Abstract
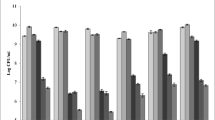
The present study aimed at characterizing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) strains isolated from traditional sourdoughs collected in different regions of Morocco. Isolated strains were firstly identified using Gram staining and catalase reaction test. Presumptive LAB strains were then checked for various phenotypical properties including growth at 45 °C, resistance to NaCl, enzyme production, acidification capacity, diacetyl and exopolysaccharide (EPS) production, and antifungal activity. Finally, selected LAB strains were identified using 16S rDNA sequencing. Results showed that 32.1% of the isolates were thermophilic (45 °C) and 83.9% were resistant to NaCl (6.5%). Moreover, 51.7 and 37.5% were able to produce diacetyl and EPS, respectively. Regarding enzyme production, 55.3 and 7.1% of the isolates showed lipolytic and proteolytic activities, respectively. Low pH values (3.37–3.76) were obtained after 24 h of incubation of LAB strains in de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) broth. Antifungal activity test against Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus niger and Penicillium spp. showed an inhibition rate up to 50%. Bacterial DNA sequencing showed that LAB isolates belong to seven species, chiefly Levilactobacillus brevis, Lentilactobacillus parabuchneri, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Pediococcus pentosaceus, Enterococcus hirae, Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum, and Companilactobacillus paralimentarius. These findings, for the first time in Moroccan sourdoughs, indicate that the isolated LAB strains have good multifunctional properties and could be suitable as good starters for sourdough bread production under controlled conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare data transparency.
References
Abouloifa H, Gaamouche S, Rokni Y et al (2021) Antifungal activity of probiotic Lactobacillus strains isolated from natural fermented green olives and their application as food bio-preservative. Biol Control 152:104450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2020.104450
Abouloifa H, Rokni Y, Bellaouchi R et al (2020) Characterization of probiotic properties of antifungal Lactobacillus strains isolated from traditional fermenting green olives. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 12:683–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09543-8
Badji T, Durand N, Bendali F et al (2023) In vitro detoxification of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A by lactic acid bacteria isolated from Algerian fermented foods. Biol Control 179:105181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2023.105181
Bartkiene E, Lele V, Sakiene V et al (2019) Improvement of the antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria in combination with berries/fruits and dairy industry by-products. J Sci Food Agric 99:3992–4002. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9625
Bartkiene E, Lele V, Ruzauskas M et al (2020) Lactic acid bacteria isolation from spontaneous sourdough and their characterization including antimicrobial and antifungal properties evaluation. Microorganisms 8:64. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010064
Ben Salah-Abbès J, Mannai M, Belgacem H et al (2021) Efficacy of lactic acid bacteria supplementation against Fusarium graminearum growth in vitro and inhibition of zearalenone causing inflammation and oxidative stress in vivo. Toxicon 202:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2021.09.010
Bennani S, Mchiouer K, Rokni Y et al (2017) Characterisation and identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Moroccan raw cow’s milk. J Mater Environ Sci 8:4934–4944
Bom S, Jagan L, Rao M et al (2018) Isolation of lactic acid bacteria starters from jeung - pyun for sourdough fermentation. Food Sci Biotechnol 27:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0274-0
Boraam F, Faid M, Larpent J et al (1993) Lactic acid bacteria and yeasts associated with traditional Moroccan sour-dough bread fermentation. Sci Aliment 13:501–509
Boyaci Gunduz CP, Agirman B, Gaglio R et al (2022) Evaluation of the variations in chemical and microbiological properties of the sourdoughs produced with selected lactic acid bacteria strains during fermentation. Food Chem X 14:100357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100357
Brandt MJ (2019) Industrial production of sourdoughs for the baking branch: an overview. Int J Food Microbiol 302:3–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.09.008
Çakır E, Arıcı M, Durak MZ (2020) Biodiversity and techno-functional properties of lactic acid bacteria in fermented hull-less barley sourdough. J Biosci Bioeng 130:450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2020.05.002
Carbonetto B, Nidelet T, Guezenec S et al (2020) Interactions between kazachstania humilis yeast species and lactic acid bacteria in sourdough. Microorganisms 8:240. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020240
Chaoui A, Faid M, Belahsen R (2006) Making bread with sourdough improves iron bioavailability from reconstituted fortified wheat flour in mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol 20:217–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2006.04.002
Cizeikiene D, Jagelaviciute J, Stankevicius M et al (2020) Thermophilic lactic acid bacteria affect the characteristics of sourdough and whole-grain wheat bread. Food Biosci 38:100791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100791
Damiani P, Gobbetti M, Cossignani L et al (1996) The sourdough microflora. characterization of hetero- and homofermentative lactic acid bacteria, yeasts and their interactions on the basis of the volatile compounds produced. LWT - Food Sci Technol 29:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1006/fstl.1996.0009
Faid M, Boraam F, Achbab A et al (1993) Yeast-lactic acid bacteria interactions in Moroccan Sour-dough Bread Fermentation. LWT - Food Sci Technol 26:443–446. https://doi.org/10.1006/fstl.1993.1087
Faid M, Boraam F, Zyani I et al (1994) Characterization of sourdough bread ferments made in the laboratory by traditional methods. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 198:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01193176
Fekri A, Torbati M, Yari Khosrowshahi A et al (2020) Functional effects of phytate-degrading, probiotic lactic acid bacteria and yeast strains isolated from iranian traditional sourdough on the technological and nutritional properties of whole wheat bread. Food Chem 306:125620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125620
Felicia C (2015) The technological evaluation of sourdoughs prepared in different conditions. Manag Sustain Dev 7:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1515/msd-2015-0019
Fraberger V, Ammer C, Domig KJ (2020) Functional properties and sustainability improvement of sourdough bread by lactic acid bacteria. Microorganisms 8:1895
Fujimoto A, Ito K, Narushima N et al (2019) Identification of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts, and characterization of food components of sourdoughs used in Japanese bakeries. J Biosci Bioeng 127:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.10.014
Gänzle MG, Zheng J (2019) Lifestyles of sourdough lactobacilli: do they matter for microbial ecology and bread quality? Int J Food Microbiol 302:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.08.019
Gobbetti M, Corsetti A, Rossi J (1995) Interaction between lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in sour-dough using a rheofermentometer. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:625–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361004
Hadaegh H, Ardabili SMS, Ebrahimi MT et al (2019) Effect of using Lactobacillus Brevis IBRC- M10790 and Baker’s yeast on Phytate degradation of sourdough and Barbari bread. J Food Biosc Technol 9:11–18
Ho VTT, Fleet GH, Zhao J (2018) Unravelling the contribution of lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria to cocoa fermentation using inoculated organisms. Int J Food Microbiol 279:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.04.040
Ismaili Alaoui M, Hamama A, Saidi B et al (2017) Chemical Composition, microbial profile and identification of lactic acid bacteria of moroccan fermented camel milk “Lfrik.” Curr Res Nutr Food Sci 5:383–390. https://doi.org/10.12944/CRNFSJ.5.3.24
İspirli H, Özmen D, Yılmaz MT et al (2020) Impact of glucan type exopolysaccharide (EPS) production on technological characteristics of sourdough bread. Food Control 107:106812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.106812
Jin J, Nguyen TTH, Humayun S et al (2021) Characteristics of sourdough bread fermented with Pediococcus pentosaceus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its bio-preservative effect against Aspergillus flavus. Food Chem 345:128787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128787
Kaya Y, Erten T, Vurmaz M et al (2022) Comparison of the probiotic characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolated from sourdough and infant feces. Food Biosci 47:101722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101722
Khedid K, Faid M, Mokhtari A et al (2009) Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the one humped camel milk produced in Morocco. Microbiol Res 164:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2006.10.008
Marco I, Silva C, Moraes M et al (2022) A systematic review of drying methods and their impact on technological characteristics of sourdough type III. Biotechnol Res Innov 6:1–17. https://doi.org/10.4322/biori.202203
Matevosyan LA, Bazukyan IL, Trchounian AH (2020) Antifungal activity of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their associations: The effects of Ca and Mg divalent cations. Curr Microbiol 77:959–966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01897-5
Mota-Gutierrez J, Franciosa I, Ruggirello M, Dolci P (2021) Technological, functional and safety properties of lactobacilli isolates from soft wheat sourdough and their potential use as antimould cultures. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37:146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03114-2
Moujabbir S, Aboukhalaf A, Kalili A et al (2023) Sourdoughs used in the preparation of traditional bread in the province of figuig in eastern Morocco. Int J Food Stud 12:71–83. https://doi.org/10.7455/ijfs/12.1.2023.a5
Muhialdin BJ, Hassan Z, Saari N (2018) In vitro antifungal activity of lactic acid bacteria low molecular peptides against spoilage fungi of bakery products. Ann Microbiol 68:557–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1363-x
Nionelli L, Montemurro M, Pontonio E et al (2018) Pro-technological and functional characterization of lactic acid bacteria to be used as starters for hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) sourdough fermentation and wheat bread fortification. Int J Food Microbiol 279:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.04.036
Novotni D, Gänzle M, Rocha JM (2021) Composition and activity of microbiota in sourdough and their effect on bread quality and safety. In: Galanakis CM (ed) Trends in wheat and bread making. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 129–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821048-2.00005-2
Olojede AO, Sanni AI, Banwo K (2022) Improvement of texture nutritional qualities and consumers perceptions of sorghum-based sourdough bread made with Pediococcus pentosaceus and Weissella confusa Strains. Fermentation 8:32. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8010032
Păcularu-Burada B, Georgescu LA, Vasile MA et al (2020) Selection of wild lactic acid bacteria strains as promoters of postbiotics in gluten-free sourdoughs. Microorganisms 8:643. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050643
Pelin C, Gunduz B, Gaglio R et al (2020) Molecular analysis of the dominant lactic acid bacteria of chickpea liquid starters and doughs and propagation of chickpea sourdoughs with selected Weissella confusa. J Food Microbiol 91:103490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2020.103490
Reale A, Di Renzo T, Boscaino F et al (2019) Lactic acid bacteria biota and aroma profile of italian traditional sourdoughs from the irpinian area in Italy. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01621
Rocha JM, Brás A, Miranda J, Malcata FX (2023) Broa: a Portuguese traditional sourdough bread, made of maize and rye flours. In: Garcia-Vaquero M, Pastor K, Orhun GE, McElhatton A, Rocha JMF (eds) Traditional European Breads. Springer, Cham, pp 251–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23352-4_13
Rocha JM (2011) Microbiological and lipid profiles of broa: contributions for the characterization of a traditional portuguese bread. Thesis Doctoral, University of Lisbon
Rocha JM, Malcata FX (1999) On the microbiological profile of traditional portuguese sourdough. J Food Prot 62:1416–1429. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-62.12.1416
Rocha JM, Malcata FX (2016) Microbial ecology dynamics in portuguese broa sourdough. J Food Qual 39:634–648. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfq.12244
Rocha JM, Malcata FX (2012) Microbiological profile of maize and rye flours, and sourdough used for the manufacture of traditional portuguese bread. Food Microbiol 31:72–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2012.01.008
Rokni Y, Abouloifa H, Bellaouchi R et al (2021) Characterization of β-glucosidase of Lactobacillus plantarum FSO1 and Candida pelliculosa L18 isolated from traditional fermented green olive. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 19:117. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-021-00213-3
Sana M, Minervini F, Cagno R (2012) Technological, functional and safety aspects of enterococci in fermented vegetable products : a mini-review. Ann Microbiol 62:469–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0363-x
Sanz-Penella JM, Tamayo-Ramos JA, Haros M (2011) Application of bifidobacteria as starter culture in whole wheat sourdough breadmaking. Food Bioprocess Technol 5:2370–2380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0547-1
Wang D, Liu W, Ren Y et al (2016) Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria from traditional dairy products in Baotou and Bayannur of Midwestern inner Mongolia and q-PCR analysis of predominant species. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour 36:499–507. https://doi.org/10.5851/kosfa.2016.36.4.499
Zhang C, Brandt MJ, Schwab C, Gänzle MG (2010) Propionic acid production by cofermentation of Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus diolivorans in sourdough. Food Microbiol 27:390–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2009.11.019
Zotta T, Piraino P, Parente E et al (2008) Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from sourdoughs for Cornetto, a traditional bread produced in Basilicata (Southern Italy). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1785–1795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9671-0
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the project “PHC Maghreb (09MAG20)”. The authors would like to acknowledge the CNRST and the Ministry MESRSI (Morocco) for the grant given and the CIRAD of Montpellier (France) for the technical facilities. The authors would like also to acknowledge the COST Action 18101 SOURDOMICS-Sourdough biotechnology network towards novel, healthier and sustainable food and bioprocesses (https://sourdomics.com/; https://www.cost.eu/actions/CA18101/, accessed on 31st July 2023), where the author A. Zinedine is member of the working groups 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, and 8, and the author J.M. Rocha is the Chair and Grant Holder Scientific Representative and is supported by COST (European Co-operation in Science and Technology) (https://www.cost.eu/, accessed on 31st July 2023). COST is a funding agency for research and innovation networks. Author J.M. Rocha also acknowledges the Universidade Católica Portuguesa, CBQF—Centro de Biotecnologia e Química Fina—Laboratório Associado, Escola Superior de Biotecnologia, Porto, Portugal, as well as the support made by LA/P/0045/2020 (ALiCE) and UIDB/00511/2020-UIDP/00511/2020 (LEPABE) funded by national funds through FCT/MCTES (PIDDAC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by MB, AA, and NM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MB and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals experiments.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
EL Boujamaai, M., Mannani, N., Aloui, A. et al. Biodiversity and biotechnological properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional Moroccan sourdoughs. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 331 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03784-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03784-0