Abstract
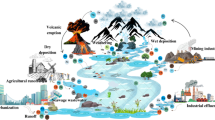
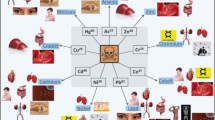
The presence of harmful heavy metals (HMs) in the aquatic environment can damage the environment and threaten human health. Traditional remediation techniques can have secondary impacts. Thus, more sustainable approaches must be developed. Microalgae have biological properties (such as high photosynthetic efficiency and growth), which are of great advantage in the HMs removal. In this study, the effect of various concentrations (2×, 4×, and 6×) of copper (Cu), cobalt (Co), and zinc (Zn) on microalgae (C. sorokiniana GEEL-01, P. kessleri GEEL-02, D. asymmetricus GEEL-05) was investigated. The microalgal growth kinetics, HMs removal, total nitrogen (TN), total phosphor (TP), and fatty acids (FAs) compositions were analyzed. The highest growth of 1.474 OD680nm and 1.348 OD680nm was obtained at 2× and 4×, respectively, for P. kessleri GEEL-02. P. kessleri GEEL-02 showed high removal efficiency of Cu, Co, and Zn (38.92–55.44%), (36.27–68.38%), and (32.94–51.71%), respectively. Fatty acids (FAs) analysis showed that saturated FAs in C. sorokiniana GEEL-01 and P. kessleri GEEL-02 increased at 2× and 4× concentrations while decreasing at 6×. For P. kessleri GEEL-02, the properties of biodiesel including the degree of unsaturation (UD) and cetane value (CN) increased at 2×, 4×, and 6× as compared to the control. Thus, this study demonstrated that the three microalgae (particularly P. kessleri GEEL-02) are more suitable for nutrient and HMs removal coupled with biomass/biodiesel production.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data obtained in this study presented in the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- BBM:
-
Bold basal medium
- CFPP:
-
Cold filter plugging point
- CN:
-
Cetane number
- Cu:
-
Copper
- Co:
-
Cobalt
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- FAs:
-
Fatty acids
- Fe:
-
Iron
- H+ :
-
Proton
- HMs:
-
Heavy metals
- IV:
-
Iodine value
- LCSF:
-
Long-chain saturation factor
- Mn:
-
Manganese
- Mo:
-
Molybdenum
- MUFA:
-
Monounsaturated fatty acids
- Ni:
-
Nickel
- NO× :
-
Nitrogen oxides
- OD:
-
Optical density
- OH− :
-
Hydroxyl ion
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SO× :
-
Sulphur oxides
- SV:
-
Saponification value
- TN:
-
Total nitrogen
- TP:
-
Total phosphorus
- UD:
-
Unsaturation degree
- Zn:
-
Zinc
- 2×:
-
Two times
- 4×:
-
Four times
- 6×:
-
Six times
References
Abinandan S, Subashchandrabose SR, Panneerselvan L et al (2019) Potential of acid-tolerant microalgae, Desmodesmus sp. MAS1 and Heterochlorella sp. MAS3, in heavy metal removal and biodiesel production at acidic pH. Bioresour Technol 278:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.053
Abou-Shanab RAI, Matter IA, Kim S-N et al (2011) Characterization and identification of lipid-producing microalgae species isolated from a freshwater lake. Biomass Bioenergy 35:3079–3085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.04.021
Ajayan KV, Harilal CC, Selvaraju M (2018) Phycoremediation resultant lipid production and antioxidant changes in green microalgae Chlorella Sp. Int J Phytoremed 20:1144–1151. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2017.1413333
Ajayan KV, Selvaraju M, Unnikannan P, Sruthi P (2015) Phycoremediation of tannery wastewater using microalgae Scenedesmus species. Int J Phytoremed 17:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2014.989313
Altun Ş (2014) Effect of the degree of unsaturation of biodiesel fuels on the exhaust emissions of a diesel power generator. Fuel (Lond) 117:450–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.028
Arif M, Wang L, Salama E-S et al (2020) Microalgae isolation for nutrient removal assessment and biodiesel production. Bioenergy Res 13:1247–1259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-020-10136-5
Arunakumara KKIU, Zhang X (2008) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and toxicity with special reference to microalgae. J Ocean Univ China 7:60–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0060-y
Ashour M, Elshobary ME, El-Shenody R et al (2019) Evaluation of a native oleaginous marine microalga Nannochloropsis oceanica for dual use in biodiesel production and aquaculture feed. Biomass Bioenergy 120:439–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.12.009
Barabas I, Todoru I-A (2011) Biodiesel Quality, Standards and Properties. In: Biodiesel- Quality, Emissions and By-Products. InTech
Bharti RK, Dhar DW, Prasanna R, Saxena AK (2018) Assessment of biomass and lipid productivity and biodiesel quality of an indigenous microalga Chlorella sorokiniana MIC-G5. Int J Green Energy 15:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2017.1351368
Blanco-Vieites M, Suárez-Montes D, Delgado F et al (2022) Removal of heavy metals and hydrocarbons by microalgae from wastewater in the steel industry. Algal Res 64:102700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2022.102700
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1139/o59-099
Cameron H, Mata MT, Riquelme C (2018) The effect of heavy metals on the viability of Tetraselmis marina AC16-MESO and an evaluation of the potential use of this microalga in bioremediation. PeerJ 6:e5295. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5295
Chen G, Shan R, Li S, Shi J (2015) A biomimetic silicification approach to synthesize CaO–SiO 2 catalyst for the transesterification of palm oil into biodiesel. Fuel (Lond) 153:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.02.109
Chen M, Tang H, Ma H et al (2011) Effect of nutrients on growth and lipid accumulation in the green algae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Bioresour Technol 102:1649–1655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.062
Cheng P, Wang J, Liu T (2015) Effect of cobalt enrichment on growth and hydrocarbon accumulation of Botryococcus braunii with immobilized biofilm attached cultivation. Bioresour Technol 177:204–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.088
Cheng P, Wang Y, Liu T, Liu D (2017) Biofilm attached cultivation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa is a developed system for swine wastewater treatment and lipid production. Front Plant Sci 8:1594. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01594
Chi Z, O’Fallon JV, Chen S (2011) Bicarbonate produced from carbon capture for algae culture. Trends Biotechnol 29:537–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.06.006
Del Rosario M-M, Correa-Murrieta MA, Villegas-Peralta Y et al (2019) Uptake of copper from acid mine drainage by the microalgae Nannochloropsis oculata. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:6311–6318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3963-1
Dou X, Lu X-H, Lu M-Z et al (2013) The effects of trace elements on the lipid productivity and fatty acid composition of Nannochloropis oculata. J Renew Energy 2013:671545. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/671545
Elkomy RG, Rizk OE (2019) Bioremoval of Copper by Marine Blue Green Algae Phormodium formosum and Oscillatoria simplicissima. Indian J Sci Technol 12:1–7. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2019/v12i1/134088
El-Sheekh MM, El-Naggar AH, Osman MEH, El-Mazaly E (2003) Effect of cobalt on growth, pigments and the photosynthetic electron transport in Monoraphidium minutum and Nitzchia perminuta. Braz J Plant Physiol 15:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1677-04202003000300005
Expósito N, Kumar V, Sierra J et al (2017) Performance of Raphidocelis subcapitata exposed to heavy metal mixtures. Sci Total Environ 601–602:865–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.177
Fakhry EM, El Maghraby DM (2015) Lipid accumulation in response to nitrogen limitation and variation of temperature in Nannochloropsis salina. Bot Stud 56:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-015-0085-7
Fraile A, Penche S, González F et al (2005) Biosorption of copper, zinc, cadmium and nickel by Chlorella vulgaris. Chem Ecol 21:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540512331334933
Francisco ÉC, Neves DB, Jacob-Lopes E, Franco TT (2010) Microalgae as feedstock for biodiesel production: Carbon dioxide sequestration, lipid production and biofuel quality. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2338
Franklin NM, Adams MS, Stauber JL, Lim RP (2001) Development of an improved rapid enzyme inhibition bioassay with marine and freshwater microalgae using flow cytometry. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:469–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010199
Gebara RC, de Alho LOG, da Mansano AS et al (2023) Single and combined effects of Zn and Al on photosystem II of the green microalgae Raphidocelis subcapitata assessed by pulse-amplitude modulated (PAM) fluorometry. Aquat Toxicol 254:106369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2022.106369
Gomes PIA, Asaeda T (2009) Phycoremediation of chromium (VI) by Nitella and impact of calcium encrustation. J Hazard Mater 166:1332–1338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.055
Gomes PIA, Asaeda T (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals by calcifying macro-algae (Nitella pseudoflabellata): implications of redox insensitive end products. Chemosphere 92:1328–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.05.043
Gopinath A, Puhan S, Nagarajan G (2009) Theoretical modeling of iodine value and saponification value of biodiesel fuels from their fatty acid composition. Renew Energy 34:1806–1811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2008.11.023
Guschina IA, Harwood JL (2006) Lead and copper effects on lipid metabolism in cultured lichen photobionts with different phosphorus status. Phytochemistry 67:1731–1739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.01.023
Hamed SM, El Shimi HI, van Dijk JR et al (2022) A novel integrated system for heavy metals removal and biodiesel production via green microalgae: a techno-economic feasibility assessment. J Environ Chem Eng 10:108804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108804
Hamed SM, Selim S, Klöck G, AbdElgawad H (2017) Sensitivity of two green microalgae to copper stress: Growth, oxidative and antioxidants analyses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.048
Hanifzadeh M, Garcia EC, Viamajala S (2018) Production of lipid and carbohydrate from microalgae without compromising biomass productivities: role of Ca and Mg. Renew Energy 127:989–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.012
He Q, Yu G, Wang W et al (2017) Once-through CO2 absorption for simultaneous biogas upgrading and fertilizer production. Fuel Process Technol 166:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.05.027
Hoang AT, Sirohi R, Pandey A et al (2022) Biofuel production from microalgae: challenges and chances. Phytochem Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-022-09819-y
Hoekman SK, Broch A, Robbins C et al (2012) Review of biodiesel composition, properties, and specifications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:143–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.07.143
Hu S, Hu J, Sun Y et al (2021) Simultaneous heavy metal removal and sludge deep dewatering with Fe(II) assisted electrooxidation technology. J Hazard Mater 405:124072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124072
Islam MA, Ayoko GA, Brown R et al (2013) Influence of fatty acid structure on fuel properties of algae derived biodiesel. Procedia Eng 56:591–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.03.164
Ji F, Liu Y, Hao R et al (2014) Biomass production and nutrients removal by a new microalgae strain Desmodesmus sp. in anaerobic digestion wastewater. Bioresour Technol 161:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.034
Kamyab H, Chelliapan S, Lee CT et al (2019) Microalgae cultivation using various sources of organic substrate for high lipid content. Green Energy Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99867-1_154
Kamyab H, Chelliapan S, Shahbazian-Yassar R et al (1989) 2017) Evaluation of lipid content in microalgae biomass using palm oil mill effluent (pome. JOM 69:1361–1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2428-1
Kamyab H, Din MFM, Hosseini SE et al (2016) Optimum lipid production using agro-industrial wastewater treated microalgae as biofuel substrate. Clean Technol Environ Policy 18:2513–2523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1212-1
Kumar D, Santhanam P, Ananth S et al (2014) Effect of different dosages of zinc on the growth and biomass in five marine microalgae. Int J Fish Aquac 6:1–8. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJFA2013.0393
Kumar S, Dahms K, Won H-U et al (2015) Microalgae—a promising tool for heavy metal remediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:329–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.019
Lee Y-C, Chang S-P (2011) The biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by Spirogyra and Cladophora filamentous macroalgae. Bioresour Technol 102:5297–5304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.103
Lei Y-J, Tian Y, Zhang J et al (2018) Microalgae cultivation and nutrients removal from sewage sludge after ozonizing in algal-bacteria system. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.096
Leong YK, Chang J-S (2020) Bioremediation of heavy metals using microalgae: recent advances and mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 303:122886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122886
Lepage G, Roy CC (1984) Improved recovery of fatty acid through direct transesterification without prior extraction or purification. J Lipid Res 25:1391–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2275(20)34457-6
Liu Y, Zhan J-J, Hong Y (2017) Effects of metal ions on the cultivation of an oleaginous microalga Chlorella sp. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:26594–26604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0258-x
Lu H, Feng Y, Wu Y et al (2016) Phototrophic periphyton techniques combine phosphorous removal and recovery for sustainable salt-soil zone. Sci Total Environ 568:838–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.010
Lu H, Xie R, Almoallim SH et al (2023) Utilization of the Nannochloropsis microalgae biochar prepared via microwave assisted pyrolysis on the mixed biomass fuel pellets. Environ Res 231:116078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116078
Monteiro CM, Fonseca SC, Castro PML, Malcata FX (2011) Toxicity of cadmium and zinc on two microalgae, Scenedesmus obliquus and Desmodesmus pleiomorphus, from Northern Portugal. J Appl Phycol 23:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9542-6
Moreno-Garcia L, Adjallé K, Barnabé S, Raghavan GSV (2017) Microalgae biomass production for a biorefinery system: Recent advances and the way towards sustainability. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:493–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.024
Mund NK, Liu Y, Chen S (2022) Advances in metabolic engineering of cyanobacteria for production of biofuels. Fuel (Lond) 322:124117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124117
Ndayisenga F, Yu Z, Yu Y et al (2018) Bioelectricity generation using microalgal biomass as electron donor in a bio-anode microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 270:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.052
Pandey A, Srivastava S, Kumar S (2019) Isolation, screening and comprehensive characterization of candidate microalgae for biofuel feedstock production and dairy effluent treatment: a sustainable approach. Bioresour Technol 293:121998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121998
Patel A, Arora N, Mehtani J et al (2017) Assessment of fuel properties on the basis of fatty acid profiles of oleaginous yeast for potential biodiesel production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 77:604–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.016
Patel A, Matsakas L, Hrůzová K et al (2019) Biosynthesis of nutraceutical fatty acids by the oleaginous marine microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum utilizing hydrolysates from organosolv-pretreated birch and spruce biomass. Mar Drugs 17:119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020119
Qie F, Zhu J, Rong J, Zong B (2019) Biological removal of nitrogen oxides by microalgae, a promising strategy from nitrogen oxides to protein production. Bioresour Technol 292:122037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122037
Rai PK, Mallick N, Rai LC (1993) Physiological and biochemical studies on an acid-tolerant Chlorella vulgaris under copper stress. J Gen Appl Microbiol 39:529–540. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.39.529
Ramírez-Verduzco LF, Rodríguez-Rodríguez JE, del Jaramillo-Jacob AR (2012) Predicting cetane number, kinematic viscosity, density and higher heating value of biodiesel from its fatty acid methyl ester composition. Fuel (London) 91:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.06.070
Renu AM, Singh K (2017) Heavy metal removal from wastewater using various adsorbents: a review. J Water Reuse Desalination 7:387–419. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2016.104
Rodrigues MS, Ferreira LS, de Carvalho JCM et al (2012) Metal biosorption onto dry biomass of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis and Chlorella vulgaris: multi-metal systems. J Hazard Mater 217–218:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.03.022
Rugnini L, Costa G, Congestri R et al (2018) Phosphorus and metal removal combined with lipid production by the green microalga Desmodesmus sp.: an integrated approach. Plant Physiol Biochem 125:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.01.032
Rugnini L, Costa G, Congestri R, Bruno L (2017) Testing of two different strains of green microalgae for Cu and Ni removal from aqueous media. Sci Total Environ 601–602:959–967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.222
Sajjadi B, Chen W-Y, Raman AAA, Ibrahim S (2018) Microalgae lipid and biomass for biofuel production: a comprehensive review on lipid enhancement strategies and their effects on fatty acid composition. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 97:200–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.07.050
Salama E-S, Roh H-S, Dev S et al (2019) Algae as a green technology for heavy metals removal from various wastewater. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2648-3
Santos FM, Mazur LP, Mayer DA et al (2019) Inhibition effect of zinc, cadmium, and nickel ions in microalgal growth and nutrient uptake from water: an experimental approach. Chem Eng J 366:358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.080
Serrà A, Artal R, García-Amorós J et al (2020) Circular zero-residue process using microalgae for efficient water decontamination, biofuel production, and carbon dioxide fixation. Chem Eng J 388:124278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124278
Shen X, Dai M, Yang J et al (2022) A critical review on the phytoremediation of heavy metals from environment: performance and challenges. Chemosphere 291:132979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132979
Shrestha R, Ban S, Devkota S et al (2021) Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105688
Siripornadulsil S, Traina S, Verma DPS, Sayre RT (2002) Molecular mechanisms of proline-mediated tolerance to toxic heavy metals in transgenic microalgae. Plant Cell 14:2837–2847. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.004853
Sultana N, Hossain SMZ, Mohammed ME et al (2020) Experimental study and parameters optimization of microalgae based heavy metals removal process using a hybrid response surface methodology-crow search algorithm. Sci Rep 10:15068. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72236-8
Talebi AF, Mohtashami SK, Tabatabaei M et al (2013) Fatty acids profiling: a selective criterion for screening microalgae strains for biodiesel production. Algal Res 2:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2013.04.003
Tripathi R, Gupta A, Thakur IS (2019) An integrated approach for phycoremediation of wastewater and sustainable biodiesel production by green microalgae, Scenedesmus sp. ISTGA1. Renew Energy 135:617–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.12.056
Umamaheswari J, Shanthakumar S (2016) Efficacy of microalgae for industrial wastewater treatment: a review on operating conditions, treatment efficiency and biomass productivity. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 15:265–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-016-9397-7
Wang L, Wang L, Manzi HP et al (2022) Isolation and screening of Tetradesmus dimorphus and Desmodesmus asymmetricus from natural habitats in Northwestern China for clean fuel production and N, P removal. Biomass Convers Biorefin 12:1503–1512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01034-z
Yang I-S, Salama E-S, Kim J-O et al (2016) Cultivation and harvesting of microalgae in photobioreactor for biodiesel production and simultaneous nutrient removal. Energy Convers Manag 117:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.03.017
Yu G, Wang X, Liu J et al (2021) Applications of nanomaterials for heavy metal removal from water and soil: a review. Sustainability 13:713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020713
Yu Q, Liu T-J, Zeng Y-N et al (2023) Efficient lipid synthesis of Chlorella pyrenoidosa promoted under heavy metals from electric arc furnace slag. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137648
Zhang H, Zhang G, Wen X et al (2014) Effects of pH on the photosynthesis, growth and lipid production of Chlorella sp. XQ-200419. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 38:1084–1091. https://doi.org/10.7541/2014.159
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Najran University for funding this work, under the Research Groups Funding program grant code (NU/RG/SERC/12/23).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZS: methodology, visualization, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, and writing-original draft. MJ: conceptualization and methodology, funding acquisition, and project administration. SAA: conceptualization and methodology. FAH: conceptualization and methodology. AAA: visualization, review. LW: software, investigation, and formal analysis. NT: methodology, conceptualization, visualization, review and editing, and supervision. E-SS: conceptualization, supervision, resources, data curation, validation, writing-review and editing, funding acquisition, and project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Article collection on SDG7 Affordable and Clean.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Z., Jalalah, M., Alsareii, S.A. et al. Supplementation of micro-nutrients to growth media of microalgae-induced biomass and fatty acids composition for clean energy generation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03815-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03815-w