Abstract
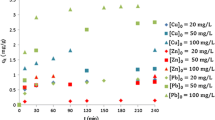
The current work presents the competitive removal of zinc (Zn) and cadmium (Cd) ions by adsorption using the roots of the Canna indica plant in order to study the metal-plant interactions at the microscopic scale that occur in constructed wetlands and phytoremediation processes. The sorption process was described in association with the data generated from Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Kinetic variables and constants were calculated, optimized, and analyzed. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model provided the best fit to the experimental data and the sorption equilibrium was achieved in nearly 300 min. The equilibrium isotherms of zinc and cadmium were described using the nonlinear models of Langmuir, Freundlich, Sips, and their multi-component equivalents. The dimensionless separation factor (RL) showed that the adsorption system in this study is favorable. The Langmuir monolayer adsorption capacities were 71.20 and 298.6 μg g−1 for Zn2+ and Cd2+ respectively. The parameters of the metal adsorption isotherm fitted better to the extended Freundlich isotherm. This study reveals the association between surface properties and the biosorption capacity of heavy metals by plant roots on the one hand and the implication of the ion exchange mechanism through chemisorption on the uptake of Zn2+ and Cd2+ ions from aqueous solution by this adsorbent on the other hand.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abbas, A., Hussain, M. A., Amin, M., Sher, M., Tahir, M. N., & Tremel, W. (2015). Succinate-bonded pullulan: An efficient and reusable super-sorbent for cadmium-uptake from spiked high-hardness groundwater. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 37, 51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.04.013
Abbas, A., Hussain, M. A., Sher, M., Irfan, M. I., Tahir, M. N., Tremel, W., Hussain, S. Z., & Hussain, I. (2017). Design, characterization and evaluation of hydroxyethylcellulose based novel regenerable supersorbent for heavy metal ions uptake and competitive adsorption. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 102, 170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.024
Abdelwaheb, M., Ayeb, A., Dhaouadi, H., Dridi-Dhaouadi, S., & Peña, A. (2022). Risk of water contamination: adsorption of dimethoate on a Mediterranean soil. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2022.2058244
Al-Ghouti, M. A., & Da’ana, D. A. (2020). Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 393, 122383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
Ali, A., Ajaz Hussain, M., Abbas, A., Tahir Haseeb, M., Azhar, I., Muhammad, G., Hussain, S.Z, Hussain, I., Alotaibi, N. F. (2023). Succinylated Salvia spinosa hydrogel: Modification, characterization, cadmium-uptake from spiked high-hardness groundwater and statistical analysis of sorption data. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 376, 121438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2023.121438
Clemens, S., Palmgren, M. G., & Krämer, U. (2002). A long way ahead: Understanding and engineering plant metal accumulation. Trends in Plant Science, 7(7), 309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02295-1
Dhouibi, N., Binous, H., Dhaouadi, H., & Dridi-Dhaouadi, S. (2020). Hydrodistillation residues of Centaurea nicaeensis plant for copper and zinc ions removal: Novel concept for waste re-use. Journal of Cleaner Production, 261, 121106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121106
Ebrahimzadeh Rajaei, G., Aghaie, H., Zare, K., & Aghaie, M. (2013). Adsorption of Cu(II) and Zn(II) ions from aqueous solutions onto fine powder of Typha latifolia L. root: Kinetics and isotherm studies. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 39(8), 3579–3594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-012-0864-7
Farid-ul-Haqa, M., Alia, A., Hussain, M. A., Abbasa, A., Kausarb, F., Aminc, H. M., Shera, M., Hussain, S. Z., & Hussain, I. (2021). Chemical modification of a polysaccharide from Artemisia vulgaris engenders a supersorbent for the removal of Cd2+ from spiked high-hardness groundwater. Desalination and Water Treatment, 212, 129–142.
Fawzy, M., Nasr, M., Adel, S., Nagy, H., & Helmi, S. (2016). Environmental approach and artificial intelligence for Ni(II) and Cd(II) biosorption from aqueous solution using Typha domingensis biomass. Ecological Engineering, 95, 743–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.07.007
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2010). Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 156(1), 2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Genchi, G., Sinicropi, M. S., Lauria, G., Carocci, A., & Catalano, A. (2020). The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113782
Ghezali, K., Bentahar, N., Barsan, N., Nedeff, V., & Moșneguțu, E. (2022). Potential of canna indica in vertical flow constructed wetlands for heavy metals and nitrogen removal from algiers refinery wastewater. Sustainability, 14(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084394
Girdhar, M., Tabassum, Z., Singh, K., & Mohan, A. (2022). A review on the resistance and accumulation of heavy metals by different microbial strains. Biodegradation Technology of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants, 219.
Girish, C. (2017). Various isotherm models for multicomponent adsorption: A review. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol, 8(10), 80–86.
Hussain, M. A., Abbas, A., Habib, M. G., Ali, A., Farid-ul-Haq, M., Hussain, M., Shafiq, Z., & Irfan, M. I. (2021). Adsorptive removal of Ni (II) and Co (II) from aqueous solution using succinate-bonded polysaccharide isolated from Artemisia vulgaris seed mucilage. Desalination and Water Treatment, 231, 182–195.
Hsini, N., Abdelwaheb, M., Dhaouadi, H., & Dridi-Dhaouadi, S. (2020). Valorization of solid wastes from Dittrichia essential oil extraction as biosorbents for cadmium removal: biosorbent characterizations and isotherm modeling. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 17(11), 4611–4622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02803-z
Iqbal, M., Saeed, A., & Zafar, S. I. (2009). FTIR spectrophotometry, kinetics and adsorption isotherms modeling, ion exchange, and EDX analysis for understanding the mechanism of Cd2+ and Pb2+ removal by mango peel waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(1), 161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.141
Jamwal, P., Raj, A. V., Raveendran, L., Shirin, S., Connelly, S., Yeluripati, J., Richards, S., Rao, L., Helliwell, R., & Tamburini, M. (2021). Evaluating the performance of horizontal sub-surface flow constructed wetlands: A case study from southern India. Ecological Engineering, 162, 106170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2021.106170
Jiang, X., Zhang, S., Yin, X., Tian, Y., Liu, Y., Deng, Z., & Wang, L. (2023). Contrasting effects of a novel biochar-microalgae complex on arsenic and mercury removal. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 262, 115144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115144
Karungamye, P. N. (2022). Potential of Canna indica in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: A review. Conservation, 2(3), 499–513. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation2030034
Khan, F. S. A., Mubarak, N. M., Tan, Y. H., Khalid, M., Karri, R. R., Walvekar, R., Abdullah, E. C., Nizamuddin, S., & Mazari, S. A. (2021). A comprehensive review on magnetic carbon nanotubes and carbon nanotube-based buckypaper for removal of heavy metals and dyes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 413, 125375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125375
Komkiene, J., & Baltrenaite, E. (2016). Biochar as adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions [cadmium(II), copper(II), lead(II), zinc(II)] from aqueous phase. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13(2), 471–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0873-3
Kumar, P. S., Ramalingam, S., Sathyaselvabala, V., Kirupha, S. D., Murugesan, A., & Sivanesan, S. (2012). Removal of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution by agricultural waste cashew nut shell. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 29(6), 756–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0259-2
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40(9), 1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Lodhi, B. A., Abbas, A., Hussain, M. A., Hussain, S. Z., Sher, M., & Hussain, I. (2019). Design, characterization and appraisal of chemically modified polysaccharide based mucilage from Ocimum basilicum (basil) seeds for the removal of Cd(II) from spiked high-hardness ground water. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 274, 15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.056
Lopez-Ramon, M. V., Stoeckli, F., Moreno-Castilla, C., & Carrasco-Marin, F. (1999). On the characterization of acidic and basic surface sites on carbons by various techniques. Carbon, 37(8), 1215–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00317-0
Lorenz, P., Meier, L., & Kahr, G. (1999). Determination of the cation exchange capacity (CEC) of clay minerals using the complexes of copper (II) ion with triethylenetetramine and tetraethylenepentamine. Clays and clay minerals, 47(3), 386–388.
Luo, X., Zhang, Z., Zhou, P., Liu, Y., Ma, G., & Lei, Z. (2015). Synergic adsorption of acid blue 80 and heavy metal ions (Cu2+/Ni2+) onto activated carbon and its mechanisms. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 27, 164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.12.031
Mahmood, T., Malik, S. A., & Hussain, S. T. (2010). Biosorption and recovery of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by Eichhornia crassipes (water hyacinth) ash. BioResources, 5(2), 1244–1256.
Mishra, S., Bharagava, R. N., More, N., Yadav, A., Zainith, S., Mani, S., & Chowdhary, P. (2019). Heavy metal contamination: An alarming threat to environment and human health. In R. C. Sobti, N. K. Arora, & R. Kothari (Eds.), Environmental Biotechnology: For Sustainable Future (pp. 103–125). Springer Singapore.
Mustapha, H. I., van Bruggen, J. J. A., & Lens, P. N. L. (2018). Fate of heavy metals in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands treating secondary treated petroleum refinery wastewater in Kaduna. Nigeria. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 20(1), 44–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2017.1337062
Nedjimi, B. (2021). Phytoremediation: A sustainable environmental technology for heavy metals decontamination. SN Applied Sciences, 3(3), 286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04301-4
Peng, L., Chen, S., Song, H., Zheng, M., Luo, S., & Tie, B. (2023). Quick removal of suspended cadmium from irrigation water using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes)-phosphoric fertilizer. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 234(6), 356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06365-x
Pera-Titus, M. (2011). Thermodynamic analysis of type VI adsorption isotherms in MFI zeolites. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 115(8), 3346–3357. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp109449q
Sabeen, M., Mahmood, Q., Irshad, M., Fareed, I., Khan, A., Ullah, F., Hussain, J., Hayat, Y., & Tabassum, S. (2013). Cadmium phytoremediation by <i>Arundo donax</i> L. from contaminated soil and water. BioMed Research International, 2013, 324830. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/324830
Sanka, P. M., Rwiza, M. J., & Mtei, K. M. (2020). Removal of selected heavy metal ions from industrial wastewater using rice and corn husk biochar. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 231(5), 244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04624-9
Sears, G. W. (1956). Determination of specific surface area of colloidal silica by titration with sodium hydroxide. Analytical Chemistry, 28(12), 1981–1983. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60120a048
Sen Gupta, S., & Bhattacharyya, K. G. (2008). Immobilization of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) ions on kaolinite and montmorillonite surfaces from aqueous medium. Journal of Environmental Management, 87(1), 46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.01.048
Shrestha, R., Ban, S., Devkota, S., Sharma, S., Joshi, R., Tiwari, A. P., Kim, H., & Joshi, M. K. (2021). Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4), 105688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105688
Simonin, J.-P. (2016). On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chemical Engineering Journal, 300, 254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.079
Sips, R. (1948). On the structure of a catalyst surface. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 16(5), 490–495. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1746922
Sotelo, J. L., Ovejero, G., Rodríguez, A., Álvarez, S., Galán, J., & García, J. (2014). Competitive adsorption studies of caffeine and diclofenac aqueous solutions by activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal, 240, 443–453.
Srivastava, V. C., Mall, I. D., & Mishra, I. M. (2008). Removal of cadmium(II) and zinc(II) metal ions from binary aqueous solution by rice husk ash. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 312(2), 172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.06.048
Subhashini, V., & Swamy, A. (2014). Phytoremediation of metal (Pb, Ni, Zn, Cd and Cr) contaminated soils using Canna indica. Current World. Environment, 9(3), 780–784. https://doi.org/10.12944/CWE.9.3.26
Szatanik-Kloc, A., Szerement, J., & Józefaciuk, G. (2017). The role of cell walls and pectins in cation exchange and surface area of plant roots. Journal of Plant Physiology, 215, 85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2017.05.017
Velusamy, S., Roy, A., Sundaram, S., & Kumar Mallick, T. (2021). A review on heavy metal ions and containing dyes removal through graphene oxide-based adsorption strategies for textile wastewater treatment. The Chemical Record, 21(7), 1570–1610. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202000153
Verma, L., & Singh, J. (2019). Synthesis of novel biochar from waste plant litter biomass for the removal of Arsenic (III and V) from aqueous solution: A mechanism characterization, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of Environmental Management, 248, 109235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.07.006
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank their colleagues and the technical staff at the Laboratory of Hydrocarbons Technology, and the Laboratory of Treatment and Forming of Fibrous Polymers for their invaluable assistance.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghezali, K., Abdelwaheb, M., Nedeff, V. et al. Short-term Laboratory Adsorption of Zinc and Cadmium Ions from Aqueous Solutions to Ground Canna indica Roots. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 729 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06740-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06740-8