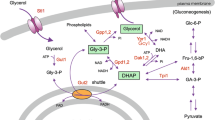
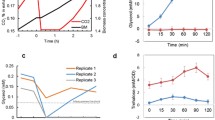
Abstract
Eukaryotic microorganisms possess mechanisms to detect osmotic variations in their surroundings, from specialized receptors and membrane transporters, to sophisticated systems such as two-component histidine kinases. Osmotic stimuli are transduced through conserved phosphorylation cascades that result in a rapid response to mitigate stress. This response allows for the maintenance of an optimal biochemical environment for cell functioning, as well as a suitable recovery in suboptimal environments that would otherwise endanger cell survival. The molecular basis of these responses has been largely studied in yeasts and bacteria. However, fewer studies have been published concerning the molecular basis of osmoregulation in other eukaryotic microorganisms such as protozoans and microalgae. Here, we review the main osmosensors reported in unicellular eukaryotic microorganisms (yeasts, microalgae and protozoa) and the pathways that maintain homeostasis in cells encountering hyperosmotic challenges.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alepuz PM, Jovanovic A, Reiser V, Ammerer G (2001) Stress-induced MAP kinase Hog1 is part of transcription activation complexes. Mol Cell 7:767–777
Araki T, Williams JG (2012) Perturbation of the actin cytoskeleton activate a Dyctiostelium STAT signaling pathway. Eur J Cell Biol 91:420–425
Araki T, Tsujioka M, Abe T, Fukuzawa M et al (2013) A STAT-regulated, stress-induced signaling pathway in Dictyostelium. J Cell Sci 116:2907–2915
Avron M (1986) The osmotic components of halotolerant algae. Trends Biochem Sci 11:5–6
Bahn YS (2008) Master and commander in fungal pathogens: the two-component system and the HOG signaling pathway. Eukaryot Cell 7:2017–2036
Beitz E (2005) Aquaporins from pathogenic protozoan parasites: structure, function and potential for chemotherapy. Biol Cell 97:373–383
Ben-Amotz A, Grunwald T (1981) Osmoregulation in the halotolerant alga Asteromonas gracilis. Plant Physiol 67:613–616
Bisson MA, Beilby MJ, Shepherd VA (2006) Electrophysiology of turgor regulation in marine siphonous green algae. J Membr Biol 211:1–14
Blum JJ (1991) Effects of osmotic pressure on the oxidative metabolism of Leishmania major Promastigotes. J Protozool 38:229–233
Blum JJ (1996) Effects of osmotic stress on metabolism, shape, and amino acid content of Leishmania. Biol Cell 87:9–16
Brown AJP, Budge S, Kaloriti D, Tillman A et al (2014) Stress adaptation in a pathogenic fungus. J Exp Biol 217:144–155
Brumlik MJ, Wei S, Finstad K, Nesbit J et al (2004) Identification of a novel mitogen-activated protein kinase in Toxoplasma gondii. Inter J Parasitol 34:1245–1254
Buchmann K, Becker B (2009) The system of contractile vacuoles in the green alga Mesostigma viride (Streptophyta). Protist 160:427–443
Burch TA, Adams WW III, Degrenne BLS, Englert CH et al (2014) Environmental manipulation of growth and energy carrier release from fresh water and marine Chlamydomonas species. J Appl Phycol. doi:10.1007/s10811-014-0433-0
Burrows C, Blum JJ (1991) Effect of hyper-osmotic stress on alanine content of Leishmania major Promastigotes. J Eukaryot Microbiol 38:47–52
Calera JA, Herman D, Calderone R (2000) Identification of YPD1, a gene of Candida albicans which encodes a two-component phosphohistidine intermediate protein. Yeast 16:1053–1059
Capra EJ, Laub MT (2012) Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems. Ann Rev Microbiol 66:325–347
Catlett NL, Yoder OC, Turgeon BG (2003) Whole-genome analysis of two-component signal transduction genes in fungal pathogens. Eukaryot Cell 2:1151–1161
Chen H, Jiang JG (2009) Osmotic responses of Dunaliella to the changes of salinity. J Cell Physiol 219:251–258
Chen D, Toone WM, Mata J, Lyne R, Burns G et al (2003) Global transcriptional responses of fission yeast to environmental stress. Mol Biol Cell 14:214–229
Chen H, Chen SL, Jiang JG (2011) Effect of Ca2+ channel block on glycerol metabolism in Dunaliella salina under hypoosmotic and hyperosmotic stresses. PLoS One 6(12):e28613
Cronkite DL, Diekman AB, Lewallen B, Phillips L (1993) Aminotransferase and the production of alanine during hyperosmotic stress in Paramecium calkinsi. J Eukaryot Microbiol 40:796–800
Docampo R, Jimenez V, Lander N, Li Z-H, Niyogi S (2013) New insights into the roles of acidocalcisomes and the Contractile Vacuole Complex in osmoregulation in Protists. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-407695-2.00002-0
Ehud I, Doreen S, Marianne SG, Doris R, Dan Z (2013) A versatile proline/alanine transporter in the unicellular pathogen Leishmania donovani regulates amino acid homoeostasis and osmotic stress responses. Biochem J 449:555–566
Furukawa K, Katsuno Y, Urao T, Yabe T et al (2002) Isolation and functional analysis of a gene, tcsB, encoding a transmembrane hybrid-type histidine kinase from Aspergillus nidulans. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5304–5310
Gacto M, Soto T, Vicente-Soler J, Villa TG, Cansado J (2003) Learning from yeasts: intracellular sensing of stress conditions. Int Microbiol 6:211–219
Ghoshal D, Mach D, Agarwal M, Goyal A (2002) Osmoregulatory isoform of dihydroxyacetone phosphate reductase from Dunaliella tertiolecta: purification and characterization. Protein Expr Purif 24:404–411
Golub T, Wacha S, Caroni P (2004) Spatial and temporal control of signaling through lipid rafts. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:542–550
Goyal A (2007) Osmoregulation in Dunaliella, Part II: photosynthesis and starch contribute carbon for glycerol synthesis during a salt stress in Dunaliella tertiolecta. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:705–710
Grønlien HK, Stock C, Aihara MS, Allen RD, Naitoh Y (2002) Relationship between the membrane potential of the contractile vacuole complex and its osmoregulatory activity in Paramecium multimicronucleatum. J Exp Biol 205:3261–3270
Hansen M, Kun JFJ, Schultz JE, Beitz E (2012) A single, bi-functional aquaglyceroporin in blood-stage Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites. J Biol Chem 277:4874–4882
Heywood P (1978) Osmoregulation in the alga Vacuolaria virescens. Structure of the contractile vacuole and the nature of its association with the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Sci 31:213–224
Hill AE, Shachar-Hill B, Shachar-Hill Y (2004) What are aquaporins for? J Membr Biol 197:1–32
Hohmann S (2002) Osmotic stress signaling and omsoadaptation in yeasts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:300–372
Hohmann S, Krantz M, Nordlander B (2007) Yeast osmoregulation. Methods Enzymol 428:29–45
Husic HD, Tolbert NE (1986) Effect of osmotic stress on carbon metabolism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Accumulation of glycerol as an osmoregulatory solute. Plant Physiol 82:594–596
Iwamoto K, Shiraiwa Y (2005) Salt-regulated mannitol metabolism in algae. Mar Biotechnol 7:407–415
Jimenez V (2014) Dealing with environmental challenges: mechanisms of adaptation in Trypanosoma cruzi. Res Microbiol 165:155–165
Jimenez C, Berl T, Rivard CJ, Edelstein CL, Capasso JM (2004) Phosphorylation of MAP kinase-like proteins mediate the response of the halotolerant alga Dunaliella viridis to hypertonic shock. BBA Mol Cell Res 1644:61–69
Krantz M, Becit E, Hohmann S (2006) Comparative genomics of the HOG-signaling system in fungi. Curr Genet 49:137–151
Kültz D (1998) Phylogenetic and functional classification of mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinases. J Mol Evol 46:571–588
LeFurgey A, Ingram P, Blum JJ (2001) Compartmental responses to acute osmotic stress in Leishmania major result in rapid loss of Na+ and Cl−. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 128:385–394
Lei G, Qiao D, Bai L, Xu H, Cao Y (2008) Isolation and characterization of a mitogen-activated protein kinase gene in the halotolerant alga Dunaliella salina. J Appl Phycol 20:13–17
Li Z-H, Alvarez VE, DeGaudenzi JG, Sant’Anna C et al (2011) Hyperosmotic stress induces aquaporin-dependent cell shrinkage, polyphosphate synthesis, amino acid accumulation, and global gene expression changes in Trypanosoma cruzi. J Biol Chem 286:43959–43971
Liska AJ, Shevchenko A, Pick U, Katz A (2004) Enhanced photosynthesis and redox energy production contribute to salinity tolerance in Dunaliella as revealed by homology-based proteomics. Plant Physiol 136:2806–2817
Ma D, Li R (2012) Current understanding of HOG-MAPK pathway in Aspergillus fumigatus. Mycopathol 175:13–23
Maeda T, Takekawa M, Saito H (1995) Activation of yeast PBS2 MAPKK by MAPKKKs or by binding of an SH3-containing osmosensor. Science 269:554–558
Mandal G, Sharma M, Kruse M, Sander-Juelch C et al (2012) Modulation of Leishmania major aquaglyceroporin activity by a mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Microbiol 85:1204–1218
Meena N, Kaur H, Mondal AK (2010) Interactions among HAMP domain repeats act as an osmosensing molecular switch in Group III hybrid histidine kinases from fungi. J Biol Chem 285:12121–12132
Nagahashi S, Mio T, Ono N, Yamada-Okabe T et al (1998) Isolation of CaSLN1 and CaNIK1, the genes for osmosensing histidine kinase homologues from the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Microbiol 144:425–432
Nakashima S, Wang S, Hisamoto N, Sakai H et al (1999) Molecular cloning and expression of a stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase-related kinase from Tetrahymena cells. J Biol Chem 274:9976–9983
O’Rourke SM, Herskowitz I, O’Shea E (2002) Yeast go the whole HOG for the hyperosmotic response. Trends Genet 18:405–412
Ohmiya R, Kato C, Yamada H, Aiba H, Mizuno T (1999) A fission yeast gene (prrl +) that encodes a response regulator implicated in oxidative stress response. J Biochem 125:1061–1066
Ota IM, Varshavsky A (1993) A yeast protein similar to bacterial two-component regulators. Science 262:566–569
Ott A, Oehme F, Keller H, Schuster SC (2000) Osmotic stress response in Dyctiostelium is mediated by cAMP. EMBO J 19:5782–5792
Park JH, Schofield PJ, Edwards M (1995) The role of alanine in the acute response of Giardia intestinalis to hypo-osmotic shock. Microbiol 141:2455–2462
Plemenitas A, Lenassi M, Konte T, Kejzar A et al (2014) Adaptation to high salt concentrations in halotolerant/halophilic fungi: a molecular perspective. Front Microbiol 5:199. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00199
Raitt DC, Posas F, Saito H (2000) Yeast Cdc42 GTPase and Ste20 PAK-like kinase regulate Sho1-dependent activation of the Hog1 MAPK pathway. EMBO J 19:4623–4631
Reiser V, Raitt DC, Saito H (2003) Yeast osmosensor Sln1 and plant cytokinin receptor Cre1 respond to changes in turgor pressure. J Cell Biol 161:1035–1040
Rep M, Krantz M, Thevelein JM, Hohmann S (2000) The transcriptional response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to osmotic shock. Hot1p and Msn2p/Msn4p are required for the induction of subsets of high osmolarity glycerol pathway-dependent genes. J Biol Chem 275:8290–8300
Rifkin RL (1973) The role of the contractile vacuole in the osmoregulation of Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Protozool 20:108–114
Rohloff P, Docampo R (2008) A contractile vacuole complex is involved in osmoregulation in Trypanosoma cruzi. Exp Parasitol 118:17–24
Roman E, Nombela C, Pla J (2005) The Sho1 adaptor protein links oxidative stress to morphogenesis and cell wall bio-synthesis in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol 25:10611–10627
Saito H (2001) Histidine phosphorylation and two-component signaling in eukaryotic cells. Chem Rev 101:2497–2510
Santos JL, Shiozaki K (2001) Fungal histidine kinases. Sci Signal 2001(98):re1–re1
Saran S, Schaap P (2004) Adenylyl cyclase is activated by an intramolecular osmosensor. Mol Biol Cell 15:1479–1486
Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN (2000) Two-component signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 69:183–215
Stoner LC, Dunham PB (1970) Regulation of cellular osmolarity and volume in Tetrahymena. J Exp Biol 53:391–399
Suescún-Bolívar LP, Iglesias-Prieto R, Thomé PE (2012) Induction of glycerol synthesis and release in cultured Symbiodinium. PLoS One 7(10):e47182
Tanigawa M, Kihara A, Terashima M, Takahara T, Maeda Y (2012) Sphingolipids regulate the yeast high-osmolarity glycerol response pathway. Mol Cell Biol 32:2861–2870
Tatebayashi K, Tanaka K, Yang H-Y, Yamamoto K, Matsushita Y (2007) Transmembrane mucins Hkr1 and Msb2 are putative osmosensors in the SHO1 branch of yeast HOG pathway. EMBO J 26:3521–3533
Tena G, Asai T, Chiu WL, Sheen J (2001) Plant mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:392–400
Thomason P, Kay R (2000) Eukaryotic signal transduction via histidine-aspartate phosphorelay. J Cell Sci 113:3141–3150
Thomé PE (2007) Cell wall involvement in the glycerol response to high osmolarity in the halotolerant yeast Debaryomyces hansenii. Anton Leeuw 91:229–235
Uzcategui NL, Szallies A, Pavlovic-Djuranovic S, Palmada M et al (2004) Cloning, heterologous expression, and characterization of three aquaglyceroporins from Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem 279:42669–42676
Vivancos AP, Jara M, Zuin A, Sansó M, Hidalgo E (2006) Oxidative stress in Schyzosaccharomyces pombe: different H2O2 levels, different response pathways. Mol Genet Genomics 276:495–502
Ward P, Equinet L, Parker J, Doerig C (2004) Protein kinases of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum: the kinome of a divergent eukaryote. BMC Genom 5:79. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-5-79
Westfall PJ, Ballon DR, Thorner J (2004) When the stress of your environment makes you go HOG wild. Science 306:1511–1512
Wiese M (2007) Leishmania MAP kinases—familiar proteins in an unusual context. Int J Parasitol 37:1053–1062
Wolanin PM, Thomason PA, Stock JB (2002) Histidine protein kinases: key signal transducers outside the animal kingdom. Genome Biol 3: Review 3013.7
Wood JM (2006) Osmosensing by bacteria. Sci STKE 357:pe43
Yamamoto K, Tatebayashi K, Tanaka K, Saito H (2010) Dynamic control of yeast MAP kinase network by induced association and dissociation between the Ste50 scaffold and the Opy2 membrane anchor. Mol Cell 40:87–98
Yang F, Ma D, Wan Z, Liu W et al (2011) The Role of sho1 in polarized growth of Aspergillus fumigatus. Mycopathol 172:347–355
Yong C, Mapes J, Hanneman J, Al-Zarban S, Ota I (2002) Role of Ptc2 type 2C Ser/Thr phosphatase in yeast high-osmolarity glycerol pathway inactivation. Eukaryot Cell 1:1032–1040
Zarrinpar A, Bhattacharyya RP, Nittler MP, Lim WA (2004) Sho1 and Pbs2 act as coscaffolds linking components in the yeast high osmolarity MAP kinase pathway. Mol Cell 14:825–832
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suescún-Bolívar, L.P., Thomé, P.E. Osmosensing and osmoregulation in unicellular eukaryotes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 435–443 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1811-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1811-8