Abstract
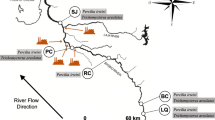
Aquatic environments are impacted by the use of pesticides in agricultural areas, and to evaluate its impact on wildlife, in situ exposure has become an alternative. In this study, the fish Rhamdia quelen was used as a bioindicator for the in situ experimental protocol. The fish were exposed for 96 h in three different sites at Vacacaí river located in Southern Brazil. After exposure, the brain, gills, liver, and muscles were collected for biochemical assays. Biomarkers of oxidative damage, neurotoxicity, detoxification, and antioxidant parameters were analyzed. The calculation of the Integrated Biomarker Response Index (IBR) was used to assess the responses of the biomarkers as an integrated approach. The most significant biochemical changes were recorded in places close to agricultural crops and in urban areas. The main results show elevated levels of carbonyl proteins in the brain, gills, and liver. Disruptions in acetylcholinesterase activity in the muscle. Other results include changes in glutathione S-transferase activity in the muscle and liver of fish indicating potential contamination. Furthermore, R. quelen proved to be an excellent bioindicator for in situ experiments, since the biomarkers responded in a manner consistent with the characteristics of the environment in which they were inserted.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ahmad F, Noldus LPJJ, Tegelenbosch R a J, Richardson MK (2012). Zebrafish embryos and larvae in behavioural assays. Behaviour. 149:1241–1281.
Amado, L. L., Garcia, M. L., Ramos, P. B., et al. (2009). A method to measure total antioxidant capacity against peroxyl radicals in aquatic organisms: Application to evaluate microcystins toxicity. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 2115–2123.
Amaral, A. M. B., Gomes, J. L. C., Weimer, G. H., Marins, A. T., Loro, V. L., & Zanella, R. (2018). Seasonal implications on toxicity biomarkers of Loricariichthys anus (Valenciennes, 1835) from a subtropical reservoir. Chemosphere, 191, 876–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.114
Amaral, A. M. B.; Moura, L. K.; Pellegrin, D.; Guerra, L. J.; Cerezer, F. O.; Saibt, N.; Prestes, O. D.; Zanella, R.; Loro, V. L.; Clasen, B. (2020). Seasonal factors driving biochemical biomarkers in two fish species from a subtropical reservoir in southern Brazil: An integrated approach. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115168
Baldisserotto B. (2020). Espécies Nativas para Piscicultura no Brasil. 3ª ed. Editora Universidade Federal de Santa Maria (UFSM). ISBN: 978–85–7391–347–7. l, 544 pg.
Barhoumi, B., Clrandeau, C., Gourves, P. Y., et al. (2014). Pollution biomonitoring in the Bizerte lagoon (Tunisia), using combined chemical and biomarker analyses in grass goby, Zosterisessor ophiocephalus (Teleostei, Gobiidae). Marine Environment Research, 101, 184–195.
Barillet, S., Adam, C., Palluel, O., & Devaux, A. (2007). Bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, and neurotoxicity in Daniorerio exposed to different isotopic compositions of uranium. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 26, 497–505.
Beauvais, S. L., Jones, S. B., Parris, J. T., Brewer, S. K., & Little, E. E. (2001). Cholinergic and behavioral neurotoxicity of carbaryl and cadmium to larval rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ecotoxicol. Environ., 49, 84–90.
Becker, A. G., Moraes, B. S., Menezes, C. C., et al. (2009). Pesticide contamination of water alters the metabolism of juvenile silver catfish, Rhamdia Quelen Ecotoxicol Environmental, 72, 1734–1739.
Becker, A. G., Parodi, T. V., Heldwein, C. G., et al. (2012). Transportation of silver catfish, Rhamdia quelen, in water with eugenol and the essential oil of Lippia alba. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 38(3), 789–796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-011-9562-4. Epub 2011 Oct 5.
Belanger SE, Balon EK, Rawlings JM (2010). Saltatory ontogeny of fishes and sensitive early life stages for ecotoxicology tests. Aquatic Toxicology, 97, 88–95.
Beliaeff, B., & Burgeot, T. (2002). Integrated biomarker response: a useful tool for ecological risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem, 78, 370–381.
Bradford MM (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Brasil (2005). Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. Resolução nº 357, de 17 de março de 2005 (CONAMA). Dispõe sobre a classificação dos corpos de água e diretrizes ambientais para o seu enquadramento, bem como estabelece as condições e padrões de lançamento de efluentes, e dá outras providências.
Braun, N., Lima, R. L., Moraes, B., et al. (2006). Survival, growth and biochemical parameters of silver catfish, Rhamdia quelen (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824), juveniles exposed to different dissolved oxygen levels. Aquaculture Research., 37, 1524–1531.
Carneiro, P. C. F., & Mikos, J. D. (2005). Freqüência alimentar e crescimento de alevinos de jundiá. Rhamdia Quelen. Ciência Rural., 35, 187–191.
Cerezer, C.; Marins, A. T.; Cerezer, F. O.; Severo, E. S.; Leitemperger, J. W.; Grubel Bandeira, N. M.; Zanella, R.; Loro, V. L.; Santos, S. (2020). Influence of pesticides and abiotic conditions on biochemical biomarkers in Aegla aff. longirostri (crustacea, anomura): Implications for conservation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 203, 110982.
Chipari-Gomes, A. R., Gomes, L. C., & Baldisserotto, B. (1999). Lethal temperatures for Rhamdia quelen fingerlings (Pimelodidae). Journal of Applied Aquaculture., 9, 11–21.
Chua, E. M., Flint, N., Wilson, S. P., & Vink, S. (2018). Potential for biomonitoring metals and metalloids using fish condition and tissue analysis in an agricultural and coal mining region. Chemosphere, 202, 598–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.080
Clasen, B., Leitemperger, J., Murussi, C., Pretto, A., Menezes, C., Dalabona, F., Marchezan, E., Adaime, M. B., Zanella, R., & Loro, V. L. (2014). Carbofuran promotes biochemical changes in carp exposed to rice field and laboratory conditions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 101, 77–82.
Clasen, B., Loro, V. L., Murussi, C. R., Pretto, A., Menezes, C., Dalabona, F., Marchezan, E., Adaime, M. B., & Zanella, R. (2018). Bioaccumulation and oxidative stress caused by pesticides in Cyprinus carpio reared in a rice-fish system. Science of the Total Environment, 626, 737–743.
Colin, N., Porte, C., Fernandes, D., Barata, C., et al. (2015). Ecological relevance of biomarkers in monitoring studies of macro-invertebrates and fish in Mediterranean rivers. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.099
Costa-Silva DG, Nunes MEM, Wallau GL, et al. (2015). Oxidative stress markers in fish (Astyanax sp. and Danio rerio) exposed to urban and agricultural effluents in the Brazilian Pampa biome. Environmental Science Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4737-7.
Crestani, M., Menezes, C., Glusczak, L., et al. (2007). Effect of clomazone herbicide on biochemical and histological aspects of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) and recovery pattern. Chemosphere, 67, 2305–2311.
Cunha, M. A. D., Zeppenfeld, C. C., Garcia, L. D. O., et al. (2010). Anesthesia of silver catfish with eugenol: Time of induction, cortisol response and sensory analysis of fillet. Ciência Rural., 40, 2107–2114.
Dalzochio, T., Rodrigues, G. Z. P., Simões, L. A. R., de Souza, M. S., Petry, I. E., Andriguetti, N. B., Silva, G. J. H., Basso, L., & da Silva Gehlen, G. (2018). In situ monitoring of the Sinos River, southern Brazil: Water quality parameters, biomarkers, and metal bioaccumulation in fish. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(10), 9485–9500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1244-7
Donato, Fadaime MB, Zanella R. Development of a multiresidue method for pesticide analysis in drinking water by solid phase extraction and determination by gas and liquid chromatography with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. 26:2077–2087.
Doyotte, A., Cossu, C., Jacquin, M. C., Babut, M., & Vasseur, P. (1997). Antioxidant enzymes, glutathione and lipid peroxidation as relevant biomarkers of experimental or field exposure in the gills and the digestive gland of the freshwater bivalve Unio tumidus. Aquatic Toxicology, 39, 93–110.
Draper, H. H., & Hadley, M. (1990). Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. MethodsEnzymol., 186, 421–431.
Ellman, G. L. (1959). Tissue Sulfhydryl Groups. Arch BiochemBiophys., 82, 70–77.
FAO – Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2018). Pesticides - Average use in Brazil. <http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/EP/visualize>. Accessed 20 Oct 2018.
Fernández-Vega, C., Sancho, E., Ferrando, M. D., & Andreu, E. (2002). Thiobencarb-induced changes in acetylcholinesterase activity of the fish Anguilla anguilla. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 72, 55–63.
Ferreira, D., Motta, A. C., Kreutz, L. C., Toni, C., Loro, V. L., & Barcellos, L. J. G. (2010). Assessment of oxidative stress in Rhamdia quelen exposed to agrichemicals. Chemosphere, 79, 914–921.
Gao, X. P., Li, G. N., Li, G. R., & Zhang, C. (2015). Modeling the effects of point and non-point source pollution on a diversion channel from Yellow River to an artificial lake in China. Water Science and Technology., 71(12), 1806–1814.
Habig, W. B., Pabst, M. J., & Jakoby, W. B. (1974). Glutathione S-transferase, the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 249, 7130–7139.
Hauser-Davis R a., Oliveira TF, Silveiraa. M, Silva TB, Ziolli RL. (2010). Case study: Comparing the use of nonlinear discriminating analysis and Artificial Neural Networks in the classification of three fish species: acaras (Geophagus brasiliensis), tilapias (Tilapia rendalli) and mullets (Mugil liza). Ecology Information, 5, 474–478.
Hernández-Moreno, D., Soler, F., Míguez, M. P., & Pérez-López, M. (2010). Brain acetylcholinesterase, malondialdehyde and reduced glutathione as biomarkers of continuous exposure of tench, Tincatinca, to carbofuran or deltamethrin. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 4976–4983.
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística – IBGE (2010). IBGE – cidades. < https://cidades.ibge.gov.br>. Accessed 14 Jan 2023.
Klobučar, G. I. V., Malev, O., Šrut, M., et al. (2012). Genotoxicity monitoring of freshwater environments using caged crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus). Chemosphere, 87, 62–67.
Lima, R. L., Braun, N., Kochhann, D., et al. (2011). Survival, growth and metabolic parameters of silver catfish, Rhamdia quelen, juveniles exposed to different waterborne nitrite levels. Neotropical Ichthyology., 9(1), 147–152.
Loro, V. L., Murussi, C., Menezes, C., Leitemperger, J., et al. (2015). Spatial and temporal biomarkers responses of Astyanax jacuhiensis (Cope, 1894) (Characiformes: Characidae) from the middle rio Uruguai. Brazil. Neotrop. Ichthyol., 13, 569–578.
Machado, A. A. D. S., Wood, C. M., Bianchini, A., & Gillis, P. L. (2014). Responses of biomarkers in wild freshwater mussels chronically exposed to complex contaminant mixtures. Ecotoxicology, 23, 1345–1358.
Marchesan, E., Sartori, G. M. S., De, A. L. A., et al. (2010). Resíduos de agrotóxicos na água de rios da Depressão Central do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Brasil. Ciência Rural., 40, 1053–1059.
Marins AT, Severo ES, Leitemperger JW, Cerezer C, Muller TE, Costa MD, Weimer G. H, Bandeira NMG, Prestes OD, Zanella R, Loro VL. (2020). Assessment of river water quality in an agricultural region of Brazil using biomarkers in a native neotropical fish, Astyanax spp. (Characidae). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 104, 575–581.
Menezes, C. C., Loro, V. L., da Fonseca, M. B., et al. (2011). Oxidative parameters of Rhamdia quelen in response to commercial herbicide containing clomazone and recovery pattern. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 100, 145–150.
Menezes C, Leitemperger J, Toni C, et al. (2013). Comparative study on effects of dietary with diphenyldiselenide on oxidative stress in carp (Cyprinus carpio) and silver catfish (Rhamdia sp.) exposed to herbicide clomazone. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 36, 706–714.
Miron, D. S., Moraes, B., Becker, A. G., et al. (2008). Ammonia and pH effects on some metabolic parameters and gill histology of silver catfish, Rhamdia quelen (Heptapteridae). Aquaculture, 277, 192–196.
Misra, H. P., & Fridovich, I. (1972). The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 247, 3170–3175.
Müller, T. E., Nunes, M. E., Menezes, C. C., et al. (2017). Sodium selenite prevents paraquat-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish. Molecular Neurobiology, 55(3), 1928–1941.
Murussi, C. R., Costa, M., Menezes, C., et al. (2015). Integrated assessment of biomarker response in carp (Cyprinus carpio) and silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to clomazone. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 68, 646–654.
Murussi, C. R., Costa, M. D., Leitemperger, J. W., et al. (2016). Exposure to different glyphosate formulations on the oxidative and histological status of Rhamdia quelen. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 42, 445–455.
Nelson, D. P., & Kiesow, L. A. (1972). Enthalpy of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by catalase at 25ºC (with molar extinction coefficients of H2O2 solutions in the UV). Analytical Biochemistry, 49, 474–478.
Oikari, A. (2006). Caging techniques for field exposures of fish to chemical contaminants. Aquatic Toxicology, 78(4), 370–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.03.010
Oost, D., Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. P. E. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in en v ironmental risk assessment: A review. Environmental Toxicol. Pharmacol., 13, 57–149.
Parvez, S., & Raisuddin, S. (2005). Protein carbonyls: Novel biomarkers of exposure to oxidative stress-inducing pesticides in freshwater fish Channa punctate (Bloch). Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 20, 112–117.
Payne, J. F., Mathieu, A., Melvin, W., & Fancey, L. L. (1996). Acetylcholinesterase, an old biomarker with a new future? Field trials in association with two urban rivers and a paper mill in Newfoundland. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 32, 225–231.
Pretto, A., Loro, V. L., Menezes, C., et al. (2011). Commercial formulation containing quinclorac and metsulfuron-methyl herbicides inhibit acetylcholinesterase and induce biochemical alterations in tissues of Leporinus obtusidens. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 74, 336–341.
Sanchez, W., Burgeot, T., & Porcher, J. M. (2013). A novel ‘Integrated Biomarker Response’ calculation based on reference deviation concept. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 2721–2725.
Saunders, D. L., Meeuwig, J. J., & Vincent, A. C. J. (2002). Freshwater protected areas: Strategies for conservation. Conservation Biology, 16, 30–41.
Scarcia, P., Calamante, G., & Torre, F. (2014). Biomarker responses in caged carp (Cyprinus carpio) and native collected fish (Leporinus obtusidens) in the Rio de la Plata Estuary, Argentina. Environ. Toxicol., 29(8), 950–960.
Soininen, J., & Kononen, K. (2004). Comparative study of monitoring South-Finnish rivers and streams using macroinvertebrate and benthic diatom community structure. Aquatic Ecology, 38, 63–75.
Vieira CED, Costa PG, Lunardelli B, et al. (2016). Multiple biomarker responses in Prochilodus lineatus subjected to short-term in situ exposure to streams from agricultural areas in Southern Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 542:44–56.
Weissteiner, C. J., Pistocchi, A., Marinov, D., Bouraoui, F., & Sala, S. (2014). Science of the Total Environment An indicator to map diffuse chemical river pollution considering buffer capacity of riparian vegetation — A pan-European case study on pesticides. Science of the Total Environment, 484, 64–73.
Xing, H., Li, S., Wang, Z., Gao, X., Xu, S., & Wang, X. (2012). Histopathological changes and antioxidant response in brain and kidney of common carp exposed to atrazine and chlorpyrifos. Chemosphere, 88, 377–383.
Zaions, M. I., & Baldisseroto, B. (2000). Na+ and K+ body levels and survival of fingerlings of Rhamdia quelen (Siluriformes, Pimelodidae) exposed to acute changes of water pH. Ciência Rural., 30, 1041–1045.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Universidade Federal de Santa Maria and Universidade Federal do Pampa for the support and facilities.
Funding
Coordenação de aperfeiçoamento de pessoal de nível superior (CAPES) provided scholarship and undergraduate student grant. Vania Lucia Loro received CNPq research fellowship (process number: 309314/2017–8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Severo, E., Marins, A., de Menezes, C. et al. Biomarkers’ Responses of Rhamdia quelen Exposed In Situ on a Brazilian River Located in Agricultural Areas. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 144 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06160-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06160-8