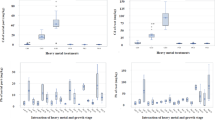
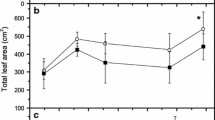
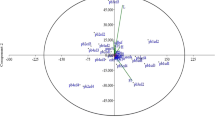
Abstract
Mine tailings can contaminate large areas of neighboring agricultural lands due to the dispersion of heavy metals, which may lead to reduction in soil fertility and toxicity in crops. The use of Fabaceae species as green manure to amend the soil and enhance the removal of heavy metals is a promising research approach. As part of a phytoremediation project for abandoned mining sites combining woody species and agricultural crops, this study aims to identify the most suitable species to be used. Thus, four Fabaceae species (Vicia faba, Cicer arietinum, Lens culinaris, and Medicago arborea) were subjected to muti-metal-contaminated soil containing high concentrations of Pb, Zn, and Cd and to control soil for 15 days. Then, the emergence rate, growth parameters, lipid peroxidation, proline and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) concentrations, antioxidant enzyme activities (catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and guaiacol peroxidase (GPX)), and heavy metals accumulation were evaluated. Results showed that V. faba was the most tolerant. A relative sensitivity at the germination stage was recorded for all species with the exception of V. faba. Metallic stress had no significant effect on thiobarbituric acid reactive susbtances (TBARS) and electrolyte leakage rates for both C. arietinum and V. faba. The latter also showed the highest proline concentration and relatively low antioxidant enzyme activities. All species showed high Pb, Zn, and Cd root contents. V. faba had the lowest translocation factors of Pb and Zn and the lowest bioaccumulation factors of Zn and Cd, which underline its phytostabilizing potential and support its use as green manure for heavy metals contaminated soils amendement and rehabilitation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request (zoubeir.bejaoui@fsb.ucar.tn).
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects or animals performed by any of the authors.
References
Abdul-Baki, A. A., & Anderson, J. D. (1973). Vigor determination in soybean seed by multiple criteria. Crop Science, 13(6), 630–633.
Aebi, H. (1984). Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymology, 105, 121–126.
Aghili, F., Gamper, H. A., Eikenberg, J., Khoshgoftarmanesh, A. H., Afyuni, M., Schulin, R., ... & Frossard, E. (2014). Green manure addition to soil increases grain zinc concentration in bread wheat. PloS one, 9(7), e101487 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101487
Ai, Y. J., Li, F. P., Gu, H. H., Chi, X. J., Yuan, X. T., & Han, D. Y. (2020). Combined effects of green manure returning and addition of sewage sludge compost on plant growth and microorganism communities in gold tailings. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 31686–31698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09118-z
Alcántara, C., Soriano, A., Saavedra, M., & Gómez, J. A. (2017). Sistemas de manejo del suelo. In D. Barranco Navero, R. Fernández Escobar, & L. Rallo Romero (Eds.), El cultivo del olivo (7th ed., pp 335–417). Mundi-Prensa.
Alexander, P. D., Alloway, B. J., & Dourado, A. M. (2006). Genotypic variations in the accumulation of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn exhibited by six commonly grown vegetables. Environmental Pollution, 144(3), 736–745.
Alscher, R. G., Erturk, N., & Heath, L. S. (2002). Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53(372), 1331–1341.
Amari, T., Ghnaya, T., & Abdelly, C. (2017). Nickel, cadmium and lead phytotoxicity and potential of halophytic plants in heavy metal extraction. South African Journal of Botany, 111, 99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2017.03.011
Ashraf, C. M., & Abu-Shakra, S. (1978). Wheat seed germination under low temperature and moisture stress 1. Agronomy Journal, 70(1), 135–139.
Bacchetta, G. I. A. N. L. U. I. G. I., Cappai, G., Carucci, A., & Tamburini, E. (2015). Use of native plants for the remediation of abandoned mine sites in Mediterranean semiarid environments. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 94(3), 326–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1467-y
Baghaie, A. H., & Aghilizefreei, A. (2020). Iron enriched green manure can increase wheat Fe concentration in Pb-polluted soil in the presence of Piriformospora indica (P. indica). Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 29(7), 721–743. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2020.1771274
Bai, Y. C., Zuo, W. G., Zhao, H. T., Mei, L. J., Gu, C. H., Guan, Y. X., ... & Feng, K. (2017). Distribution of heavy metals in maize and mudflat saline soil amended by sewage sludge. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 17(6), 1565-1578https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1630-z
Bankaji, I., Caçador, I., & Sleimi, N. (2015). Physiological and biochemical responses of Suaeda fruticosa to cadmium and copper stresses: Growth, nutrient uptake, antioxidant enzymes, phytochelatin, and glutathione levels. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(17), 13058–13069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4414-x
Bankaji, I., Cacador, I., & Sleimi, N. (2016). Assessing of tolerance to metallic and saline stresses in the halophyte Suaeda fruticosa: The indicator role of antioxidative enzymes. Ecological Indicators, 64, 297–308.
Bankaji, I., Pérez-Clemente, R. M., Caçador, I., & Sleimi, N. (2019). Accumulation potential of Atriplex halimus to zinc and lead combined with NaCl: Effects on physiological parameters and antioxidant enzymes activities. South African Journal of Botany, 123, 51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2019.02.011
Baruah, N., Mondal, S. C., Farooq, M., & Gogoi, N. (2019). Influence of heavy metals on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat, pea, and tomato. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230(12), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4329-0
Bhatti, S. S., Sambyal, V., & Nagpal, A. K. (2018). Analysis of genotoxicity of agricultural soils and metal (Fe, Mn, and Zn) accumulation in crops. International Journal of Environmental Research, 12(4), 439–449.
Blum, A., & Ebercon, A. (1981). Cell membrane stability as a measure of drought and heat tolerance in wheat 1. Crop Science, 21(1), 43–47.
Botelho, R. V., & Müller, M. M. L. (2020). Nutrient redistribution in fruit crops: Physiological implications. In A. K. Srivastava, & H. Chengxiao (Eds.), Fruit crops: Diagnosis and management of nutrient constraints (pp. 33–46). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818732-6.00003-4
Bouslimi, H., Ferreira, R., Dridi, N., Brito, P., Martins-Dias, S., Caçador, I., & Sleimi, N. (2021). Effects of barium stress in Brassica juncea and Cakile maritima: The indicator role of some antioxidant enzymes and secondary metabolites. Phyton, 90(1), 145. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2020.011752
Boussen, S., Sebei, A., Soubrand-Colin, M., Bril, H., Chaabani, F., & Abdeljaouad, S. (2010). Mobilization of lead-zinc rich particles from mine tailings in northern Tunisia by aeolian and run-off processes. Bulletin De La Société Géologique De France, 181(5), 459–471.
Boussen, S., Soubrand, M., Bril, H., Ouerfelli, K., & Abdeljaouad, S. (2013). Transfer of lead, zinc and cadmium from mine tailings to wheat (Triticum aestivum) in carbonated Mediterranean (Northern Tunisia) soils. Geoderma, 192, 227–236.
Chaabani, S., Abdelmalek-Babbou, C., Ahmed, H. B., Chaabani, A., & Sebei, A. (2017). Phytoremediation assessment of native plants growing on Pb–Zn mine site in Northern Tunisia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(16), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6894-0
Cheng, X., Drozdova, J., Danek, T., Huang, Q., Qi, W., Yang, S., ... & Zhao, X. (2018). Pollution assessment of trace elements in agricultural soils around copper mining area. Sustainability, 10(12), 4533https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124533
Cooper, J. E., & Scherer, H. W. (2012). Nitrogen fixation. In P. Marschner (Ed.), Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants (3rd ed., pp. 389–408). Academic Press.
Cuypers, A., Hendrix, S., Amaral dos Reis, R., De Smet, S., Deckers, J., Gielen, H., Jozefczak, M., Loix, C., Vercampt, H., Vangronsveld, J., & Keunen, E. (2016). Hydrogen peroxide, signaling in disguise during metal phytotoxicity. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 470. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00470
Dar, M. I., Naikoo, M. I., Rehman, F., Naushin, F., & Khan, F. A. (2016). Proline accumulation in plants: Roles in stress tolerance and plant development. In N. Iqbal, R. Nazar, & N. A. Khan (Eds.), Osmolytes and plants acclimation to changing environment: Emerging omics technologies (pp. 155–166). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2616-1_9.
Debouza, N. E., Thruppoyil, S. B., Gopi, K., Zain, S., & Ksiksi, T. (2021). Plant and seed germination responses to global change, with a focus on CO2: A review. One Ecosystem, 6, e74260. https://doi.org/10.3897/oneeco.6.e74260
Doumas, P., Munoz, M., Banni, M., Becerra, S., Bruneel, O., Casiot, C., Cleyet-Marel, J. C., Gardon, J., Noack, Y., & Sappin-Didier, V. (2018). Polymetallic pollution from abandoned mines in Mediterranean regions: a multidisciplinary approach to environmental risks. Regional environmental change, 18(3), 677–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-016-0939-x
El-Amier, Y., Elhindi, K., El-Hendawy, S., Al-Rashed, S., & Abd-ElGawad, A. (2019). Antioxidant system and biomolecules alteration in Pisum sativum under heavy metal stress and possible alleviation by 5-aminolevulinic acid. Molecules, 24(22), 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224194
Elouear, Z., Bouhamed, F., Boujelben, N., & Bouzid, J. (2016). Assessment of toxic metals dispersed from improperly disposed tailing, Jebel Ressas mine. NE Tunisia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(3), 254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5035-x
Feller, C., Blanchart, E., Bernoux, M., Lal, R., & Manlay, R. (2012). Soil fertility concepts over the past two centuries: The importance attributed to soil organic matter in developed and developing countries. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 58(sup1), S3–S21. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2012.693598
Feng, Z. T., Deng, Y. Q., Fan, H., Sun, Q. J., Sui, N., & Wang, B. S. (2014). Effects of NaCl stress on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Ulmus pumila L. seedlings in sand culture. Photosynthetica, 52(2), 313–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-014-0032-y
Fielding, J. L., & Hall, J. L. (1978). A biochemical and cytochemical study of peroxidase activity in roots of Pisum sativum: II. Distribution of enzymes in relation to root development. Journal of Experimental Botany, 29(4), 983–991.
Filippou, P., Bouchagier, P., Skotti, E., & Fotopoulos, V. (2014). Proline and reactive oxygen/nitrogen species metabolism is involved in the tolerant response of the invasive plant species Ailanthus altissima to drought and salinity. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 97, 1–10.
Gebeyehu, H. R., & Bayissa, L. D. (2020). Levels of heavy metals in soil and vegetables and associated health risks in Mojo area. Ethiopia. Plos One, 15(1), e0227883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227883
Ghorbel, M. (2012). Contamination métallique issue des dechets de l’ancien site minier de Jebel Ressas: modélisation des mécanismes de transfert et conception de cartes d’aléa post- mine dans un contexte carbonaté et sous un climat semi-aride. Evaluation du risque pour la santé humaine. Doctoral thesis. University Paul Sabatier - Toulouse III, France. Retrieved October 19, 2017, from https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00760685/document
Ghorbel, M., Munoz, M., Courjault-Radé, P., Destrigneville, C., de Parseval, P., Souissi, R., ... & Abdeljaouad, S. (2010). Health risk assessment for human exposure by direct ingestion of Pb, Cd, Zn bearing dust in the former miners’ village of Jebel Ressas (NE Tunisia). European Journal of Mineralogy, 22(5), 639-649
Gill, S. S., & Tuteja, N. (2010). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48(12), 909–930.
Giri, S., Singh, A. K., & Mahato, M. K. (2017). Metal contamination of agricultural soils in the copper mining areas of Singhbhum shear zone in India. Journal of Earth System Science, 126(4), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0833-z
Grotkopp, E., Rejmánek, M., & Rost, T. L. (2002). Toward a causal explanation of plant invasiveness: Seedling growth and life-history strategies of 29 pine (Pinus) species. The American Naturalist, 159(4), 396–419.
Gutiérrez, M., Mickus, K., & Camacho, L. M. (2016). Abandoned PbZn mining wastes and their mobility as proxy to toxicity: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 565, 392–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.143
Hachani, C., Lamhamedi, M. S., Cameselle, C., Gouveia, S., Zine El Abidine, A., Khasa, D. P., & Béjaoui, Z. (2020). Effects of ectomycorrhizal fungi and heavy metals (Pb, Zn, and Cd) on growth and mineral nutrition of Pinus halepensis seedlings in North Africa. Microorganisms, 8(12), 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8122033
Hachani, C., Lamhamedi, M. S., Zine El Abidine, A., Abassi, M., Khasa, D. P., & Béjaoui, Z. (2022). Water relations, gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence and electrolyte leakage of ectomycorrhizal Pinus halepensis seedlings in response to multi-heavy metal stresses (Pb, Zn, Cd). Microorganisms, 10(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010057
Hameed, A., Rasool, S., Azooz, M. M., Hossain, M. A., Ahanger, M. A., & Ahmad, P. (2016). Heavy metal stress: Plant responses and signalling. In P. Ahmad (Ed.), Plant metal interaction: Emerging remediation techniques (pp. 557–583). Elsevier.
Hasanuzzaman, M., Bhuyan, M. H. M., Zulfiqar, F., Raza, A., Mohsin, S. M., Mahmud, J. A., ... & Fotopoulos, V. (2020). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: Revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants, 9(8), 681https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080681
Hattab, S., Hattab, S., Flores-Casseres, M. L., Boussetta, H., Doumas, P., Hernandez, L. E., & Banni, M. (2016). Characterisation of lead-induced stress molecular biomarkers in Medicago sativa plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 123, 1–12.
He, Z., Shentu, J., Yang, X., Baligar, V. C., Zhang, T., & Stoffella, P. J. (2015). Heavy metal contamination of soils: Sources, indicators and assessment. Journal of Environmental Indicators, 9, 17–18.
Heath, R. L., & Packer, L. (1968). Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 125(1), 189–198.
International Seed Testing Association (ISTA). (2012). International rules for seed testing. Bassersdorf, Switzerland. Retrieved September 28, 2017, from https://www.seedtest.org/en/publications/international-rules-seed-testing-1168.html
Islam, E., Yang, X., Li, T., Liu, D., Jin, X., & Meng, F. (2007). Effect of Pb toxicity on root morphology, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147(3), 806–816.
Júnior, C. A. L., Oliveira, S. R., Mazzafera, P., & Arruda, M. A. Z. (2016). Expanding the information about the influence of cadmium on the metabolism of sunflowers: Evaluation of total, bioavailable, and bioaccessible content and metallobiomolecules in sunflower seeds. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 125, 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.02.003
Karaca, O., Cameselle, C., & Reddy, K. R. (2018). Mine tailing disposal sites: Contamination problems, remedial options and phytocaps for sustainable remediation. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/technology, 17(1), 205–228.
Khalid, S., Shahid, M., Niazi, N. K., Murtaza, B., Bibi, I., & Dumat, C. (2017). A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 182, 247–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.11.021
Khan, A., Khan, S., Khan, M. A., Qamar, Z., & Waqas, M. (2015). The uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by food plants, their effects on plants nutrients, and associated health risk: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(18), 13772–13799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4881-0
Kicińska, A., & Wikar, J. (2021). Ecological risk associated with agricultural production in soils contaminated by the activities of the metal ore mining and processing industry-example from southern Poland. Soil and Tillage Research, 205, 104817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104817
Lamhamedi, M. S., Renaud, M., Desjardins, P., & Veilleux, L. (2013). Root growth, plug cohesion, mineral nutrition, and carbohydrate content of (1+ 0) Picea mariana seedlings in response to a short-day treatment. Tree Planters’ Notes, 56(1), 35–46.
Li, W., Khan, M. A., Yamaguchi, S., & Kamiya, Y. (2005). Effects of heavy metals on seed germination and early seedling growth of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Growth Regulation, 46(1), 45–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-005-6324-2
Li, Z., Ma, Z., van der Kuijp, T. J., Yuan, Z., & Huang, L. (2014). A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 843–853.
Liu, S., Yang, C., Xie, W., Xia, C., & Fan, P. (2012). The effects of cadmium on germination and seedling growth of Suaeda salsa. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 16, 293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.041
Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Lu, H., Lonappan, L., Brar, S. K., He, L., ... & Yang, S. (2018). Biochar application as a soil amendment for decreasing cadmium availability in soil and accumulation in Brassica chinensis. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18(7), 2511-2519https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1927-1
Ma, L., Sun, J., Yang, Z., & Wang, L. (2015). Heavy metal contamination of agricultural soils affected by mining activities around the Ganxi River in Chenzhou. Southern China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(12), 1–9.
Mackay, D., & Fraser, A. (2000). Bioaccumulation of persistent organic chemicals: Mechanisms and models. Environmental Pollution, 110(3), 375–391.
Mahmud, J. A., Bhuyan, M. B., Nahar, K., Parvin, K., & Hasanuzzaman, M. (2020). Response and tolerance of fabaceae plants to metal/metalloid toxicity. In M. Hasanuzzaman, S. Araújo, & S. Gill (Eds.), The plant family Fabaceae (pp. 435–482). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4752-2_17
Mateos-Naranjo, E., Castellanos, E. M., & Perez-Martin, A. (2014). Zinc tolerance and accumulation in the halophytic species Juncus acutus. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 100, 114–121.
Medyńska-Juraszek, A., Bednik, M., & Chohura, P. (2020). Assessing the influence of compost and biochar amendments on the mobility and uptake of heavy metals by green leafy vegetables. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(21), 7861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217861
Mendez, M. O., & Maier, R. M. (2008). Phytoremediation of mine tailings in temperate and arid environments. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/technology, 7(1), 47–59.
Mlayah, A., Da Silva, E. F., Rocha, F., Hamza, C. B., Charef, A., & Noronha, F. (2009). The Oued Mellègue: Mining activity, stream sediments and dispersion of base metals in natural environments. North-Western Tunisia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 102(1), 27–36.
Monneveux, P., & Nemmar, M. (1986). Contribution à l’étude de la résistance à la sécheresse chez le blé tendre (Triticum aestivum L.) et chez le blé dur (Triticum durum Desf.): étude de l’accumulation de la proline au cours du cycle de développement. Agronomie, 6(6), 583–590.
Nadgórska-Socha, A., Kafel, A., Kandziora-Ciupa, M., Gospodarek, J., & Zawisza-Raszka, A. (2013). Accumulation of heavy metals and antioxidant responses in Vicia faba plants grown on monometallic contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(2), 1124–1134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1191-7
Nagajyoti, P. C., Lee, K. D., & Sreekanth, T. V. M. (2010). Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 8(3), 199–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-010-0297-8
Nakano, Y., & Asada, K. (1981). Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant and Cell Physiology, 22, 867–880.
Nguyen, N. L., Vu, C. T., To, H. M., Pham, H. N., Nguyen, H. D., Nguyen, T. D., & Nguyen Thi, K. O. (2020). The interactions among the heavy metals in soils and in weeds and their antioxidant capacity under the mining activities in Thai Nguyen Province, Vietnam. Journal of Chemistry, 2020https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8010376
Othmani, M. A., Souissi, F., Benzaazoua, M., Bouzahzah, H., Bussiere, B., & Mansouri, A. (2013). The geochemical behaviour of mine tailings from the Touiref Pb–Zn District in Tunisia in weathering cells leaching tests. Mine Water and the Environment, 32(1), 28–41.
Pais, I., & Jones, J. B. (1997). The handbook of trace elements. CRC Press.
Peralta, J. R., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., Tiemann, K. J., Gomez, E., Arteaga, S., Rascon, E., & Parsons, J. G. (2001). Uptake and effects of five heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 66(6), 727–734.
Pinto, A. P., De Varennes, A., Fonseca, R., & Teixeira, D. M. (2015). Phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals: Techniques and strategies. In A. A. Ansari, S. S. Gill, R. Gill, G. R. Lanza, & L. Newman (Eds.), Phytoremediation: Management of environmental contaminants (pp. 133–155). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10395-2_10
Pourrut, B., Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Winterton, P., & Pinelli, E. (2011). Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. In D. Whitacre (Ed.), Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology (vol. 213, pp. 113–136). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9860-6_4
Rai, R., Agrawal, M., & Agrawal, S. B. (2016). Impact of heavy metals on physiological processes of plants: With special reference to photosynthetic system. In A. Singh, S. M. Prasad, & R. P. Singh (Eds.), Plant responses to xenobiotics (pp. 127–140). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2860-1_6
Ramos, S. J., Gastauer, M., Mitre, S. K., Caldeira, C. F., Silva, J. R., Neto, A. E. F., ... & Siqueira, J. O. (2020). Plant growth and nutrient use efficiency of two native Fabaceae species for mineland revegetation in the eastern Amazon. Journal of Forestry Research, 31(6), 2287–2293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-01004-w
Rascio, N., & Navari-Izzo, F. (2011). Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: How and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? Plant Science, 180(2), 169–181.
Rucinska-Sobkowiak, R. (2010). Stres oksydacyjny wywołany działaniem metali ciężkich na rośliny. Postępy Biochemii, 56(2).
Sachdev, S., Ansari, S. A., Ansari, M. I., Fujita, M., & Hasanuzzaman, M. (2021). Abiotic stress and reactive oxygen species: Generation, signaling, and defense mechanisms. Antioxidants, 10(2), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020277
Sergiev, I., Alexieva, V., & Karanov, E. (1997). Effect of spermine, atrazine and combination between them on some endogenous protective systems and stress markers in plants. Comptes Rendus De L’academie Bulgare Des Sciences, 51(3), 121–124.
Shu, X., Yin, L., Zhang, Q., & Wang, W. (2012). Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, antioxidant enzyme activities, and photosynthesis in cuttings and seedlings of Jatropha curcas L. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19(3), 893–902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0625-y
Singh, S. N., Goyal, S. K., Rai, J. P., & Singh, S. R. (2014). Heavy metal accumulation in plants grown in peri-urban metal contaminated areas of eastern UP. Agriways, 2(1), 8–11.
Smirnoff, N., & Arnaud, D. (2019). Hydrogen peroxide metabolism and functions in plants. New Phytologist, 221(3), 1197–1214. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15488
Sofo, A., Scopa, A., Nuzzaci, M., & Vitti, A. (2015). Ascorbate peroxidase and catalase activities and their genetic regulation in plants subjected to drought and salinity stresses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(6), 13561–13578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613561
Souguir, D. (2009). Modifications métaboliques, moléculaires et génotoxicité induites par le cadmium chez Vicia faba. Doctoral thesis. University Blaise Pascal - Clermont-Ferrand II; University of Auvergne - Clermont-Ferrand I; University of Carthage, Tunisia. Retrieved January 07, 2019, from https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/49293456.pdf
Steel, G. D., Torrie, J. H., & Dickey, D. A. (1997). Principles and procedures of statistics: A biometrical approach (3rd ed.). The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc.
Timmer, V. R., & Miller, B. D. (1991). Effects of contrasting fertilization and moisture regimes on biomass, nutrients, and water relations of container grown red pine seedlings. New Forests, 5(4), 335–348.
Verma, S., & Dubey, R. S. (2003). Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Science, 164(4), 645–655.
Wang, F., Zhang, S., Cheng, P., Zhang, S., & Sun, Y. (2020). Effects of soil amendments on heavy metal immobilization and accumulation by maize grown in a multiple-metal-contaminated soil and their potential for safe crop production. Toxics, 8, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040102
Wei, W., Ma, R., Sun, Z., Zhou, A., Bu, J., Long, X., & Liu, Y. (2018). Effects of mining activities on the release of heavy metals (HMs) in a typical mountain headwater region, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(9), 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091987
Weis, J. S., & Weis, P. (2004). Metal uptake, transport and release by wetland plants: Implications for phytoremediation and restoration. Environment International, 30(5), 685–700.
Wilkins, D. A. (1978). The measurement of tolerance to edaphic factors by means of root growth. New Phytologist, 80(3), 623–633.
Xu, X., Liu, C., Zhao, X., Li, R., & Deng, W. (2014). Involvement of an antioxidant defense system in the adaptive response to cadmium in maize seedlings (Zea mays L.). Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology, 93(5), 618–624.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Pr. Noura Ben Youssef, head of the Laboratory of Field Crops at the National Institute of Agronomic Research of Tunisia (INRAT), for providing the seeds used in this study. We also thank Salima Bahri, engineer in statistics and information analysis in INRGREF, for performing the statistical analyses. We are greatful to the nursery staff of INGRREF for their help during the collection of soil samples.
Funding
This research was supported by the University of Carthage and the National Institue of Research in Rural Engineering, Water and Forests (INRGREF), Tunisia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hachani, C., Lamhamedi, M.S., Abassi, M. et al. Effects of Heavy Metal-Polluted Soil (Pb, Zn, and Cd) on Seed Emergence, Seedling Growth, and Antioxidant Activity in Four Fabaceae Species. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 263 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05725-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05725-3