Abstract
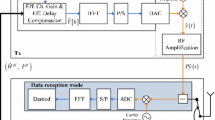
This paper presents a novel transceiver architecture for in-band full duplex radio. A transceiver for full duplex radio requires a self-interference (SI) canceler to remove the SI occurring from the transmitter to the receiver, and a full duplex transceiver generally has two SI cancelers: one at the analog RF stage and the other at the baseband stage. The output from the SI canceler at the RF stage includes much residual SI, and it decreases the number of bits allocated to the analog baseband signal at the analog-to-digital converter. A 1-tap analog baseband SI canceler that uses a replica signal including only the direct path component of the residual SI has been presented for preventing degradation. However, the architecture cannot remove the SI well due to the high Ricial K-factor. To address the problem, the presented architecture has an SI canceler at the analog baseband stage, and this canceler employs a replica signal that is output from a digital-to-analog converter. Because the replica signal is generated in the digital domain, the architecture can generate a multipath replica signal, and improved performance can be expected. Numerical and theoretical analyses are shown to validate the effectiveness of the presented architecture.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sabharwal, A., Schniter, P., Dongning, G., Bliss, D. W., Rangarajan, S., & Wichman, R. (2014). In-band full-duplex wireless: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(9), 1637–1652.
Annamalai, P., Bapat, J., & Das, D. (2019). A novel frequency allocation scheme for in band full duplex systems in 5G networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 8(2), 364–367.
Yadav, A., Dobre, O. A., & Ansari, N. (2017). Energy and traffic aware full-duplex communications for 5G systems. IEEE Access, 5, 11278–11290.
Bany Salameh, H. (2021). Quantifying the impact of time-sharing on route capacity in cognitive radio networks with full-duplex capability. IEEE Communications Letters, 25(1), 94–98.
Xu, D., Yu, X., Sun, Y., Ng, D. W. K., & Schober, R. (2020). Resource allocation for IRS-assisted full-duplex cognitive radio systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 68(12), 7376–7394.
Zhang, Y., Wu, Q., & Shikh-Bahaei, M. R. (2020). On ensemble learning-based secure fusion strategy for robust cooperative sensing in full-duplex cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 68(10), 6086–6100.
Korpi, D., Riihonen, T., Syrjälä, V., Anttila, L., Valkama, M., & Wichman, R. (2014). Full-duplex transceiver system calculations: Analysis of ADC and linearity challenges. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(7), 3821–3836.
Korpi, D., Anttila, L., Syrjälä, V., & Valkama, M. (2014). Widely linear digital self-interference cancellation in direct-conversion full-duplex transceiver. IEEE JSAC, 32(9), 1674–1687.
Syrjälä, V., Valkama, M., Anttila, L., Riihonen, T., & Korpi, D. (2014). Analysis of oscillator phase-noise effects on self-interference cancellation in full-duplex OFDM radio transceivers. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(6), 2977–2990.
Korpi, D., Huusara, T., Choi, Y. -S., Anttila, L., Talwar, S., & Valkama, M. Digital self-interference cancellation under nonideal RF components: Advanced algorithms and measured performance. In Proceedings of IEEE SPAWC 2015 (pp. 286–290).
Duarte, M., Dick, C., & Sabharwal, A. (2012). Experiment-driven characterization of full-duplex wireless systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(12), 4296–4307.
Lee, J.-H., Jung, J.-H., Kim, S.-C., & Kim, Y.-H. (2015). Analog cancellation for full-duplex wireless in multipath self-interference channels. IEICE Transactions on Communications, E98–B(4), 646–652.
Huusari, T., Choi, Y. -S., Liikkanen, P., Korpi, D., Talwar, S., & Valkama, M. (2015). Wideband self-adaptive RF cancellation circuit for full-duplex radio: Operating principle and measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE VTC2015-Spring (pp. 1–7).
Fukui, T., Komatsu, K., Miyaji, Y., & Uehara, H. (2020). Analog self-interference cancellation using auxiliary transmitter considering IQ imbalance and amplifier nonlinearity. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 19(11), 7439–7452.
Kolodziej, K. E., Cookson, A. U., & Perry, B. T. (2021). RF canceller tuning acceleration using neural network machine learning for in-band full-duplex systems. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2, 1158–1170.
Elsayed, M., El-Banna, A. A. A., Dobre, O. A., Shiu, W., & Wang, P. (2021). Low complexity neural network structures for self-interference cancellation in full-duplex radio. IEEE Communications Letters, 25(1), 181–185.
Bernhardt, M., Gregorio, F., Cousseau, J., & Riihonen, T. (2018). Self-interference cancelation through advanced sampling. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 66(7), 1721–1733.
Narieda, S. (2016). Antenna selection for reduction of Rician distributed self interference effects in full duplex radio. Electronics Letters, 52(3), 234–235.
Péerz, J. P. A., Pueyo, S. C., & López, B. C. (2011). Automatic gain control. Springer.
Murray, B. M., & Collings, I. B. (2006). AGC and quantization effects in A zero-forcing MIMO wireless system. In Proceedings of the IEEE VTC 2006-Spring (pp. 1802–1806).
Narieda, S. (2014). Receiver performances considering effects of gain control and quantization in FDM-based narrowband communication systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 78(1), 741–754.
Shi, K., Zhou, Y., Kelleci, B., Fischer, T. W., Serpedin, E., & Karşılayan, A. İ. (2007). Impacts of narrowband interference on OFDM-UWB receivers: Analysis and mitigation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(3), 1118–1128.
Kaufman, B., Lilleberg, J., & Aazhang, B. (2013). An analog baseband approach for designing full-duplex radios. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (pp. 987–991).
Kester, W. (2004). Analog-digital conversion. Analog Devices Inc.
Understanding Data Converters. (1995). Texas instruments application report SLAA013, mixed-signal products.
Razavi, B. (2011). RF microelectronics (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP19K04374.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narieda, S. Analog Baseband Self-Interference Canceler with Digitally Generated Replica Signal for Full Duplex. Wireless Pers Commun 126, 1769–1788 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09821-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09821-9