Abstract
Purpose
To identify obstruction sites of the upper airway during sleep in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) under dynamic conditions and improve knowledge to guide surgical treatment and advancements.
Materials and methods
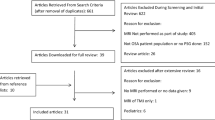
The study included 15 patients (5 females and 10 males) who were diagnosed as having OSAS. Overall mean age was 40.2 years (± 7.01 years). All the patients underwent drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE) and dynamic sleep MRI. The presence, location, and direction of airway collapse were assessed. Dynamic MRI findings were correlated to DISE. Data of the site and direction of airway collapse were correlated with those of endoscopic findings and interobserver agreement was done.
Results
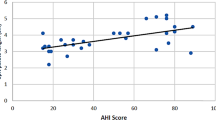
The dynamic images in sagittal section showed collapse of the upper airway at retropalatal level in 14 patients (93.33%) and at retroglossal level in seven patients (46.7%) and of these 14 patients; seven had combined retropalatal and retroglossal collapse. These findings were highly correlated with DISE findings with an excellent interobserver agreement for retropalatal and retroglossal levels (Kappa = 1 and 0.867, P value = 0.000), respectively. Objective measurements of the direction of collapse in axial dynamic sleep MRI images showed significant statistical correlation with endoscopic findings regarding retropalatal anteroposterior and circumferential collapse (Kappa = 0.58 and 0.52, P value = 0.02 and 0.03, respectively).
Conclusion
Dynamic sleep MRI can reliably characterize the actual site of dynamic airway obstruction and has the potential of improving predictions of successful surgical outcomes in OSAS patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moon IJ, Han DH, Kim JW, et al. Sleep magnetic resonance imaging as a new diagnostic method in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(12):2546–54.
Santosham R, Anand S, et al. Role of dynamic MR imaging in obstructive sleep apnoea. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;60(1):25–9.
Chasens ER. Obstructive sleep apnea, daytime sleepiness, and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2007;33(3):475–82.
Hung J, Whitford EG, Parsons RW, et al. Association of sleep apnoea with myocardial infarction in men. Lancet. 1990;336(8710):261–4.
Das AM, Khayat R. Hypertension in obstructive sleep apnea: risk and therapy. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009;7(6):619–26.
Li KK. Surgical therapy for adult obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med Rev. 2005;9(3):201–9.
Naya M, Vicente E, Llorente E, et al. Predictive value of the Muller maneuver in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2000;51(1):40–5.
Barrera JE, Holbrook AB, Santos J, et al. Sleep MRI: novel technique to identify airway obstruction in obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140(3):423–5.
Chen NH, Li KK, Li SY, et al. Airway assessment by volumetric computed tomography in snorers and subjects with obstructive sleep apnea in a Far-East Asian population (Chinese). Laryngoscope. 2002;112(4):721–6.
Barrera JE. Sleep magnetic resonance imaging: dynamic characteristics of the airway during sleep in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Laryngoscope. 2011;121(6):1327–35.
Donnelly LF, Surdulescu V, Chini BA, et al. Upper airway motion depicted at cine MR imaging performed during sleep: comparison between young patients with and those without obstructive sleep apnea. Radiology. 2003;227(1):239–45.
Shott SR, Donnelly LF. Cine magnetic resonance imaging: evaluation of persistent airway obstruction after tonsil and adenoidectomy in children with Down syndrome. Laryngoscope. 2004;114(10):1724–9.
Chen YJ, Shih TT, Chang YC, et al. Acoustic-integrated dynamic MR imaging for a patient with obstructive sleep apnea. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;33(10):1350–2.
Donnelly LF, Shott SR, LaRose CR, et al. Causes of persistent obstructive sleep apnea despite previous tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in children with down syndrome as depicted on static and dynamic cine MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(1):175–81.
Donnelly LF, Casper KA, Chen B. Correlation on cine MR imaging of size of adenoid and palatine tonsils with degree of upper airway motion in asymptomatic sedated children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179(2):503–8.
Donnelly LF, Casper KA, Chen B, et al. Defining normal upper airway motion in asymptomatic children during sleep by means of cine MR techniques. Radiology. 2002;223(1):176–80.
Kendzerska T, Mollayeva T, Gershon AS, et al. Untreated obstructive sleep apnea and the risk for serious long-term adverse outcomes: a systematic review. Sleep Med Rev. 2014;18(1):49–59.
Abdel Razek AA. Diagnostic role of magnetic resonance imaging in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2015;39(4):565–71.
Moon SJLC, Han DH, et al. Comparison of polysomnographic findings according to obstruction sites in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;50:779–83.
Wang YL, McDonald JP, Liu YH, et al. Analysis of the dynamic changes in the soft palate and uvula in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea using ultrafast magnetic resonance imaging. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(4):8596–608.
Moriwaki H, Inoue Y, Namba K, et al. Clinical significance of upper airway obstruction pattern during apneic episodes on ultrafast dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2009;36(2):187–91.
Rodriguez-Bruno K, Goldberg AN, McCulloch CE, et al. Test-retest reliability of drug-induced sleep endoscopy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140(5):646–51.
Schwab RJ, Gupta KB, Gefter WB, et al. Upper airway and soft tissue anatomy in normal subjects and patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Significance of the lateral pharyngeal walls. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152(5 Pt 1):1673–89.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors (Omneya Gamaleldin, Ahmed Bahgat, Omnia Anwar, Mahmoud Seif-Elnasr, Lamya Eissa, Ahmed Abdel Khalek Abdel Razek, Gihan Mohamed Shehata and Mohamed Hossameldin Khalifa) have no conflicts of interest. This includes financial or personal relationships that inappropriately influence (bias) his or her actions.
Ethical approval
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gamaleldin, O., Bahgat, A., Anwar, O. et al. Role of dynamic sleep MRI in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Oral Radiol 37, 376–384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-020-00455-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-020-00455-w