Abstract
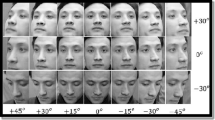
Personal identification systems that use face recognition work well for test images with frontal view face, but often fail when the input face is a pose view. Most face databases come from picture ID sources such as passports or driver’s licenses. In such databases, only the frontal view is available. This paper proposes a method of 2D pose-invariant face recognition that assumes the search database contains only frontal view faces. Given a non-frontal view of a test face, the pose-view angle is first calculated by matching the test image with a database of canonical faces with head rotations to find the best matched image. This database of canonical faces is used only to find the head rotation. The database does not contain images of the test face itself, but has a selection of template faces, each face having rotation images of − 45°, − 30°, − 15°, 0°, 15°, 30°, and 45°. The landmark features in the best matched rotated canonical face such as say rotation 15° and it’s corresponding frontal face of rotation 0° are used to create a warp transformation to convert the 15° rotated test face to a frontal face. This warp will introduce some distortion artifacts since some features of the non-frontal input face are not visible due to self-occlusion. The warped image is, therefore, enhanced by mixing intensities using the left/right facial symmetry assumption. The enhanced synthesized frontal face image is then used to find the best match target in the frontal face database. We test our approach using CMU Multi-PIE database images. Our method performs with acceptable and similar accuracy to conventional methods, while using only frontal faces in the test database.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, W., Chellappa, R., Phillips, P. J., & Rosenfeld, A. (2003). Face recognition: A literature survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 35(4), 399–458.
Hassaballah, M., & Aly, S. (2015). Face recognition: Challenges, achievements and future directions. IET Computer Vision, 9(4), 614–626.
Ding, C., & Tao, D. (2016). A comprehensive survey on pose-invariant face recognition. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 7(3), 37:1–37:42.
Blanz, V., & Vetter, T. (2003). Face recognition based on fitting a 3d morphable model. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 5(9), 1063–1074.
Lee, M. W., & Ranganath, S. (2003). Pose-invariant face recognition using a 3d deformable model. Pattern Recognition, 36(8), 835–1846.
Jiang, D., Hu, Y., Yan, S., Zhang, L., Zhang, H., & Gao, W. (2005). Efficient 3d reconstruction for face recognition. Pattern Recognition, 38(6), 787–798.
Asthana, A., Marks, T. K., Jones, M. J., Tieu, K. H., & Rohith, M. (2011). Fully automatic pose invariant face recognition via 3d pose normalization. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 937–944.
Yi, D., Lei, Z., & Li, S. Z. (2013). Towards pose robust face recognition. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3539–3545.
Ding, C., Xu, C., & Tao, D. (2015). Multi-task pose-invariant face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 24(3), 980–993.
Ding, C., & Tao, D. (2017). Pose-invariant face recognition with homography-based normalization. Pattern Recognition, 66, 144–152.
Gross, R., Mattews, I., & Baker, S. (2004). Appearance-based face recognition and light-fields. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 26(4), 449–465.
Chai, X., Shan, S., & Chen, X. (2007). Locally linear regression for pose-invariant face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 16(7), 1716–1725.
Ashraf, A. B., Lucey, S., & Chen, T. (2008). Learning patch correspondences for improved viewpoint invariant face recognition. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1–8.
Gao, H., Ekenel, H. K., & Stiefelhagen, R. (2009). Pose normalization for local appearance based face recognition. In International conference on advances in biometrics, pp. 32–41.
Ho, H. T., & Chellappa, R. (2013). Pose-invariant face recognition using Markov random fields. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(4), 1573–1584.
Kan, M., Shan, S., Chang, H., & Chen, X. (2014). Stacked progressive auto-encoders (SPAE) for face recognition across poses. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Zhu, Z., Luo, P., Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2013). Deep learning identity-preserving face space. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 113–120.
Zhang, Y., Shao, M., Wong, E. K., & Fu, Y. (2013). Random faces guided sparse many-to-one encoder for pose-invariant face recognition. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 2416–2423.
Yim, J., Jung, H., Yoo, B., Choi, C., Park, D., & Kim, J. (2015). Rotating your face using multitask deep neural network. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 676–684.
Gentle, J. E. (2007). Matrix transformations and factorizations. In Matrix algebra: Theory, computations, and applications in statistics. Springer. ISBN 9780387708737.
Gross, R., Matthews, I., Cohn, J., Kanade, T., & Baker, S. (2009). Multi-PIE. Image and Vision Computing, 28, 807–813.
Petpairote, C., Madarasmi, S., & Chamnongthai, K. (2017). Personalised-face neutralisation using best-matched face shape with a neutral-face database. IET Computer Vision. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cvi.2017.0352.
Cootes, T. F., Edwards, G. J., & Taylor, C. J. (2001). Active appearance models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 23(6), 681–685.
Cristinacce, D., & Cootes, T. F. (2006). Feature detection and tracking with constrained local models. In British Machine Vision Conference, Vol. 3, pp. 929–938.
Zhu, X., & Ramanan, D. (2012). Face detection, pose estimation, and landmark localization in the wild. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248014.
Parkhi, O. M., Vedaldi, A., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Deep face recognition. In British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 1–12.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep convolution networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556.
Matthews, I., & Baker, S. (2004). Active appearance models revisited. International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2), 135–164.
Zhang, W., Shan, S., Gao, W., Chen, X., & Zhang, H. (2005). Local Gabor binary pattern histogram sequence (LGBPHS): A novel non-statistical model for face representation and recognition. In IEEE international conference on computer vision. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2005.147.
Turk, M., & Pentland, A. (1991). Eigenfaces for recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 3(1), 71–86.
Timo, A., Abdenour, H., & Matti, P. (2004). Face recognition with local binary patterns. In European Conference on computer vision, pp. 469–481.
Arqub, O. A., & Abo-Hammour, Z. (2014). Numerical solution of systems of second-order boundary value problems using continuous genetic algorithm. Information Sciences, 279, 396–415.
Arqub, O. A., Smadi, M. A., Momani, S., & Hayat, T. (2016). Numerical solutions of fuzzy differential equations using reproducing kernel Hilbert space method. Soft Computing, 20(8), 3283–3302.
Sim, T., Baker, S., & Bsat, M. (2002). The CMU pose, illumination, and expression (PIE) database. In International conference auto face and gesture recognition, Washington, DC, pp. 46–51.
Lin, J., Ming, J., & Crookes, D. (2011). Robust face recognition with partial occlusion, illumination variation and limited training data by optimal feature selection. IET Computer Vision, 5(1), 23–32.
Kafai, M., An, L., & Bhanu, B. (2014). Reference face graph for face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 9(12), 2132–2143.
Acknowledgements
The financial support provided by the Thailand Research Fund through the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. Program (Grant No. PHD/0056/2551), and the King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petpairote, C., Madarasmi, S. & Chamnongthai, K. 2D Pose-Invariant Face Recognition Using Single Frontal-View Face Database. Wireless Pers Commun 118, 2015–2031 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07063-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07063-1