Abstract
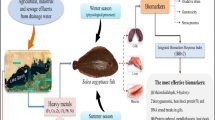
Subcellular biochemical biomarkers are valuable early warning indicators of environmental contaminant effects. Thus, the present study evaluated several biomarkers and the relationships among them in wild freshwater mussels (Lasmigona costata) from a gradient of metal exposure and differential levels of other urban-related influences in the Grand River (ON, Canada). The biomarkers examined are related to metal exposure [gill ion and metal concentrations (Na, K, Ca, Mg, Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn)], oxidative status [reactive oxygen species (ROS), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), antioxidant capacity (ACAP)], sulfhydryl (SH) metabolism [glutathione (GSH), protein sulfhydryl groups (SH protein), glutathione S-transferase (GST), glutathione reductase (GR)], and lipid peroxidation. Gill metal concentration increased proportionally to waterborne metal concentration and disturbances in osmotic and divalent cations (Ca and Mg) concentrations were observed. This suggests that the observed effects are associated with metal exposure, although simultaneous relationships with other contaminants are also possible. Oxidative status biomarkers (ROS, SOD, CAT and ACAP) were more sensitive to urban-influences than gill metal concentration. In contrast, biomarkers involving SH metabolism (GSH, SH protein, total SH, GR and GST) were more correlated with gill metal concentration. Oxidative damage occurred when both metal and urban-related influences were high. Mechanistically, the way of dealing with oxidative stress changed when mussels were exposed to high levels of contaminants. The reduction in ROS content, SOD and CAT activity, and ACAP accompanying the stimulation of detoxification metabolism via SH (GSH and SH protein contents, GST and GR activities) and their association with gill metal concentration are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsop D, Wood CM (2011) Metal uptake and acute toxicity in zebrafish: common mechanisms across multiple metals. Aquat Toxicol 105:385–393
Amado LL, Garcia ML, Ramos PB, Freitas RF, Zafalon B, Ferreira JLR, Yunes JS, Monserrat JM (2009) A method to measure total antioxidant capacity against peroxyl radicals in aquatic organisms: Application to evaluate microcystins toxicity. Sci Tot Environ 407:2115–2123
Beutler E (1975) Red cell metabolism: a manual of biochemical methods. Grune & Straton, New York
Box A, Sureda A, Galgani F, Pons A, Deudero S (2007) Assessment of environmental pollution at Balearic Islands applying oxidative stress biomarkers in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Comp Biochem Physiol C 146:531–539
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1975) Purification and characterization of the flavoenzyme glutathione reductase from rat liver. J Biol Chem 250:5475–5480
Cooke S (2006) Water quality in the Grand River: a summary of current conditions (2000–2004) and long term trends. Grand River Conservation Authority. http://www.grandriver.ca/water/2006_WaterQuality_complete.pdf Accessed Jan 2014
Depledge MH, Aagaard A, Györkös P (1995) Assessment of trace metal toxicity using molecular, physiological and behavioural biomarkers. Mar Poll Bull 31:9–27
Farcy E, Gagné F, Martel L, Fortier M, Trépanier S, Brousseau P, Fournier M (2011) Short-term physiological effects of a xenobiotic mixture on the freshwater mussel Elliptio complanata exposed to municipal effluents. Environ Res 111:1096–1106
Frank R, Logan L (1988) Pesticide and industrial chemical residues at the mouth of the Grand, Saugeen and Thames rivers, Ontario, Canada, 1981–85. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 17:741–754
Gagné F, André C, Cejka P, Hausler R, Fournier M (2011) Evidence of neuroendocrine disruption in freshwater mussels exposed to municipal wastewaters. Sci Tot Environ 409:3711–3718
Giacomin M, Gillis PL, Bianchini A, Wood CM (2013) Interactive effects of copper and dissolved organic matter on sodium uptake, copper bioaccumulation, and oxidative stress in juvenile freshwater mussels (Lampsilis siliquoidea). Aquat Toxicol 144–145:105–115
Géret F, Jouan A, Turpin V, Bebianno MJ, Cosson RP (2002) Influence of metal exposure on metallothionein synthesis and lipid peroxidation in two bivalve mollusks: the oyster (Crassostreagigas) and the mussel (Mytilus edulis). Aquat Living Resour 15:61–66
Géret F, Serafim A, Bebianno MJ (2003) Antioxidant enzyme activities, metallothioneins and lipid peroxidation as biomarkers in Ruditapes decussatus? Ecotoxicology 12:417–426
Gillis PL (2011) Assessing the toxicity of sodium chloride to the glochidia of freshwater mussel: implications for salinization of surface waters. Environ Pollut 159:1702–1708
Gillis PL (2012) Cumulative impacts of urban runoff and municipal wastewater effluents on wild freshwater mussels (Lasmigona costata). Sci Total Environ 431:348–356
Gillis PL, Gagné F, McInnis R, Hooey TM, Choy ES, André C, Hoque ME, Metcalfe CD (2014a) The impact of municipal wastewater effluents on field-deployed freshwater mussels on the Grand River (ON). Environ Toxicol Chem 33:131–143
Gillis PL, Higgins SK, Jorge MB (2014b) Evidence of oxidative stress in wild freshwater mussels (Lasmigona costata) chronically exposed to urban-derived contaminants. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 102:62–69
Gonzalez-Rey M, Bebianno MJ (2011) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) ibuprofen distresses antioxidant defense system in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis gills. Aquat Toxicol 105:264–269
Grand River Conservation Authority (2013) http://www.grandriver.ca/. Accessed 10 Sept 2013
Grosell M, Nielsen C, Bianchini A (2002) Sodium turnover rate determines sensitivity to acute copper and silver exposure in freshwater animals. Comp Biochem Physiol C 133:287–303
Jorge MB, Loro VL, Bianchini A, Wood CM, Gillis PL (2013) Mortality, bioaccumulation and physiological responses in juvenile freshwater mussels (Lampsilis siliquoidea) chronically exposed to copper. Aquat Toxicol 123:137–147
Keen JH, Habig WH, Jakoby WB (1976) Mechanism for several activities of the glutathione-S-transferase. J Biol Chem 20:6183–6188
Loomer HA, Cooke SE (2011) Water quality in the Grand River watershed: current conditions and trends (2003–2008). Grand River Conservation Authority/ http://www.grandriver.ca/water/2011_WaterQualityReport.pdf. Accessed Dec 2013
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101:13–30
Lydeard C, Cowie RH, Ponder WF, Bogan AE, Bouchet P, Clark SA, Cummings KW, Frest TJ, Gargominy O, Herbert DG, Hershler R, Perez KE, Roth B, Seddon M, Strong EE, Thompson FG (2004) The global decline of nonmarine mussels. BioScience 54:321–330
Machado AAS, Hoff MLM, Klein RD, Cardozo JG, Giacomin MM, Pinho GLL, Bianchini A (2013) Biomarkers of waterborne copper exposure in the guppy Poecilia vivipara acclimated to salt water. Aquat Toxicol 138–139:60–69
Mackie GL (1996) Diversity and status of Unionidae (Bivalvia) in the Grand River, a tributary of Lake Erie, and its drainage basin. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, Peterborough
Martín-Díaz ML, Gagné F, Blaise C (2009) The use of biochemical responses to assess ecotoxicological effects of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) after injection in the mussel Elliptio complanata. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 28:237–242
Mazon AF, Monteiro EAS, Pinheiro GHD, Fernandes MN (2002) Hematological and physiological changes induced by short-term exposure to copper in the freshwater fish Prochilodus scrofa. Braz J Biol 62:621–631
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase an enzymatic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6065
Metcalfe CM, Miao XS, Koenig BG, Struger J (2003) Distribution of acidic and neutral drugs in surface waters near sewage treatment plants in the lower Great Lakes, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2881–2889
Metcalfe CD, Chu S, Judt C, Li H, Oakes KD, Servos MR, Andrews DM (2010) Antidepressants and their metabolites in municipal waste water, and downstream exposure in an urban watershed. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:79–89
Metcalfe-Smith JL, Staton SK, Mackie GL, Lang NM (1998) Changes in the biodiversity of freshwater mussels in the Canadian water of lower Great Lakes drainage basin over the past 140 years. J Great Lakes Res 24:845–858
Metcalfe-Smith JL, Mackie GL, Maio JD, Staton SK (2000) Changes over time in the diversity and distribution of freshwater mussels (Unionidae) in the Grand River, southwestern Ontario. J Great Lakes Res 26:445–459
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Monserrat JM, Martínez PB, Geracitano LA, Amado LL, Martins CMG, Pinho GLL, Chaves IS, Ferreira-Cravo M, Ventura-Lima J, Bianchini A (2007) Pollution biomarkers in estuarine animals: Critical review and new perspectives. Comp Biochem Physiol C 146:221–234
Nemerow NL (1991) Stream, lake, estuary, and ocean pollution, 2nd edn. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Nenadic O, Greenacre M (2007) Correspondence analysis in R, with two- and three-dimensional graphics: the ca package. J Stat Softw 20(3). http://www.jstatsoft.org/v20/i03/.Accessed 19 Dec 2013
Neves RJ, Bogan AE, Williams JD, Ahlstedt SA, Hartfield PW (1997) Status of aquatic mollusks in the southeastern United States: a downward spiral of diversity. In: Benz GW, Collins DE (eds) Aquatic fauna in peril: the southeastern perspective special publication 1, Southeast Aquatic Research Institute, Lenz Design and Communications, Decatur, GA, pp 43–85
Nogueira LS, Wood CM, Gillis PL, Bianchini A (2013) Isolation and fractionation of gill cells from freshwater (Lasmigona costata) and seawater (Mesodesma mactroides) bivalves for use in toxicological studies with copper. Cytotechnology 65:773–783
Oliveira LF, Souza MM (2007) Aquatic invertebrates under waterborne lead exposure: Ionic and osmotic balance. Comp Biochem Physiol A 148:S66–S79
Ontario Provincial Water Quality Monitoring Network (2012) Website. http://www.ene.gov.on.ca/environment/en/monitoring_and_reporting/provincial_water_quality_monitoring_network/. Accessed 13 Jan 2012
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 9 Nov 2013
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound and non-protein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Serafim A, Lopes B, Company R, Cravo A, Gomes T, Sousa V, Bebianno MJ (2011) A multi-biomarker approach in cross-transplanted mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicology 20:1959–1974
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radical Biol Med 18:321–336
Strayer DL, Downing JA, Haag WR, King TL, Layzer JB, Newton TJ, Nichols SJ (2004) Changing perspectives on pearly mussels, North America’s most imperiled animals. Bioscience 54:429–439
Tetreault GR, Bennett CJ, Shires K, Knight B, Servos MR, McMaster ME (2011) Intersex and reproductive impairment of wild fish exposed to multiple municipal wastewater discharges. Aquat Toxicol 104:278–290
Viarengo A, Lowe D, Bolognesi C, Fabbri E, Koehler A (2007) The use of biomarkers in biomonitoring: a 2-tier approach assessing the level of pollutant-induced stress syndrome in sentinel organisms. Comp Biochem Physiol C 146:281–300
Viarengo A, Nott JA (1993) Mechanisms of heavy metal cation homeostasis in marine invertebrates. Comp Physiol Chem C 104:355–372
Wang S, Oakes KD, Bragg LM, Pawliszyn J, Dixon G, Servos MR (2011) Validation and use of in vivo solid phase micro-extraction (SPME) for the detection of emerging contaminants in fish. Chemosphere 85:1472–1480
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sarah Higgins, Rodney McInnis and Tina Hooey (Environment Canada) for field and laboratory assistance. Financial support was provided by the International Development Research Centre (IDRC, Ottawa, Canada), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Ensino Superior (CAPES—Programa Ciências do Mar, Brasília, DF, Brazil) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq—Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia de Toxicologia Aquática, Brasília, DF, Brazil). A. Bianchini is a Research Fellow from the Brazilian CNPq (Proc. # 304430/2009-9) and supported by the International Canada Research Chair Program from IDRC. C.M. Wood is supported by the Canada Research Chair Program. P.L. Gillis is supported by Environment Canada.
Ethical standards
All the methods for obtaining the results presented here comply with the current laws of Canada.
Conflict of interest
Everyone meriting authorship in this work has been above named and the authors state that they have no conflict of interest regarding this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machado, A.A.S., Wood, C.M., Bianchini, A. et al. Responses of biomarkers in wild freshwater mussels chronically exposed to complex contaminant mixtures. Ecotoxicology 23, 1345–1358 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1277-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1277-8