Abstract
Oil–water separation is necessary to mitigate the impacts of oily wastewater released from industrial processes, frequently occurred oil spillages during transportation, and oil and gas exploration on ecology and environment. Since oil and water are immiscible, the solid surfaces can be engineered using various nanomaterials to alter their wettability characteristics for effective oil–water separation. In this context, carbon-based membranes (i.e., graphene oxide (GO), carbon nanotubes, and carbon nanofibers) have received significant attention in the past decade or so. Additionally, their surficial modifications with a variety of nanomaterials (i.e., MXenes, MnO2, TiO2, ZnO, MoS2) improved their wettability, permeation flux, and selectively for various oil–water emulsions which renders them efficient to remove oil or water from oil–water emulsions via adsorption, absorption, and simple filtration. Various types of modified carbon-based membranes have been developed and successfully applied for separating oil–water emulsions in the laboratory. In addition to their excellent separation performance, they exhibit tremendous mechanical durability and regenerative properties for their extended reuse. Consequently, owing to these principal characteristics, they can be considered as promising candidates for efficient oil–water separation. However, their utilization is still limited for commercial-scale applications due to their low cost-effectiveness and reusability over longer periods of time.
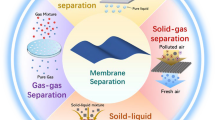
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable
References
Abdalla, O., Wahab, M. A., & Abdala, A. (2020). Mixed matrix membranes containing aspartic acid functionalized graphene oxide for enhanced oil-water emulsion separation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(5), 104269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104269
Al-Anzi, B. S., & Siang, O. C. (2017). Recent developments of carbon based nanomaterials and membranes for oily wastewater treatment. RSC Advances, 7(34), 20981–20994. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02501g
Ali, N., Bilal, M., Khan, A., Ali, F., & Iqbal, H. M. N. (2020). Design, engineering and analytical perspectives of membrane materials with smart surfaces for efficient oil/water separation. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 127, 115902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115902
Alammar, A., Park, S. H., Williams, C. J., Derby, B., & Szekely, G. (2020). Oil-in-water separation with graphene-based nanocomposite membranes for produced water treatment. Journal of Membrane Science, 603, 118007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118007
Adebajo, M. O., Frost, R. L., Theo Kloprogge, J., Carmody, O., & Kokot, S. (2003). Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: A review of synthesis and absorbing properties. Journal of Porous Materials, 10, 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027484117065
An, Y.-P., Yang, J., Yang, H.-C., Ming-Bang, W., & Zhi-Kang, X. (2018). Janus membranes with charged carbon nanotube coatings for deemulsification and separation of oil-in-water emulsions. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 10(11), 9832–9840. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b19700
Baig, N., Alghunaimi, F. I., & Saleh, T. A. (2019). Hydrophobic and oleophilic carbon nanofiber impregnated styrofoam for oil and water separation: A green technology. Chemical Engineering Journal, 360, 1613–1622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.042
Baig, N., Alghunaimi, F. I., Dossary, H. S., & Saleh, T. A. (2019). Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic carbon nanofiber grafted polyurethane for oil-water separation. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 123, 327–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.01.007
Baig, N., & Saleh, T. A. (2018). Initiator-free natural light-driven vapor phase synthesis of a porous network of 3D polystyrene branched carbon nanofiber grafted polyurethane for hexane /water separation. ChemistrySelect, 3(28), 8312–8318. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201801549
Baig, U., Faizan, M., & Waheed, A. (2022). A review on super-wettable porous membranes and materials based on bio-polymeric chitosan for oil-water separation. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 303, 102635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2022.102635
Bastida, F., Jehmlich, N., Lima, K., Morris, B. E. L., Richnow, H. H., Hernández, T., Von Bergen, M., & García, C. (2016). The ecological and physiological responses of the microbial community from a semiarid soil to hydrocarbon contamination and its bioremediation using compost amendment. Journal of Proteomics, 135, 162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2015.07.023
Berepiki, A., Kent, R., Machado, L. F., & Dixon, N. (2020). Development of high-performance whole cell biosensors aided by statistical modeling. ACS Synthetic Biology, 9(3), 576–589. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00448
Bharati, R., Sundaramurthy, S., & Thakur, C. (2017). Nanomaterials and food-processing wastewater. In Water Purification (pp. 479–516). Elsevier Inc..
Calcagnile, P., Fragouli, D., Bayer, I. S., Anyfantis, G. C., Luigi Martiradonna, P., Cozzoli, D., Cingolani, R., & Athanassiou, A. (2012). Magnetically driven floating foams for the removal of oil contaminants from water. ACS Nano, 6, 5413–5419. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn3012948
Chen, P.-C., & Zhi-Kang, X. (2013). Mineral-coated polymer membranes with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for effective oil/water separation. Scientific Reports, 3, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02776
Cheng, X. Q., Sun, Z., Yang, X., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, P., Liang, H., Ma, J., & Shao, L. (2020). Construction of superhydrophilic hierarchical polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membranes by: In situ asymmetry engineering for unprecedently ultrafast oil-water emulsion separation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 8(33), 16933–16942. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta03011b
Cheng, Y., Barras, A., Shixiang, L., Wenguo, X., Szunerits, S., & Boukherroub, R. (2020). Fabrication of superhydrophobic/superoleophilic functionalized reduced graphene oxide/polydopamine/PFDT membrane for efficient oil/water separation. Separation and Purification Technology, 236, 116240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116240
Choi, Y., Kim, S. S., Kim, J. H., Kang, J., Choi, E., Choi, S. E., Kim, J. P., Kwon, O., & Kim, D. W. (2020). Graphene oxide nanoribbon hydrogel: Viscoelastic behavior and use as a molecular separation membrane. ACS Nano, 14(9), 12195–12202. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c05902
Cui, W., Fan, T., Li, Y., Wang, X., Liu, X., Chao Jing, L., Ramakrishna, S., & Long, Y. Z. (2022). Robust functional janus nanofibrous membranes for efficient harsh environmental air filtration and oil/water separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 663, 121018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2022.121018
Dmitrieva, E. S., Anokhina, T. S., Novitsky, E. G., Volkov, V. V., Borisov, I. L., & Volkov, A. V. (2022). Polymeric membranes for oil-water separation: A review. Polymers, 14(5), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050980
Fan, Y., Wei, L., Meng, X., Zhang, W., Yang, N., Jin, Y., Wang, X., Zhao, M., & Liu, S. (2019). An unprecedented high-temperature-tolerance 2D laminar MXene membrane for ultrafast hydrogen sieving. Journal of Membrane Science, 569, 117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.10.017
Fang, W., Liu, L., Li, T., Dang, Z., Qiao, C., Jinku, X., & Wang, Y. (2016). "Electrospun N-substituted polyurethane membranes with self-healing ability for self-cleaning and oil/water separation." Chemistry–A. European Journal, 22(3), 878–883. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201504340
George, J. K., & Verma, N. (2022). Super-hydrophobic/super-oleophilic carbon nanofiber-embedded resorcinol-formaldehyde composite membrane for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsion. Journal of Membrane Science, 654, 120538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2022.120538
Guan, L.-Z., Zhao, L., Wan, Y.-J., & Tang, L.-C. (2018). Three-dimensional graphene-based polymer nanocomposites: Preparation, properties and applications. Nanoscale, 10(31), 14788–14811. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr03044h
Guerin, T. F. (2002). Heavy equipment maintenance wastes and environmental management in the mining industry. Journal of Environmental Management, 66(2), 185–199. https://doi.org/10.1006/jema.2002.0583
Guo, Z., Long, B., Gao, S., Luo, J., Wang, L., Huang, X., Wang, D., Xue, H., & Gao, J. (2021). Carbon nanofiber based superhydrophobic foam composite for high performance oil/water separation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 402, 123838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123838
Han, R., & Peiyi, W. (2019). High-performance graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane with continuous nanochannels prepared by the in situ oxidation of MXene. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 7(11), 6475–6481. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta00137a
Han, X., & Guo, Z. (2021). Graphene and its derivative composite materials with special wettability: Potential application in oil-water separation. Carbon, 172, 647–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.10.060
Hu, J., Gui, L., Zhu, M., Liu, K., Chen, Y., Wang, X., & Lin, J. (2022). Smart Janus membrane for on-demand separation of oil, bacteria, dye, and metal ions from complex wastewater. Chemical Engineering Science, 253, 117586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2022.117586
Jayaramulu, K., Geyer, F., Schneemann, A., Kment, Š., Otyepka, M., Zboril, R., Vollmer, D., & Fischer, R. A. (2019). Hydrophobic metal–organic frameworks. Advanced Materials, 31(32), 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201900820
Jiang, Y.-H., Zhang, Y.-Q., Gao, C., An, Q.-D., Xiao, Z.-Y., & Zhai, S.-R. (2022). Superhydrophobic aerogel membrane with integrated functions of biopolymers for efficient oil/water separation. Separation and Purification Technology, 282, 120138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120138
Jin, X., Al-Qatatsheh, A., Subhani, K., & Salim, N. V. (2021). Biomimetic and flexible 3D carbon nanofiber networks with fire-resistant and high oil-sorption capabilities. Chemical Engineering Journal, 412, 128635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128635
Junaidi, N. F., Diana, N. H., Othman, M. Z., Shahruddin, N. H., Alias, F. M., Lau, W. J., & Ismail, A. F. (2020). Fabrication and characterization of graphene oxide–polyethersulfone (GO–PES) composite flat sheet and hollow fiber membranes for oil–water separation. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 95(5), 1308–1320. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6366
Junaidi, N. F., Diana, N. H., Othman, N. S., Fuzil, M. S., Shayuti, M., Alias, N. H., Shahruddin, M. Z., Marpani, F., Lau, W. J., Ismail, A. F., & Aba, N. F. D. (2021). Recent development of graphene oxide-based membranes for oil–water separation: A review. Separation and Purification Technology, 258, 118000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118000
Juraij, K., Chingakham, C., Manaf, O., Sagitha, P., Suni, V., Sajith, V., & Sujith, A. (2022). Polyurethane/multi-walled carbon nanotube electrospun composite membrane for oil/water separation. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 139(19), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.52117
Li, P., Cai, Q., Lin, W., Chen, B., & Zhang, B. (2016). Offshore oil spill response practices and emerging challenges. Marine pollution bulletin, 110(1), 6–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.020
Li, Z., Wang, B., Qin, X., Wang, Y., Liu, C., Shao, Q., Wang, N., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Shen, C., & Guo, Z. (2018). Superhydrophobic/superoleophilic polycarbonate/carbon nanotubes porous monolith for selective oil adsorption from water. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 6(11), 13747–13755. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b01637
Liu, D., Wang, S., Tao, W., & Li, Y. (2021). A robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge loaded with multi-walled carbon nanotubes for efficient and selective oil-water separation. Nanomaterials, 11(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123344
Liu, W., Xian, W., Liu, S., Cheng, X., & Zhang, C. (2022). CNT@LDH functionalized poly(lactic acid) membranes with super oil–water separation and real-time press sensing properties. Polymer Composites, 43(9), 6548–6559. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.26968
Liu, Y., Yanlei, S., Guan, J., Cao, J., Zhang, R., He, M., & Jiang, Z. (2018). Asymmetric aerogel membranes with ultrafast water permeation for the separation of oil-in-water emulsion. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 10(31), 26546–26554. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b09362
Liu, Y., Zhang, F., Zhu, W., Dong, S., Sang, Z., Yan, X., Li, S., Liang, J., & Dou, S. X. (2020). A multifunctional hierarchical porous SiO2/GO membrane for high efficiency oil/water separation and dye removal. Carbon, 160, 88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.01.002
Liu, Z., Weifu, W., Liu, Y., Qin, C., Meng, M., Jiang, Y., Qiu, J., & Peng, J. (2018). A mussel inspired highly stable graphene oxide membrane for efficient oil-in-water emulsions separation. Separation and Purification Technology, 199, 37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.01.041
Lu, Y., & Yuan, W. (2017). Superhydrophobic/superoleophilic and reinforced ethyl cellulose sponges for oil/water separation: Synergistic strategies of cross-linking, carbon nanotube composite, and nanosilica modification. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9(34), 29167–29176. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b09160
Ma, J., Ping, D., & Dong, X. (2017). Recent developments of graphene oxide-based membranes: A review. Membranes, 7(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7030052
Meng, F.-N., Zhang, M.-Q., Ding, K., Zhang, T., & Gong, Y.-K. (2018). Cell membrane mimetic PVDF microfiltration membrane with enhanced antifouling and separation performance for oil/water mixtures. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6(7), 3231–3241. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta10135j
Naresh, V., & Lee, N. (2021). A review on biosensors and recent development of nanostructured materials-enabled biosensors. Sensors, 21(4), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041109
Noamani, S., Niroomand, S., Rastgar, M., & Sadrzadeh, M. (2019). Carbon-based polymer nanocomposite membranes for oily wastewater treatment. Npj Clean Water, 2(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-019-0044-z
Othman, N. H., Fuzil, N. S., Alias, N. H., Shahruddin, M. Z., Shayuti, M. S. M., Lau, W. J., Ismail, A. F., Abidin, S. Z., Sulaiman, S., & Kusworo, T. D. (2022). Fabrication of MoS2–RGO and MoS2–ZIF-8 membranes supported on flat alumina substrate for effective oil removal. Emergent Materials, 5(4), 1169–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00343-x
Ou, X., Yang, X., Zheng, J., & Liu, M. (2019). Free-standing graphene oxide-chitin nanocrystal composite membrane for dye adsorption and oil/water separation. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 7(15), 13379–13390. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02619
Pan, Y., Liu, L., Zhang, Z., Huang, S., Hao, Z., & Zhao, X. (2019). Surfaces with controllable super-wettability and applications for smart oil-water separation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 378, 122178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122178
Paul, S., Bhoumick, M. C., Roy, S., & Mitra, S. (2022). Carbon nanotube enhanced membrane filtration for trace level dewatering of hydrocarbons. Separation and Purification Technology, 292, 121047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121047
Qian, D., Chen, D., Li, N., Qingfeng, X., Li, H., He, J., & Jianmei, L. (2018). TiO2/sulfonated graphene oxide/Ag nanoparticle membrane: In situ separation and photodegradation of oil/water emulsions. Journal of Membrane Science, 554, 16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.12.084
Qu, R., Li, X., Zhang, W., Liu, Y., Zhai, H., Wei, Y., & Feng, L. (2020). Photothermally induced: In situ double emulsion separation by a carbon nanotube/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) modified membrane with superwetting properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 8(16), 7677–7686. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta02919j
Rao, L., You, X., Chen, B., Shen, L., Yanchao, X., Zhang, M., Hong, H., Li, R., & Lin, H. (2022). A novel composite membrane for simultaneous separation and catalytic degradation of oil/water emulsion with high performance. Chemosphere, 288, 132490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132490
Rasouli, S., Rezaei, N., Hamedi, H., Zendehboudi, S., & Duan, X. (2021). Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic membranes for oil-water separation application: A comprehensive review. Materials & Design, 204, 109599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109599
Saththasivam, J., Yiming, W., Wang, K., Jin, J., & Liu, Z. (2018). A novel architecture for carbon nanotube membranes towards fast and efficient oil/water separation. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 4–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25788-9
Serhan, M., Sprowls, M., Jackemeyer, D., Long, M., Perez, I. D., Maret, W., Tao, N., & Forzani, E. (2019). Total iron measurement in human serum with a smartphone. AIChE Annual Meeting, Conference Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1039/x0xx00000x
Singhal, A. V., George, R., Sharma, A. K., Malwal, D., & Lahiri, I. (2020). Development of superhydrophillic tannic acid-crosslinked graphene oxide membranes for efficient treatment of oil contaminated water with enhanced stability. Heliyon, 6(10), e05127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05127
Venkatesh, K., Arthanareeswaran, G., Bose, A. C., Kumar, P. S., & Kweon, J. (2021). Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes/titanium oxide-PVDF nanofiber membrane for effective separation of oil/water emulsion. Separation and Purification Technology, 257, 117926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117926
Ventikos, N. P., Vergetis, E., Psaraftis, H. N., & Triantafyllou, G. (2004). A high-level synthesis of oil spill response equipment and countermeasures. Journal of hazardous materials, 107(1-2), 51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2003.11.009
Visco, A., Quattrocchi, A., Nocita, D., Montanini, R., & Pistone, A. (2021). Polyurethane foams loaded with carbon nanofibers for oil spill recovery: Mechanical properties under fatigue conditions and selective absorption in oil/water mixtures. Nanomaterials, 11(3), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030735
Wang, G., Miao, J., Ma, X., Lou, C.-W., Lin, J.-H., Long, Y.-Z., Ramakrishna, S., & Fan, T. (2022). Robust multifunctional RGO/MXene@PPS fibrous membrane for harsh environmental applications. Separation and Purification Technology, 302, 122014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122014
Wang, Y., & Gong, X. (2017). Special oleophobic and hydrophilic surfaces: Approaches, mechanisms, and applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 5(8), 3759–3773. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA10474F
Wong, T.-S., Sun, T., Feng, L., & Aizenberg, J. (2013). Interfacial materials with special wettability. MRS Bull, 38, 366–371. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2013.99
Wu, X., Luo, Z., Lei, Y., Wen, B., & Yang, D. (2020). Hierarchical TiO2nanorod arrays/carbon nanofiber membranes for oil-in-water emulsion separation. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 59(48), 21097–21105. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04831
Xue, Z., Cao, Y., Liu, N., Feng, L., & Jiang, L. (2014). Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2(8), 2445–2460. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta13397d
Xiao, X., Zongxue, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, J., & Zhu, Q. X. X. (2022). Application of in-situ microbubble method on SEP@MnO2/RGO composite membrane for efficient and long-acting treatment of oil field wastewater. Diamond and Related Materials, 130, 109499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109499
Xie, W., Chen, M., Wei, S., Huang, Z., & Li, Z. (2022). Lignin nanoparticles-intercalated reduced graphene oxide/glass fiber composite membranes for highly efficient oil-in-water emulsions separation in harsh environment. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 648, 129190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129190
Xu, H., Jia, W., Ren, S., & Wang, J. (2019). Magnetically responsive multi-wall carbon nanotubes as recyclable demulsifier for oil removal from crude oil-in-water emulsion with different PH levels. Carbon, 145, 229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.024
Yang, Y., Ren, Z., Zhao, S., & Guo, Z. (2020). Robust superhydrophobic composite featuring three-dimensional porous metal rubber with an embedded carbon nanofiber network for emulsion separation. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 59(13), 6172–6182. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b07053
Ye, C., Voet, V. S. D., Folkersma, R., & Loos, K. (2021). Robust Superamphiphilic membrane with a closed-loop life cycle. Advanced Materials, 33(15), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202008460
Ye, F., Zhang, Z., Mi, Y., Huang, Z., Yuan, H., Zhang, Z., & Luo, Y. (2020). Carbon nanotubes grafted with β-cyclodextrin by an ultrasonication method and its demulsification performance in oily wastewater. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 600, 124939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124939
Ye, S., Wang, B., Shi, Y., Wang, B., Zhang, Y., Feng, Y., Han, W., Liu, C., & Shen, C. (2020). Superhydrophobic and superelastic thermoplastic polyurethane/multiwalled carbon nanotubes porous monolith for durable oil/water separation. Composites Communications, 21, 100378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.100378
Yin, X., He, Y., Li, H., Ma, X., Zhou, L., He, T., & Li, S. (2021). One-step in-situ fabrication of carbon nanotube/stainless steel mesh membrane with excellent anti-fouling properties for effective gravity-driven filtration of oil-in-water emulsions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 592, 87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.02.043
Yu, Z., Shao, L., Li, X., Zeng, H., & Liu, Y. (2019). One-step preparation of sepiolite/graphene oxide membrane for multifunctional oil-in-water emulsions separation. Applied Clay Science, 181, 105208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105208
Yue, X., Li, Z., Zhang, T., Yang, D., & Qiu, F. (2019). Design and fabrication of superwetting fiber-based membranes for oil/water separation applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 364, 292–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.149
Zhang, N., Yang, X., Wang, Y., Qi, Y., Zhang, Y., Luo, J., Cui, P., & Jiang, W. (2022). A review on oil/water emulsion separation membrane material. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(2), 107257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107257
Zhang, P., Gong, J.-L., Zeng, G.-M., Song, B., Cao, W. C., Liu, H.-Y., Huan, S.-Y., & Peng, P. (2019). Novel ‘loose’ GO/MoS2 composites membranes with enhanced permeability for effective salts and dyes rejection at low pressure. Journal of Membrane Science, 574, 112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.12.046
Zhang, S., Huang, X., Wang, D., Xiao, W., Huo, L., Zhao, M., Wang, L., & Gao, J. (2020). Flexible and superhydrophobic composites with dual polymer nanofiber and carbon nanofiber network for high-performance chemical vapor sensing and oil/water separation. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c15110
Zhang, S., Liang, S., Gao, Y., Yang, W., & Huang, X. (2023). Nonpolar cross-stacked super-aligned carbon nanotube membrane for efficient wastewater treatment. Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering, 17(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-023-1630-3
Zhang, T., Bin, G., Qiu, F., Peng, X., Yue, X., & Yang, D. (2018). Preparation of carbon nanotubes/polyurethane hybrids as a synergistic absorbent for efficient oil/water separation. Fibers and Polymers, 19(10), 2195–2202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-8399-1
Zhang, X., Wang, B., Wang, B., Feng, Y., Han, W., Liu, C., & Shen, C. (2021). Superhydrophobic cellulose acetate/multiwalled carbon nanotube monolith with fiber cluster network for selective oil/water separation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 259, 117750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117750
Zhao, X., Cheng, L., Jia, N., Wang, R., Liu, L., & Gao, C. (2020). Polyphenol-metal manipulated nanohybridization of CNT membranes with FeOOH nanorods for high-flux, antifouling and self-cleaning oil/water separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 600, 117857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.117857
Zhao, Y., Guo, J., Li, Y., Zhang, X., An, A. K., & Wang, Z. (2022). Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PH-CNT membrane for emulsified oil-water separation. Desalination, 526, 115536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2021.115536
Zhou, F., Wang, Y., Dai, L., Fang, X., Kai, Q., & Zhi, X. (2022). Anchoring metal organic frameworks on nanofibers via etching-assisted strategy: Toward water-in-oil emulsion separation membranes. Separation and Purification Technology, 281, 119812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119812
Zhu, Q., Chu, Y., Wang, Z., Chen, N., Lin, L., Liu, F., & Pan, Q. (2013). Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 1(17), 5386–5393. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta00125c
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to their respective universities for providing facility of literature survey.
Data and Code Availability
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.R.: conceptualization, visualization, and writing — original draft. Z.B.B., K.R., and S.M.: project administration and writing — original draft. Z.B.B., K.R., and S.M.: investigation, formal analysis, and writing — review and editing. Z.B.B., K.R., and S.M.,: writing — review and editing, formal analysis, and writing — review and editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved it for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Babar, Z.B., Rizwan, K. & Munir, S. Multifunctional Smart Nano-membranes for the Removal of Oil-Based Pollutants from Marine Sources: A Tool for Sustainable Environment. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 80 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06864-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06864-x