroblasts. Cell Tissue Res 361(2):541–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2118-7
Jorgensen NR, Syberg S, Ellegaard M (2015) The role of P2X receptors in bone biology. Curr Med Chem 22(7):902–914. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867321666141215094749
Volonte C, Apolloni S, Skaper SD, Burnstock G (2012) P2X7 receptors: channels, pores and more. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 11(6):705–721. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152712803581137
Amstrup J, Novak I (2003) P2X7 receptor activates extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1 and ERK2 independently of Ca2+ influx. Biochem J 374(1):51–61. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20030585
Yan Z, Li S, Liang Z, Tomić M, Stojilkovic SS (2008) The P2X7 receptor channel pore dilates under physiological ion conditions. J Gen Physiol 132(5):563–573. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.200810059
Smart ML, Panchal RG, Bowser DN, Williams DA, Petrou S (2002) Pore formation is not associated with macroscopic redistribution of P2X7 receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283(1):C77–C84. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00456.2001
Buell G, Chessell IP, Michel AD, Collo G, Salazzo M, Herren S, Gretener D, Grahames C, Kaur R, Kosco-Vilbois MH, Humphrey PP (1998) Blockade of human P2X7 receptor function with a monoclonal antibody. Blood 92(10):3521–3528
Karasawa A, Michalski K, Mikhelzon P, Kawate T (2017) The P2X7 receptor forms a dye-permeable pore independent of its intracellular domain but dependent on membrane lipid composition. elife 6. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31186
Michel AD, Thompson KM, Simon J, Boyfield I, Fonfria E, Humphrey PPA (2006) Species and response dependent differences in the effects of MAPK inhibitors on P2X(7) receptor function. Br J Pharmacol 149(7):948–957. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706938
Wickert LE, Blanchette JB, Waldschmidt NV, Bertics PJ, Denu JM, Denlinger LC, Lenertz LY (2013) The C-terminus of human nucleotide receptor P2X7 is critical for receptor oligomerization and N-linked glycosylation. PLoS One 8(5):e63789. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063789
Milius D, Groger-Arndt H, Stanchev D et al (2007) Oxygen/glucose deprivation increases the integration of recombinant P2X7 receptors into the plasma membrane of HEK293 cells. Toxicology 238(1):60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2007.05.028
Ferrari D, Pizzirani C, Gulinelli S, Callegari G, Chiozzi P, Idzko M, Panther E, Virgilio F (2007) Modulation of P2X7 receptor functions by polymyxin B: crucial role of the hydrophobic tail of the antibiotic molecule. Br J Pharmacol 150(4):445–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706994
Sun C, Heid ME, Keyel PA, Salter RD (2013) The second transmembrane domain of P2X7 contributes to dilated pore formation. PLoS One 8(4):e61886. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061886
Bradley HJ, Liu X, Collins V, Owide J, Goli GR, Smith M, Surprenant A, White SJ, Jiang LH (2010) Identification of an intracellular microdomain of the P2X7 receptor that is crucial in basolateral membrane targeting in epithelial cells. FEBS Lett 584(23):4740–4744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2010.11.007
Masin M, Young C, Lim K et al (2012) Expression, assembly and function of novel C-terminal truncated variants of the mouse P2X7 receptor: re-evaluation of P2X7 knockouts. Br J Pharmacol 165(4):978–993. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01624.x
Acknowledgements
Great thanks to Helle Kinggaard Lilja-Fischer for many hours spent on calcium signalling optimization and Susanne Syberg for excellent teaching of YO-PRO-1 dye uptake assay. Also, thanks to Martin Fredensborg Rath for the use of his equipment.
Funding
The study was supported financially by the Lundbeck Foundation and FP7-CIG grant 334443.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Karin Dreisig declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Nikolaj Pagh Kristensen declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Maja Wallentin Dommer declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Niklas Rye Jørgensen declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Birgitte Rahbek Kornum declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreisig, K., Kristensen, N.P., Dommer, M.W. et al. N-terminal tagging of human P2X7 receptor disturbs calcium influx and dye uptake. Purinergic Signalling 14, 83–90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-017-9598-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-017-9598-8