Abstract
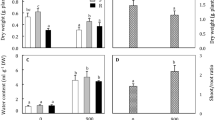
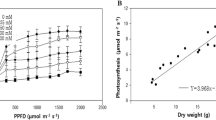
The effects of NaCl stress on the growth and photosynthetic characters of Ulmus pumila L. seedlings were investigated under sand culture condition. With increasing NaCl concentration, main stem height, branch number, leaf number, and leaf area declined, while Na+ content and the Na+/K+ ratio in both expanded and expanding leaves increased. Na+ content was significantly higher in expanded leaves than in those just expanding. Chlorophyll (Chl) a and Chl b contents declined as NaCl concentration increased. The net photosynthetic rate, intercellular CO2 concentration, stomatal conductance, and transpiration rate also declined, but stomatal limitation value increased as NaCl concentration increased. Both the maximal quantum yield of PSII photochemistry and the effective quantum yield of PSII photochemistry declined as NaCl concentration rose. These results suggest that the accumulation of Na+ in already expanded leaves might reduce damage to the expanding leaves and help U. pumila endure high salinity. The reduced photosynthesis in response to salt stress was mainly caused by stomatal limitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C a :
-
ambient CO2 concentration
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- C i :
-
intercellular CO2 concentration
- DM:
-
dry mass
- E :
-
transpiration rate
- F0 :
-
minimal fluorescence yield of the dark-adapted state
- Fm :
-
maximal fluorescence yield of the dark-adapted state
- Fm′:
-
maximal fluorescence yield of the light-adapted state
- Fs :
-
steady-state fluorescence yield
- Fv :
-
variable fluorescence
- Fv/Fm :
-
maximal quantum yield of PSII photochemistry
- FM:
-
fresh mass
- g s :
-
stomatal conductance
- LA:
-
leaf area
- Ls :
-
stomatal limitation value
- P N :
-
net photosynthetic rate
- QA :
-
primary quinone acceptor of PSII
- QB :
-
secondary quinone acceptor of PSII
- S0, S100, S200, S300:
-
treatment with 0, 100, 200, and 300 mM NaCl, respectively
- ΦPSII :
-
effective quantum yield of PSII photochemistry
References
Abdeshahian, M., Nabipour, M., Meskarbashee, M.: Chlorophyll fluorescence as criterion for the diagnosis salt stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum) plants. — World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 4: 523–525, 2010.
Baker, N.R.: Chlorophyll fluorescence: A probe of photosynthesis in vivo. — Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59: 89–113, 2008.
Bhatnagar-Mathur, P., Vadez, V., Sharma, K.K.: Transgenic approaches for abiotic stress tolerance in plants: retrospect and prospects. — Plant Cell Rep. 27: 411–424, 2008.
Carter, J.L., Colmer, T.D., Veneklaas, E.J.: Variable tolerance of wetland tree species to combined salinity and waterlogging is related to regulation of ion uptake and production of organic solutes. — New Phytol. 169: 123–133, 2006.
Chen, Y.P., Chen, Y.N., Li, W.H., Xu, C.C.: Characterization of photosynthesis of Populus euphratica grown in the arid region. — Photosynthetica 44: 622–626, 2006.
Chinnusamy, V., Jagendorf, A., Zhu, J.K.: Understanding and improving salt tolerance in plants. — Crop Sci. 45: 437–448, 2005.
Clapham, D.E.: Calcium signaling. — Cell 80: 259–268, 1995.
Dongsansuk, A., Lütz, C., Neuner, G.: Effects of temperature and irradiance on quantum yield of PSII photochemistry and xanthophyll cycle in a tropical and a temperate species. — Photosynthetica 51: 13–21, 2013.
Farquhar, G.D., Sharkey, T.D.: Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 33: 317–345, 1982.
Fu, M.Y., Li, C., Ma, F.W.: Physiological responses and tolerance to NaCl stress in different biotypes of Malus prunifolia. — Euphytica 189: 101–109, 2013.
Ghoulam, C., Foursy, A., Fares, K.: Effects of salt stress on growth, inorganic ions and proline accumulation in relation to osmotic adjustment in five sugar beet cultivars. — Environ. Exp. Bot. 47: 39–50, 2002.
Gill, S.S., Tajrishi, M., Madan, M., Tuteja, N.: A DESD-box helicase functions in salinity stress tolerance by improving photosynthesis and antioxidant machinery in rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. PB1). — Plant Mol. Biol. 82: 1–22, 2013.
Gong, B., Wen, D., VandenLangenberg, K., et al.: Comparative effects of NaCl and NaHCO3 stress on photosynthetic parameters, nutrient metabolism, and the antioxidant system in tomato leaves. — Sci. Hortic. — Amsterdam 157: 1–12, 2013.
Gorai, M., Ennajeh, M., Khemira, H., Neffati, M.: Influence of NaCl-salinity on growth, photosynthesis, water relations and solute accumulation in Phragmites australis. — Acta Physiol. Plant. 33: 963–971, 2011.
Greenway, H., Munns, R.: Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. — Ann. Rev. Plant Phys. 31: 149–190, 1980.
Grotkopp, E., Rejmanek, M., Rost, T.L.: Toward a causal explanation of plant invasiveness: Seedling growth and life-history strategies of 29 pine (Pinus) species. — Am. Nat. 159: 396–419, 2002.
Herrero, J., Pérez-Coveta, O.: Soil salinity changes over 24 years in a Mediterranean irrigated district. — Geoderma 125: 287–308, 2005.
Huang, Z.R., Long, X.H., Wang, L., et al.: Growth, photosynthesis and H+-ATPase activity in two Jerusalem artichoke varieties under NaCl-induced stress. — Process Biochem. 47: 591–596, 2012.
Lee, G.J., Duncan, R.R., Carrow, R.N.: Nutrient uptake responses and inorganic ion contribution to solute potential under salinity stress in halophytic seashore paspalums. — Crop Sci. 47: 2504–2512, 2007.
Lu, C.M., Qiu, N.W., Wang, B.S., Zhang, J.H.: Salinity treatment shows no effects on photosystem II photochemistry, but increases the resistance of photosystem II to heat stress in halophyte Suaeda salsa. — J. Exp. Bot. 54: 851–860, 2003.
Ma, Q., Yue, L.J., Zhang, J.L., et al.: Sodium chloride improves photosynthesis and water status in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. — Tree Physiol. 32: 4–13, 2012.
Moghaieb, R.E.A., Saneoka, H., Fujita, K.: Effect of salinity on osmotic adjustment, glycinebetaine accumulation and the betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase gene expression in two halophytic plants, Salicornia europaea and Suaeda maritima. — Plant Sci. 166: 1345–1349, 2004.
Munns, R.: Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. — Plant Cell Environ. 25: 239–250, 2002.
Munns, R.: Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. — New Phytol. 167: 645–663, 2005.
Munns, R., Tester, M.: Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. — Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59: 651–681, 2008.
Porra, R.J., Thompson, W.A., Kriedemann, P.E.: Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophyll a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. — BBA-Biomembranes 975: 384–394, 1989.
Qiu, N.W., Lu, Q.T., Lu, C.M.: Photosynthesis, photosystem II efficiency and the xanthophylls cycle in the salt-adapted halophyte Atriplex centralasiatica. — New Phytol. 159: 479–486, 2003.
Raschke, K.: Stomatal action. — Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 26: 309–340, 1975.
Rozema, J., Flowers, T.: Ecology. Crops for a salinized world. — Science 322: 1478–1480, 2008.
Satoh, K., Smith, C.M., Fork, D.C.: Effects of salinity on primary processes of photosynthesis in the red alga Porphyra perforata. — Plant Physiol. 73: 643–647, 1983.
Seemann, J.R., Sharkey, T.D.: Salinity and nitrogen effects on photosynthesis, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and metabolite pool sizes in Phaseolus vulgaris L. — Plant Physiol. 82: 555–560, 1986.
Silva, E.N., Ribeiro, R.V., Ferreira-Silva, S.L., et al.: Comparative effects of salinity and water stress on photosynthesis, water relations and growth of Jatropha curcas plants. — J. Arid Environ. 74: 1130–1137, 2010.
Silva, E.N., Ribeiro, R.V., Ferreira-Silva, S.L., et al.: Salt stress induced damages on the photosynthesis of physic nut young plants. — Sci. Agric. 68: 62–68, 2011.
Song, J., Chen, M., Feng, G., et al.: Effect of salinity on growth, ion accumulation and the roles of ions in osmotic adjustment of two populations of Suaeda salsa. — Plant Soil 314: 133–141, 2009.
Tarchoune, I., Degl’Innocenti, E., Kaddour, R., et al.: Effects of NaCl or Na2SO4 salinity on plant growth, ion content and photosynthetic activity in Ocimum basilicum L. — Acta Physiol. Plant. 34: 607–615, 2012.
Tavakkoli, E., Fatehi, F., Coventry, S., et al.: Additive effects of Na+ and Cl− ions on barley growth under salinity stress. — J. Exp. Bot. 62: 2189–2203, 2011.
Tester, M., Davenport, R.: Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. — Ann. Bot. 91: 503–527, 2003.
Wani, A.S., Ahmad, A., Hayat, S., Fariduddin, Q.: Salt-induced modulation in the growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant system in two varieties of Brassica juncea. — Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 20: 183–193, 2013.
Wu, X.X., Ding, H.D., Zhu, Z.W., et al.: Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on photosynthesis of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) seedlings under salt stress. — Afr. J. Biotechnol. 11: 8665–8671, 2012.
Yamazaki, J., Shinomiya, Y.: Effect of partial shading on the photosynthetic apparatus and photosystem stoichiometry in sunflower leaves. — Photosynthetica 51: 3–12, 2013.
Zribi, L., Fatma, G., Fatma, R., et al.: Application of chlorophyll fluorescence for the diagnosis of salt stress in tomato “Solanum lycopersicum (variety Rio Grande)”. — Sci. Hortic.-Amsterdam 120: 367–372, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This research was supported by the National Natural Science Research Foundation of China, project No. 30870138 and No. 31070158, and key projects in the national science and technology pillar program during the eleventh five-year plan period (2009BADA7B05).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Z.T., Deng, Y.Q., Fan, H. et al. Effects of NaCl stress on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Ulmus pumila L. seedlings in sand culture. Photosynthetica 52, 313–320 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-014-0032-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-014-0032-y