Abstract
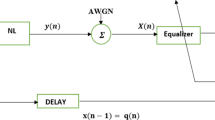
In this paper we briefly describe the design, implementation, and evaluation of a novel adaptive optimization approach for the feed-forward software defined equalization (FFSDE) method using the least mean squared (LMS) algorithm. In our design, we adaptively change the filter length (N) and step size (\(\mu\)) to achieve the optimal bit error rate value. We used a vector signal generator RF PXI-5670 and a vector signal analyzer (VSA) RF PXI-5660 to test the validity of our approach. We implemented our method for the M-ary quadrature amplitude modulation (M-QAM) scheme in the VSA (which served as a receiver). The experimental results showed that we achieved high convergence speed and accuracy for rapidly changing transmitter channel characteristics. The automatic optimal setting feature of the LMS Algorithm parameters N and \(\mu\), enabled us to solve the hardware configuration problem for the FFSDE method. Determination of the LMS Algorithm training sequence size for the particular M-QAM allowed us to eliminate redundant data of the training sequence and increase the throughput.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agilent Technologies: Option AYA Flexible Modulation Analysis 89600 Vector Signal Analysis Software (2011). http://www.tevetllc.com/documents/pdf/manuals/89601B/89600-AYA-demo.pdf
Al-Wohaishi, M., Martinek, R., & Zidek, J. (2011). Analysis of m-qam data communication system using 3d eye diagram. In V. Snasel, J. Platos & E. El-Qawasmeh (Eds.), Digital information processing and communications (vol. 189, pp. 337–348). Berlin: Springer.
Arslan, H. (2007). Cognitive radio, software defined radio, and adaptive wireless systems (Vol. 10). Berlin: Springer.
Arslan, M. Y., Sundaresan, K., & Rangarajan, S. (2015). Software-defined networking in cellular radio access networks: Potential and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(1), 150–156.
Civicioglu, P., & Besdok, E. (2013). A conceptual comparison of the cuckoo-search, particle swarm optimization, differential evolution and artificial bee colony algorithms. Artificial Intelligence Review, 39(4), 315–346.
Eliaz, A. (2015). Feed forward equalization for highly-spectrally-efficient communications. US Patent 9,166,833
Ge, X., Cheng, H., Guizani, M., & Han, T. (2014). 5G wireless backhaul networks: Challenges and research advances. IEEE Network, 28(6), 6–11.
Gui, G., Peng, W., & Adachi, F. (2013). Improved adaptive sparse channel estimation based on the least mean square algorithm. In Wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), 2013 IEEE (pp. 3105–3109). IEEE.
Hassun, R., Flaherty, M., Matreci, R., & Taylor, M. (1997). Effective evaluation of link quality using error vector magnitude techniques. In Proceedings of wireless communications conference (pp. 89–94). IEEE.
Hossain, E., Rasti, M., Tabassum, H., & Abdelnasser, A. (2014). Evolution toward 5G multi-tier cellular wireless networks: An interference management perspective. IEEE Wireless Communications, 21(3), 118–127.
Koudelka, P., Latal, J., Siska, P., Vitasek, J., Liner, A., Martinek, R., et al. (2014). Indoor visible light communication: modeling and analysis of multi-state modulation. In SPIE optical engineering+applications (pp. 92241I–92241I). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Koudelka, P., Soltys, P., Martinek, R., Latal, J., Siska, P., Kepak, S., et al. (2014). Utilization of m-qam modulation during optical wireless car to car communication. In 2014 Optoelectronics and communication conference and Australian Conference on optical fibre technology (pp. 452–454). IEEE.
Lee, J., & Kao, H. A. (2015). A cyber-physical systems architecture for industry 4.0-based manufacturing systems. Manufacturing Letters, 3, 18–23.
Lu, J., Letaief, K. B., Chuang, J. C. I., & Liou, M. L. (1999). M-psk and m-qam ber computation using signal-space concepts. IEEE Transactions on communications, 47(2), 181–184.
Luby, M., Vicisano, L., Gemmell, J., Rizzo, L., Handley, M., & Crowcroft, J. (2002). The use of forward error correction (FEC) in reliable multicast. Technical report
Marriwala, N., Sahu, O., & Vohra, A. (2013). 8-QAM software defined radio based approach for channel encoding and decoding using forward error correction. Wireless Personal Communications, 72(4), 2957–2969.
Martinek, R., Vanus, J., Bilik, P., Al-Wohaishi, M., & Zidek, J. (2016). The implementation of equalization algorithms for real transmission channels. In International instrumentation and measurement technology conference (I2MTC), Taipei, Taiwan.
Martinek, R., & Zidek, J. (2013). The implementation of channel coding into the digital transmission chain consisting of VSG PXI-5670-VSA PXI-5661. Przeglad Elektrotchniczny, 89(7), 64–68.
Martinek, R., & Zidek, J. (2014). The real implementation of anfis channel equalizer on the system of software-defined radio. IETE Journal of Research, 60(2), 183–193.
Martinek, R., Zidek, J., & Tomala, K. (2013). BER measurement in software defined radio systems. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 89(2b), 205–210.
Martinek, R., et al. (2016). Modelling of wireless fading channels with RF impairments using virtual instruments. In IEEE wireless and microwave technology conference, Clearwater Beach, Florida.
Medbo, J., Börner, K., Haneda, K., Hovinen, V., Imai, T., Järvelainen, J., et al. (2014). Channel modelling for the fifth generation mobile communications. In 2014 8th European conference on antennas and propagation (EuCAP) (pp. 219–223). IEEE.
Radek, M., & Zidek, J. (2013). The implementation of channel coding into the digital transmission chain consisting of VSG PXI-5670-VSA PXI-5661. Przeglad Elektrotchniczny, 89(7), 64–68.
Soldani, D., Barani, B., Tafazolli, R., Manzalini, A., & Chih-Lin, I. (2015). Software defined 5G networks for anything as a service [guest editorial]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(9), 72–73.
Tang, X., Alouini, M. S., & Goldsmith, A. J. (1999). Effect of channel estimation error on M-QAM BER performance in rayleigh fading. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 47(12), 1856–1864.
Wang, C. X., Haider, F., Gao, X., You, X. H., Yang, Y., Yuan, D., et al. (2014). Cellular architecture and key technologies for 5G wireless communication networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(2), 122–130.
Wei, H., Huang, Y., Zhang, T., & Li, L. (2016). An universal MMSE channel estimator for OFDM receiver. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-016-3643-8.
Wortmann, F., Flüchter, K., et al. (2015). Internet of things. Business & Information Systems Engineering, 57(3), 221–224.
Xia, F., Yang, L. T., Wang, L., & Vinel, A. (2012). Internet of things. International Journal of Communication Systems, 25(9), 1101.
Yang, M., Li, Y., Jin, D., Zeng, L., Wu, X., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Software-defined and virtualized future mobile and wireless networks: A survey. Mobile Networks and Applications, 20(1), 4–18.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the project SP2017/158, Development of algorithms and systems for control, measurement and safety applications III of Student Grant System, VSB-TU Ostrava and by the project SP2017/128 of the Student Grant System, VSB-TU Ostrava, Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinek, R., Konecny, J., Koudelka, P. et al. Adaptive Optimization of Control Parameters for Feed-Forward Software Defined Equalization. Wireless Pers Commun 95, 4001–4011 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4036-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4036-3