Abstract
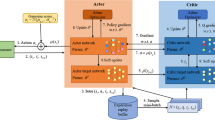
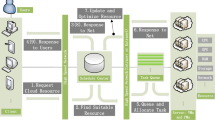
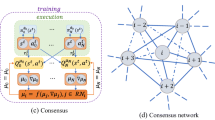
As a promising computing paradigm, mobile edge computing (MEC) can assist Internet of Things (IoT) devices in processing computation-intensive tasks. However, because of the different locations, limited resources, and dynamic loads of IoT devices and edge servers, designing a distributed computation offloading approach for the IoT system is challenging. In this paper, considering the delay-sensitive tasks and the binary offloading mechanism, we focus on designing a collaborative offloading scheme between different IoT devices. In order to reduce the overall consumed energy of IoT devices based on guaranteeing the delay constraints of tasks, we propose a distributed offloading algorithm by utilizing the value-based multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MADRL) method. Specifically, with the individual networks deployed locally and the collaborative network deployed at the edge, IoT devices can learn their offloading policies from expericence data, and then determine their offloading decisions independently. Compared with several baseline algorithms, the proposed algorithm can better achieve our optimiaztion goal, which is demonstrated by the experiment results.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The corresponding author will provide the datasets of this work on reasonable request.
References
Ren, J., Hou, T., Wang, H., Tian, H., Wei, H., Zheng, H., & Zhang, X. (2021). Collaborative task offloading and resource scheduling framework for heterogeneous edge computing. Wireless Networks. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02768-y
Yang, L., Zou, Y., Xu, M., Xu, Y., Yu, D., & Cheng, X. (2022). Distributed Consensus for blockchains in Internet-of-Things networks. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 27(5), 817–831.
Xu, X., Gu, J., Yan, H., Liu, W., Qi, L., & Zhou, X. (2023). Reputation-aware supplier assessment for blockchain-enabled supply chain in industry 4.0. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 19(4), 5485–5494.
Qi, L., Yang, Y., Zhou, X., Rafique, W., & Ma, J. (2022). Fast anomaly identification based on multi-aspect data streams for intelligent intrusion detection toward secure industry 4.0. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18(9), 6503–6511.
Wu, S., Shen, S., Xu, X., Chen, Y., Zhou, X., Liu, D., Xue, X., & Qi, L. (2022). Popularity-aware and diverse web APIs recommendation based on correlation graph. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 10(2), 771–782.
Qi, L., Lin, W., Zhang, X., Dou, W., Xu, X., & Chen, J. (2023). A correlation graph based approach for personalized and compatible web APIs recommendation in mobile APP development. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 35(6), 5444–5457.
Yang, C., Xu, X., Zhou, X., & Qi, L. (2022). Deep Q-network driven task offloading for efficient multimedia data analysis in edge computing. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing Communications and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1145/3548687
Xu, M., Zhao, F., Zou, Y., Liu, C., Cheng, X., & Dressler, F. (2022). BLOWN: a blockchain protocol for single-hop wireless networks under adversarial SINR. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2022.3162117
Yu, D., Zou, Z., Chen, S., Tao, Y., Tian, B., Lv, W., & Cheng, X. (2021). Decentralized parallel SGD with privacy preservation in vehicular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(6), 5211–5220.
Jia, Y., Liu, B., Dou, W., Xu, X., Zhou, X., Qi, L., & Yan, Z. (2022). CroApp: A CNN-based resource optimization approach in edge computing environment. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18(9), 6300–6307.
He, Q., Tan, S., Chen, F., Xu, X., Qi, L., Hei, X., Jin, H., & Yang, Y. (2023). EDIndex: Enabling fast data queries in edge storage systems. In: Proceedings of the 46th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.
Xu, X., Fang, Z., Qi, L., Zhang, X., He, Q., & Zhou, X. (2021). TripRes: Traffic flow prediction driven resource reservation for multimedia IoV with edge computing. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing Communications and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1145/3401979
Guo, F., Zhang, H., Ji, H., Li, X., & Leung, V. C. (2018). An efficient computation offloading management scheme in the densely deployed small cell networks with mobile edge computing. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 26(6), 2651–2664.
Xue, J., & An, Y. (2021). Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-task multi-server NOMA-MEC networks. IEEE Access, 9, 16152–16163.
Wang, J., Feng, D., Zhang, S., Liu, A., & Xia, X. G. (2021). Joint computation offloading and resource allocation for MEC-enabled IoT systems with imperfect CSI. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(5), 3462–3475.
Kovacevic, I., Harjula, E., Glisic, S., Lorenzo, B., & Ylianttila, M. (2021). Cloud and edge computation offloading for latency limited services. IEEE Access, 9, 55764–55776.
Chen, X., Jiao, L., Li, W., & Fu, X. (2016). Efficient multi-user computation offloading for mobile-edge cloud computing. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 24(5), 2795–2808.
Chen, Z., & Wang, X. (2020). Decentralized computation offloading for multi-user mobile edge computing: A deep reinforcement learning approach. Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-020-01801-6
Tang, M., & Wong, V. W. S. (2022). Deep reinforcement learning for task offloading in mobile edge computing systems. IEEE transactions on mobile computing, 21(6), 1985–1997.
Gan, Z., Lin, R., & Zou, H. (2022). A multi-agent deep reinforcement learning approach for computation offloading in 5G mobile edge Computing. In: Proceedings of the 22nd IEEE international symposium on cluster, cloud and internet computing (pp. 645–648). https://doi.org/10.1109/CCGrid54584.2022.00074
Huang, X., Leng, S., Maharjan, S., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for computation offloading and interference coordination in small cell networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(9), 9282–9293.
Cao, Z., Zhou, P., Li, R., Huang, S., & Wu, D. (2020). Multiagent deep reinforcement learning for joint multichannel access and task offloading of mobile-edge computing in industry 4.0. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(7), 6201–6213.
Nguyen, D. C., Pathirana, P. N., Ding, M., & Seneviratne, A. (2021). Deep reinforcement learning for collaborative offloading in heterogeneous edge networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 21st international symposium on cluster, cloud and internet computing, (pp. 297–303). https://doi.org/10.1109/CCGrid51090.2021.00039
Xiao, Y., Song, Y., & Liu, J. (2022). Towards energy efficient resource allocation: when green mobile edge computing meets multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on communications (pp. 4056–4061). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICC45855.2022.9838659
Rashid, T., Samvelyan, M., De Witt, C. S., Farquhar, G., Foerster, J., & Whiteson, S. (2018). Qmix: Monotonic value function factorisation for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.11485
Oliehoek, F. A., & Amato, C. (2016). A concise introduction to decentralized POMDPs. Springer.
Sunehag, P., Lever, G., Gruslys, A., Czarnecki, W.M., Zambaldi, V., Jaderberg, M., Lanctot, M., Sonnerat, N., Leibo, J.Z., Tuyls, K., & Graepel, T. (2017). Value-decomposition networks for cooperative multi-agent learning based on team reward. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems (pp. 2085–2087)
Hasselt, H. V., Guez, A., Silver, D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1509.06461
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61702264, 62076130), the Open Research Project of State Key Laboratory of Novel Software Technology (Nanjing University, No. KFKT2022B28), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2020YFB1805503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Meng, S., Shang, J. et al. Value-based multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for collaborative computation offloading in internet of things networks. Wireless Netw (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03553-9
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03553-9