Abstract
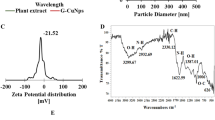
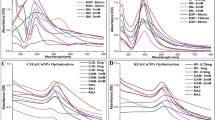
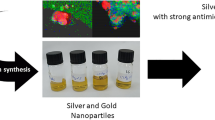
Wild-type microorganisms have become tolerant to higher antibiotic and antimicrobial agent concentrations due to the global increase in antibiotic consumption. Green-synthesized nanoparticles (NPs) have been proposed as potential antimicrobial agents to overcome the problem. This research prepared cadmium nanoparticles (Cd NPs) using Artemisia persica extract. To clarify the biological behavior of Cd NPs and Cd (NO3)2, cytotoxicity, antibacterial, anti-biofilm, and biocompatible experiments were performed. Since Cd toxicity is associated with liver, kidney damage, and other deficits, HepG2 and HUVEC cell lines were employed as the in vitro cytotoxicity models. Cd NPs had a lower cytotoxic effect than Cd (NO3)2 against both HepG2 and HUVEC cells. The Cd NPs exhibited no hemolysis activity. The antibacterial and anti-biofilm studies were conducted using gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and gram-negative Proteus mirabilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with the ability to form severe adherent biofilms. The antibacterial activity of Cd NPs against clinically isolated S. aureus, P. mirabilis, and P. aeruginosa was above 2560 µg mL− 1. The Cd NPs (640 µg mL− 1) decreased the biofilm formation of S. aureus, P. mirabilis, and P. aeruginosa by 24.6%, 31.6%, and 26.4%, respectively.
Moreover, adding Cd NPs (100 µg/disc) to antibiotic discs increased the antibacterial activity of vancomycin, gentamicin, tetracycline, streptomycin, meropenem, and kanamycin against Methicillin-resistant S. aureus, significantly. Due to the emergence of resistant microorganisms, Cd NPs can be used as an exciting material to counterattack global health problems. Further research is needed to clarify the molecular mechanisms underlying Cd NPs’ pharmacological and toxicological effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abd AN, Al-Marjani MF, Kadham ZA (2016) Antibacterial activity of cadmium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by chemical method. J Multidiscip Eng Sci Technol 3:5007–5011
Aisida SO et al (2020) Biogenic synthesis of iron oxide nanorods using Moringa oleifera leaf extract for antibacterial applications. Appl Nanosci 10:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01099-x
Alsaggaf MS, Elbaz AF, Badawy E, Moussa SH (2020) Anticancer and antibacterial activity of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles by Aspergillus niger. Adv Polym Technol 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4909054
Ameri A et al (2020) Rapid and Facile Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant Properties and Cytotoxic Effects Against Fibroblast-Like (HSkMC) and Human Lung Carcinoma (A549) Cell Lines. Biol Trace Elem Res 197:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01984-0
Anjomshoa M et al (2015) A mononuclear Cu (II) complex with 5, 6-diphenyl-3-(2-pyridyl)-1, 2, 4-triazine: synthesis, crystal structure, DNA-and BSA-binding, molecular modeling, and anticancer activity against MCF-7, A-549, and HT-29 cell lines. Eur J Med Chem 96:66–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.020
Azizi M, Ghourchian H, Yazdian F, Alizadehzeinabad H (2018) Albumin coated cadmium nanoparticles as chemotherapeutic agent against MDA-MB 231 human breast cancer cell line. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:787–797. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1436064
Bankier C, Matharu R, Cheong Y, Ren G, Cloutman-Green E, Ciric L (2019) Synergistic antibacterial effects of metallic nanoparticle combinations. Sci Rep 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52473-2
Bezza FA, Tichapondwa SM, Chirwa EM (2020) Fabrication of monodispersed copper oxide nanoparticles with potential application as antimicrobial agents. Sci Rep 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73497-z
Chari N, Felix L, Davoodbasha M, Sulaiman Ali A, Nooruddin T (2017) In vitro and in vivo antibiofilm effect of copper nanoparticles against aquaculture pathogens. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 10:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2017.04.013
Cho SJ, Maysinger D, Jain M, Röder B, Hackbarth S, Winnik FMJL (2007) Long-term exposure to CdTe quantum dots causes functional impairments in live cells. Langmuir 23:1974–1980. https://doi.org/10.1021/la060093j
Chung EJ, Leon L, Rinaldi C (2019) Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: Fundamental Concepts, Biological Interactions and Clinical Applications. Elsevier
Dabhane H et al (2021) A review on environmentally benevolent synthesis of CdS nanoparticle and their applications. Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2021.06.002
Daniel M-C, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr030698+
Dhanabalan K, Gurunathan K (2015) Microemulsion Mediated Synthesis and Characterization of CdS Nanoparticles and Its Anti-Biofilm Efficacy Against Escherichia Coli ATCC 25922. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15:4200–4204. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2015.9597
Elje E et al (2020) Hepato(Geno)Toxicity Assessment of Nanoparticles in a HepG2 Liver Spheroid Model. Nanomaterials (Basel) 10:545. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030545
Faramarzi S, Anzabi Y, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri HJAoM (2020) Nanobiotechnology approach in intracellular selenium nanoparticle synthesis using Saccharomyces cerevisiae—fabrication and characterization. Arch Microbiol 202:1203–1209
Forootanfar H et al (2014) Antioxidant and cytotoxic effect of biologically synthesized selenium nanoparticles in comparison to selenium dioxide. J Trace Elem Med Biol 28:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2013.07.005
Forootanfar H, Amirpour-Rostami S, Jafari M, Forootanfar A, Yousefizadeh Z, Shakibaie M (2015) Microbial-assisted synthesis and evaluation the cytotoxic effect of tellurium nanorods. Mater Sci Eng C 49:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.12.078
Gholami Z, Dadmehr M, Jelodar NB, Hosseini M, Parizi APJMRE (2020) One-pot biosynthesis of CdS quantum dots through in vitro regeneration of hairy roots of Rhaphanus sativus L. and their apoptosis effect on MCF-7 and AGS cancerous human cell lines. Mater Res Express 7:015056. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab66ea
Ghotekar S (2019) A review on plant extract mediated biogenic synthesis of CdO nanoparticles and their recent applications. Asian J green chem 3. https://doi.org/10.22034/AJGC.2018.140313.1084
Gounani Z et al (2019) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles carrying multiple antibiotics provide enhanced synergistic effect and improved biocompatibility. Colloids Surf B 175:498–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.12.035
Gupta R (2019) Cadmium Nanoparticles and Its Toxicity. J Crit Rev 6:1–7. https://doi.org/10.22159/jcr.2019v6i5.34073
Hajra A, Dutta S, Mondal NK (2016) Mosquito larvicidal activity of cadmium nanoparticles synthesized from petal extracts of marigold (Tagetes sp.) and rose (Rosa sp.) flower. J Parasit Dis 40:1519–1527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-015-0719-4
Haq Bhat IU, Yi YS (2019) Green synthesis and antibacterial activity of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles (CdSNPs) using Panicum sarmentosum. Asian J Green Chem 3:455–469
Jayappa MD et al (2020) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the leaf, stem and in vitro grown callus of Mussaenda frondosa L.: characterization and their applications. Appl Nanosci 10:3057–3074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01382-2
Kalinowska D, Grabowska-Jadach I, Drozd M, Pietrzak MJAN (2018) Comparative studies of biological activity of cadmium-based quantum dots with different surface modifications. Appl Nanosci 8:309–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0787-8
Kamble MM et al (2020) Optical, structural and morphological study of CdS nanoparticles: role of sulfur source. Nanomaterials and Energy 9:72–81
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem 12:908–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
Kloepfer J, Mielke R, Wong M, Nealson K, Stucky G, Nadeau J (2003) Quantum dots as strain-and metabolism-specific microbiological labels. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4205–4213. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.7.4205-4213.2003
Kominkova M et al (2017) Comparative study on toxicity of extracellularly biosynthesized and laboratory synthesized CdTe quantum dots. J Biotechnol 241:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.10.024
Malarkodi C, Rajeshkumar S, Paulkumar K, Vanaja M, Gnanajobitha G, Annadurai G (2014) Biosynthesis and antimicrobial activity of semiconductor nanoparticles against oral pathogens. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/347167
Martinez-Alonso C, Rodriguez-Castaneda CA, Moreno-Romero P, Coria-Monroy CS, Hu H (2014) Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Microwave Heating for Hybrid Solar Cell Applications. Int J Photoenergy 2014:1–11. Rodriguez
Mba IE, Nweze EI (2021) Nanoparticles as therapeutic options for treating multidrug-resistant bacteria: research progress, challenges, and prospects. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37:108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03070-x
Mohanty A et al (2014) Biogenic tellurium nanorods as a novel antivirulence agent inhibiting pyoverdine production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biotechnol Bioeng 111:858–865. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25147
Muruganandam S, Anbalagan G, Murugadoss G (2014) Synthesis and structural, optical and thermal properties of CdS: Zn 2 + nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 4:1013–1019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-013-0284-z
Muzquiz-Ramos E, Guerrero-Chávez V, Macías-Martínez BI, Lopez-Badillo C, García-Cerda L (2015) Synthesis and characterization of maghemite nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications. Ceram Int 41:397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.08.083
Narayanan KB, Sakthivel N (2010) Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles by microbes. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 156:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2010.02.001
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Sajjadi M, Issaabadi Z (2019) Chap. 1 - An Introduction to Nanotechnology. In: Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Sajjadi M, Issaabadi Z, Atarod M (eds) Interface Science and Technology. Elsevier, pp 1–27
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajjadi M, Dadashi J, Ghafuri H (2020) Pd-based nanoparticles: Plant-assisted biosynthesis, characterization, mechanism, stability, catalytic and antimicrobial activities. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 276:102103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102103
Nazari P et al (2014) The antimicrobial effects and metabolomic footprinting of carboxyl-capped bismuth nanoparticles against Helicobacter pylori. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:570–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0571-x
Nguyen KC, Seligy VL, Tayabali AF (2013a) Cadmium telluride quantum dot nanoparticle cytotoxicity and effects on model immune responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nanotoxicology 7:202–211. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2011.648667
Nguyen KC, Willmore WG, Tayabali AF (2013b) Cadmium telluride quantum dots cause oxidative stress leading to extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Toxicology 306:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2013.02.010
Rajeshkumar S, Ponnanikajamideen M, Malarkodi C, Malini M, Annadurai G (2014) Microbe-mediated synthesis of antimicrobial semiconductor nanoparticles by marine bacteria. J Nanostructure Chem 4:96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-014-0096-z
Rajeshkumar S et al (2021) Cytotoxicity behaviour of response surface model optimized gold nanoparticles by utilizing fucoidan extracted from padina tetrastromatica. J Mol Struct 1228:129440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129440
Rodriguez-Fragoso L, Gutiérrez-Sancha I, Rodríguez-Fragoso P, Rodríguez-López A, Reyes-Esparza J (2014) Pharmacokinetic properties and safety of cadmium-containing quantum dots as drug delivery systems. In: Sezer AD (ed) Application of Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery. IntechOpen, London, pp 469–499
Rodriguez-Fragoso P, Reyes-Esparza J, Leon-Buitimea A, Rodriguez-Fragoso L (2012) Synthesis, characterization and toxicological evaluation of maltodextrin capped cadmium sulfide nanoparticles in human cell lines and chicken embryos. J Nanobiotechnol 10:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-10-47
Sahoo M, Vishwakarma S, Panigrahi C, Kumar J (2021) Nanotechnology: Current applications and future scope in food. Food front 2:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/fft2.58
Salari Z et al (2017) Microwave-assisted biosynthesis of zinc nanoparticles and their cytotoxic and antioxidant activity. J Trace Elem Med Biol 39:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.09.001
Sekar PV, Parvathi VD, Sumitha R (2019) Green nanotechnology in cadmium sulphide nanoparticles and understanding its toxicity and antimicrobial properties. Biomed Res 30:805–809. https://doi.org/10.35841/biomedicalresearch.30-19-324
Shakibaie M et al (2019a) Antibacterial and anti-biofilm effects of microwave-assisted biologically synthesized zinc nanoparticles. Nanomed J 6:223–231. https://doi.org/10.22038/nmj.2019.06.00009
Shakibaie M, Forootanfar H, Golkari Y, Mohammadi-Khorsand T, Shakibaie MR (2015) Anti-biofilm activity of biogenic selenium nanoparticles and selenium dioxide against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Proteus mirabilis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 29:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.07.020
Shakibaie M, Hajighasemi E, Adeli-Sardou M, Doostmohammadi M, Forootanfar H (2019b) Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activities of Bi subnitrate and BiNPs produced by Delftia sp. SFG against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Proteus mirabilis. IET Nanobiotechnol 13:377–381. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5102
Shakibaie M, Riahi-Madvar S, Ameri A, Amiri-Moghadam P, Adeli-Sardou M, Forootanfar HJoCS (2021) Microwave Assisted Biosynthesis of Cadmium Nanoparticles: Characterization, Antioxidant and Cytotoxicity Studies. J Clust Sci 32:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02107-3
Shanthi K, Sreevani V, Vimala K, Kannan S (2017) Cytotoxic effect of palladium nanoparticles synthesized from Syzygium aromaticum aqueous extracts and induction of apoptosis in cervical carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 87:1101–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0678-7
Shivaji K et al (2018) Green-synthesis-derived CdS quantum dots using tea leaf extract: antimicrobial, bioimaging, and therapeutic applications in lung cancer cells. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1:1683–1693. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b00147
Shivashankarappa A, Sanjay KR (2020) Escherichia coli-based synthesis of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles, characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity studies. Braz J Microbiol 51:939–948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00238-9
Singh N, Sahoo SK, Kumar R (2020) Hemolysis tendency of anticancer nanoparticles changes with type of blood group antigen: An insight into blood nanoparticle interactions. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 109:110645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.110645
Srinivasa Goud B, Suresh Y, Annapurna S, Singh AK, Bhikshamaiah G (2016) Green Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide Nanoparticles. Mater Today Proc 3:4003–4008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2016.11.064
Su Y et al (2009) The cytotoxicity of cadmium based, aqueous phase - synthesized, quantum dots and its modulation by surface coating. Biomaterials 30:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.09.029
Suresh J, Pradheesh G, Alexramani V, Sundrarajan M, Hong SI (2018) Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticle using insulin plant (Costus pictus D. Don) and investigation of its antimicrobial as well as anticancer activities. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:015008. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6254/aaa6f1
Tariq M et al (2021) Green synthesis of Zno@ GO nanocomposite and its’ efficient antibacterial activity. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 35:102471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102471
Thati V, Prasad A, Ct S, Gaddad SM (2010) Nanostructured zinc oxide enhances the activity of antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus. J Biosci Tech 1:64–69
Thovhogi N, Sibuyi NRS, Onani MO, Meyer M, Madiehe AM (2018) Peptide-functionalized quantum dots for potential applications in the imaging and treatment of obesity. Int J Nanomedicine 13:2551–2559. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S158687
Uddin MS (2019) Nanoparticles as Nanopharmaceuticals: Smart Drug Delivery Systems. In: Keservani RK, Sharma AK (eds) Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems. Apple Academic Press, pp 85–120
Vasudevan D, Gaddam RR, Trinchi A, Cole I (2015) Core–shell quantum dots: Properties and applications. J Alloys Compd 636:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.02.102
Vazquez-Munoz R et al (2019) Enhancement of antibiotics antimicrobial activity due to the silver nanoparticles impact on the cell membrane. PLoS ONE 14:e0224904. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224904
Wu S, Rajeshkumar S, Madasamy M, Mahendran V (2020) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Cissus vitiginea and its antioxidant and antibacterial activity against urinary tract infection pathogens. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 48:1153–1158. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2020.1817053
Zahin N et al (2020) Nanoparticles and its biomedical applications in health and diseases: special focus on drug delivery. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:19151–19168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05211-0
Zhang Y, Chen W, Zhang J, Liu J, Chen G, Pope C (2007) In vitro and in vivo toxicity of CdTe nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:497–503. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2007.125
Acknowledgements
We thank the Pharmaceutical Sciences and Cosmetic Products Research Center, Kerman University of Medical Sciences (Kerman, Iran), for its financial support and admirable participation in this study. We acknowledge the support from the Pharmaceutical Sciences and Cosmetic Products Research Center, Kerman University of Medical Sciences (Kerman, Iran).
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Pharmaceutical Sciences and Cosmetic Products Research Center, Kerman University of Medical Sciences (Kerman, Iran) (Grant number 400000795).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed to the present work as described below: Mahboubeh Adeli-Sardou contributed to the preparation and characterization of NPs. Mojtaba Shakibaie supervised the study, received the related grant, and was involved in purchasing materials and analyzing the obtained results. Hamid Forootanfar was involved in cytotoxicity studies, Fereshteh Jabari-Morouei was involved in antibacterial studies, and Soudabe Riahi-Madvar supervised the hemolytic activity studies, Sima-Sadat Ghafari-Shahrbabaki involved in the anti-biofilm studies. Mitra Mehrabani was involved in statistical analysis. The authors have equally contributed to preparing and reviewing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statements and declarations
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to this article’s content.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This work was approved by the ethical committee of Kerman University of Medical Sciences.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
All authors consented to the publication of this work. The authors all confirm the permission of publication for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Adeli-Sardou, M., Shakibaie, M., Forootanfar, H. et al. Cytotoxicity and anti-biofilm activities of biogenic cadmium nanoparticles and cadmium nitrate: a preliminary study. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 246 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03418-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03418-x