Abstract
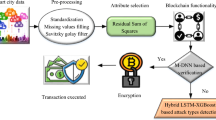
Infrastructure for the Internet of Things is being created in smart cities with long-term viability for a range of manufacturing uses, including smart manufacturing as well as smart industries. However in a smart city environment, security measures may not be effective and the existing system also have several drawbacks such as latency, privacy, scalability and security. A block chain-based IoT framework is being developed to address these problems. Initially, the raw data’s are collected from the smart cities through various IoT devices. Then the data’s are pre-processed using Adaptive Data Cleaning, it also contain a prediction method called denoising auto encoder which is used to converting the data from low into high quality form. Then the pre-processed data is given to the block chain based distributed network. Block construction, Request + transaction, transmit block to other nodes in the network, and verification are the four block chain functionalities in this network. For verifying the transaction Modified Deep Neural Network is used. The verifier must select between two possibilities after the transaction has been verified: yes or no. If the state is correct, the transaction is performed and a block is generated in the blockchain. Or else, the process will be halted if any attack is identified in the transaction. The simulation analysis shows that the proposed method obtain 96% accuracy, 0.04% error, precision is 95% so on. This demonstrates that the proposed strategy outperforms other methods currently being used. Based on this proposed method the transaction is executed securely to provide secure smart city environment.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
If all data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article and no data needs to be specifically requested.
Code Availability
No code is available for this manuscript.
References
Singh, S. K., Jeong, Y. S., & Park, J. H. (2020). A deep learning-based IoT-oriented infrastructure for secure smart city. Sustainable Cities and Society, 60, 102252.
Puliafito, A., Tricomi, G., Zafeiropoulos, A., & Papavassiliou, S. (2021). Smart cities of the future as cyber physical systems: Challenges and enabling technologies. Sensors, 21(10), 3349.
Verma, R. (2022). Smart city healthcare cyber physical system: Characteristics, technologies and challenges. Wireless Personal Communications, 122(2), 1413–1433.
Rathore, S., Kwon, B. W., & Park, J. H. (2019). BlockSecIoTNet: Blockchain-based decentralized security architecture for IoT network. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 143, 167–177.
Lee, J., Azamfar, M., & Singh, J. (2019). A blockchain enabled cyber-physical system architecture for Industry 4.0 manufacturing systems. Manufacturing Letters, 20, 34–39.
Mirabelli, G., & Solina, V. (2020). Blockchain and agricultural supply chains traceability: Research trends and future challenges. Procedia Manufacturing, 42, 414–421.
Hou, L., Liao, R. and Luo, Q. (2021) IoT and blockchain-based smart agri-food supply chains. Handbook of Smart Cities, pp.1109–1130.
Mistry, I., Tanwar, S., Tyagi, S., & Kumar, N. (2020). Blockchain for 5G-enabled IoT for industrial automation: A systematic review, solutions, and challenges. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 135, 06382.
Mohanty, S. P., Choppali, U., & Kougianos, E. (2016). Everything you wanted to know about smart cities: The internet of things is the backbone. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 5(3), 60–70.
Karthick, S. (2018). TDP: A Novel Secure and Energy Aware Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems, 11(2), 76–84.
Singh, S., Sharma, P. K., Yoon, B., Shojafar, M., Cho, G. H., & Ra, I. H. (2020). Convergence of blockchain and artificial intelligence in IoT network for the sustainable smart city. Sustainable Cities and Society, 63, 102364.
Biswas, K. & Muthukkumarasamy, V. (2016). Securing smart cities using blockchain technology. IEEE 18th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications, 1392–1393.
Esposito, C., Ficco, M., & Gupta, B. B. (2021). Blockchain-based authentication and authorization for smart city applications. Information Processing & Management, 58(2), 102468.
Kushch, S. & Prieto-Castrillo, F. (2019) Blockchain for dynamic nodes in a smart city. In 2019 IEEE 5th world forum on internet of things (WF-IoT), pp. 29–34. IEEE.
Rahman, M. A., Rashid, M. M., Hossain, M. S., Hassanain, E., Alhamid, M. F., & Guizani, M. (2019). Blockchain and IoT-based cognitive edge framework for sharing economy services in a smart city. IEEE Access, 7, 18611–18621.
Abd El-Latif, A. A., Abd-El-Atty, B., Mehmood, I., Muhammad, K., Venegas-Andraca, S. E., & Peng, J. (2021). Quantum-inspired blockchain-based cybersecurity: Securing smart edge utilities in IoT-based smart cities. Information Processing & Management, 58(4), 102549.
Li, S. (2018) Application of blockchain technology in smart city infrastructure. In 2018 IEEE international conference on smart internet of things (SmartIoT), pp. 276–2766. IEEE.
Sharma, P. K., & Park, J. H. (2018). Blockchain based hybrid network architecture for the smart city. Future Generation Computer Systems, 86, 650–655.
Rathee, G., Iqbal, R., Waqar, O., & Bashir, A. K. (2021). On the design and implementation of a blockchain enabled e-voting application within iot-oriented smart cities. IEEE Access, 9, 34165–34176.
Ferreira, C. M. S., Garrocho, C. T. B., Oliveira, R. A. R., Silva, J. S., & Cavalcanti, C. F. M. D. C. (2021). IoT registration and authentication in smart city applications with blockchain. Sensors, 21(4), 1323.
Sun, D., Wu, J., Yang, J., & Wu, H. (2021). Intelligent data collaboration in heterogeneous-device IoT platforms. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 17(3), 1–17.
Alfian, G., Syafrudin, M., Fitriyani, N. L., Anshari, M., Stasa, P., Svub, J., & Rhee, J. (2020). Deep neural network for predicting diabetic retinopathy from risk factors. Mathematics, 8(9), 1620.
Peraza-Vázquez, H., Peña-Delgado, A. F., Echavarría-Castillo, G., Morales-Cepeda, A. B., Velasco-Álvarez, J., & Ruiz-Perez, F. (2021). A bio-inspired method for engineering design optimization inspired by dingoes hunting strategies. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 1–19.
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/speedwall10/iot-device-network-logs.
Funding
There is no funding provided to prepare the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The process of writing and the content of the article does not give grounds for raising the issue of a conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to Participate
I have read and I understand the provided information.
Consent to Publish
This article does not contain any Image or video to get permission.
Informal Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S., Chaurasiya, V.K. Blockchain and IoT Based Infrastructure for Secure Smart City Using Deep Learning Algorithm with Dingo Optimization. Wireless Pers Commun 132, 17–37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10560-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10560-8