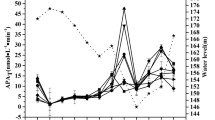
Abstract
Enzyme activity plays an important role in the functioning of aquatic ecosystems. It is sensitive to changes in environmental conditions such as pH, temperature, and nutrient concentration. The objective of this work was to determine the acid phosphatase activity (AcPA) in the Almendares and San Juan rivers (western Cuba) and its relationship with physicochemical and microbiological indicators. For this purpose, AcPA, temperature, pH, total dissolved solids, electrical conductivity, dissolved oxygen, concentration of nitrates, nitrites, ammonium, phosphates, total heterotrophs, enterococci, Escherichia coli, thermotolerant coliforms, chlorophyll a, and chemical oxygen demand (COD) were determined at three sampling stations on the Almendares River and at three sampling stations on the San Juan River. In addition, the nutrient pollution index (NPI) and the N:P ratio were calculated. In both ecosystems, spatio-temporal variability was observed in the enzymatic activity. In the Almendares River (polluted ecosystem), AcPA was positively correlated with nitrate concentration and COD, while in the San Juan River (slightly contaminated ecosystem), the AcPA correlated negatively with the pH and NPI and positively with the concentrations of total heterotrophs, Escherichia coli, chlorophyll a, and the N:P ratio. These results show the impact of anthropogenic pollution on AcPA in freshwater ecosystems with a tropical climate.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data related to physicochemical and microbiological indicators of water quality from February–June 2017 can be found as supplementary material in https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04909-z. The rest of the data is within the present article, including supplementary information of water quality on October 2017.
References
AFNOR (2009) Qualité de l’eau . Analyses biochimiques et biologiques - analyses microbiologiques. Norme NF EN ISO 16061. Association Française de Normalisation, Paris, France
Arnosti, C., Bell, C., Moorhead, D. L., Sinsabaugh, R. L., Steen, A. D., Stromberger, M., Wallenstein, M., & Weintraub, M. N. (2014). Extracellular enzymes in terrestrial, freshwater, and marine environments : perspectives on system variability and common research needs. Biogeochemistry, 177, 5–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-013-9906-5
Arnosti, C., Steen, A. D., Ziervogel, K., Ghobrial, S., & Jeffrey, W. H. (2011). Latitudinal gradients in degradation of marine dissolved organic carbon. PLoS ONE, 6, e28900. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028900
Arpajón, Y., Romeu, B., Rodríguez, A., Heydrich, M., Rojas, N., & Lugo, D. (2011). Impacto de los nutrientes inorgánicos sobre la comunidad bacteriana del río Almendares (Cuba). Higiene y Sanidad Ambiental, 11, 731–738.
Asaduzzaman, A. K. M., Rahman, M. H., & Yeasmin, T. (2011). Purification and characterization of acid phosphatase from a germinating black gram (Vigna mungo L) seedling. Arch Biol Sci Belgrade, 63, 747–756. https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS1103747A
Cabrera, Y., Aguilar, C., González-Sansón, G., Kidd, K. A., Munkittrick, K. R., & Curry, R. A. (2012). Increased mercury and body size and changes in trophic structure of Gambusia puncticulata (Poeciliidae) along the Almendares River, Cuba. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol, 63, 523–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9801-4
Cunha A, Almeida A, Coelho FJRC, Gomes NCM, Oliveira V, Santos AL (2010) Bacterial extracellular enzymatic activity in globally changing aquatic ecosystems vol 2. Formatex Microbiology,
Chróst RJ, Siuda W (2002) Ecology of microbial enzymes in lake ecosystems. In: Burns RG, Dick RP (eds) Enzymes in the Environment. Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203904039.ch2
Egli, C. M., & Janssen, E.M.-L. (2018). Proteomics approach to trace site-specific damage in aquatic extracellular enzymes during photoinactivation. Environ Sci Technol, 52, 7671–7679. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06439
Fonseca C, Hernández D, Alpízar M et al. (2021) Estado del Clima en Cuba 2020. Resumen ampliado. Revista Cubana de Meteorología 27
Giraldo, L. C., Palacio, C. A., & Aguirre, N. J. (2014). Temporal variation of the extracellular enzymatic activity ( EEA ): Case of study : Aburra-Medellín River, in the Valle de Aburra in Medellin, Antioquia, Colombia. International Journal of Environmental Protection, 4, 58–67.
Huang, X., & Morris, J. T. (2003). Trends in Phosphatase Activity along a Successional Gradient of Tidal Freshwater Marshes on the Cooper River. South Carolina Estuaries, 26, 1281–1290.
INSMET (2018) Instituto Nacional de Meteorología. El clima de Cuba www.met.inf.cu. Consulted 15–5–2018
Isiuku, B. O., & Enyoh, C. E. (2020). Pollution and health risks assessment of nitrate and phosphate concentrations in water bodies in South Eastern. Nigeria Environmental Advances, 2, 100018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2020.100018
Ivancic, I., Radic, T., Lyons, D. M., Fuks, D., Precali, R., & Kraus, R. (2009). Alkaline phosphatase activity in relation to nutrient status in the northern Adriatic Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 378, 27–35. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps07851
Izquierdo, K., Larrea, J. A., Lugo, D., & Rojas, M. M. (2020). Proteolytic enzyme activity and its relationship with physicochemical and microbiological indicators in freshwater ecosystems of western Cuba Water. Air, & Soil Pollution, 231, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04909-z
Jackson CR, Tyler HL, Millar JJ (2013) Determination of microbial extracellular enzyme activity in waters, soils, and sediments using high throughput microplate assays J Vis Exp 80: e50399 https://doi.org/10.3791/50399
Jaramillo, M. T., Aguirre, N. J., & Galvis, J. H. (2016). Using extracellular enzyme activity as a pollutant Indicator : A field study in Chinchiná River. Caldas International Journal of Environmental Protection, 6, 47–59.
Jasson, M., Olsson, H., & Pettersson, K. (1988). Phosphatases; origin, characteristics and function in lakes. Hydrobiologia, 170, 157–175.
Labry, C., Delmas, D., Youenou, A., Quere, J., Leynaert, A., Fraisse, S., Raimonet, M., & Ragueneau, O. (2016). High alkaline phosphatase activity in phosphate replete waters : The case of two macrotidal estuaries. Limnology and Oceanography. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10315
Larrea, J., Rojas, M., Bacchetti, T., Lugo, D., Heydrich, M., Estéve, A., & Boltes, K. (2014). Influencia de la contaminación química y fecal sobre la estructura de las comunidades bacterianas del río Almendares. La Habana, Cuba Investigación y Saberes, 3, 1–11.
Larrea JA, Heydrich M, Garcia I, Romeu B, Lugo D, Bacchetti T, Estéve A, Boltes AK, Rojas MM (2021) Impact of chemical and microbiological water quality on bacterial community assemblage of San Juan River (Sierra del Rosario, Biosphere Reserve, Cuba) Revista Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua 12:82–123 doi:https://doi.org/10.24850/j-tyca-2021-03-03
Larrea, J. A., Heydrich, M., Romeu, B., Lugo, D., Mahillon, J., & Rojas, M. M. (2020). Bacterial community structure of Almendares and San Juan rivers. Relationship with Water Quality Revista Cubana De Ciencias Biológicas, 8, 1–14.
Larrea, J. A., Rojas, M. M., García, I., Romeu, B., Bacchetti, T., Gillis, A., Boltes, A. K., Heydrich, M., Lugo, D., & Mahillon, J. (2018). Diversity and enzymatic potentialities of Bacillus sp. strains isolated from a polluted freshwater ecosystem in Cuba. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2411-1
Li, Y., Sun, L.-l, Sun, Y.-y, et al. (2019). Extracellular enzyme activity and its implications for organic matter cycling in northern chinese marginal seas. Front Microbiol, 10, 2137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02137
Luo, L., Han, M., Wu, R.-n, & Gu, J.-d. (2017). Impact of nitrogen pollution / deposition on extracellular enzyme activity, microbial abundance and carbon storage in coastal mangrove sediment. Chemosphere, 177, 275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.027
Nedoma J, García JC, Comerma M, Simek K, Armengol J (2006) Extracellular phosphatases in a Mediterranean reservoir: seasonal, spatial and kinetic heterogeneity Freshwater Biology 51:1264–1276 doi:doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01566.x
Olivares-Rieumont, S., De La Rosa, D., Lima, L., Graham, D. W., D’Alessandro, K., Borroto, J. M., Martínez, F., & Sánchez, J. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal levels in Almendares river sedi- ments - Havana City. Cuba. Water Research, 39, 3945–3953.
Pandey, J., & Yadav, A. (2017). Alternative alert system for Ganga river eutrophication using alkaline phosphatase as a level determinant. Ecological Indicators, 82, 327–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.06.061
Patel D, Gismondi R, Alsaffar A, Tiquia-arashiro SM (2018) Applicability of API ZYM to capture seasonal and spatial variabilities in lake and river sediments river sediments. Environmental Technology:1–13 https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1468492
Peña B, Fagundo JR, Delgado FR, Orbera L (2001) Caracterización de fuentes minerales en el Distrito Físico Geográfico Pinar del Río, Cuba. In: IV Congreso de Geología y Minería, Ingeniería Geológica e Hidrogeología, Memorias GEOMIN 2001, ISBN 959–7117–10-X. p 9
Redfield, A. C. (1958). The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. American Scientist, 64, 205–221.
Romeu, B., Quintero, H., Larrea, J., Rojas, N., & Heydrich, M. (2015). Calidad química y microbiológica de las aguas del río San Juan, Artemisa (Cuba). Higiene y Sanidad Ambiental, 15, 1367–1374.
Romeu, B., Quintero, H., Larrea, J. A., Lugo, D., Rojas, N., & Heydrich, M. (2015). Experiencias en el monitoreo ambiental: contaminación de ecosistemas dulceacuícolas de La Habana (Cuba). Higiene y Sanidad Ambiental, 15, 1325–1335.
Roy, K., Chari, M. S., Gaur, S. R., & Thakur, A. (2014). Ecological dynamics and hydrobiological correlations in freshwater ponds– recent researches and application. International Journal of Environmental Biology, 4, 112–118.
Sigee D (ed) (2005) Freshwater microbiology: biodiversity and dynamic interactions of microorganisms in the aquatic environment. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, England
Sinsabaugh, R. L., & Shah, J. J. F. (2012). Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst, 43, 313–343. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-071112-124414
Siuda, W. (1984). Phosphatases and their role in organic phosphorus transformation in natural waters. A Review Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii, 31, 207–233.
StatSoft (2007) STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 8.0.
Tabata, M., Tachibana, W., & Suzuki, S. (1988). Dependence of phosphatase activity in freshwater lakes. Jpn J Limnol, 49, 93–98.
Tiquia, S. M. (2011). Extracellular hydrolytic enzyme activities of the heterotrophic microbial communities of the Rouge River: An approach to evaluate ecosystem response to urbanization. Microbial Ecology, 62, 679–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9871-2
Torres, I. C., Turner, B. L., & Reddy, K. R. (2017). Phosphatase activities in sediments of subtropical lakes with different trophic states. Hydrobiologia, 788, 305–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-3009-y
W.H.O (2003) Guidelines for safe recreational water environments. vol 1. Geneva
Wemedo, S. A., Sampson, T., & Dick, B. (2021). Evaluating the nitrate to phosphate ratio and other physicochemical characteristics of different water sources in Yeghe community. Rivers State, Nigeria Asian Journal of Environment & Ecology, 15, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.9734/AJEE/2021/v15i130217
Weyhenmeyer GA, Hartmann J, Hessen D et al. (2019) Widespread diminishing anthropogenic efects on calcium in freshwaters. Scientific Reports 9 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46838-w
Williams, C. J., Scott, A. B., Wilson, H. F., & Xenopoulos, M. A. (2012). Effects of land use on water column bacterial activity and enzyme stoichiometry in stream ecosystems. Aquatic Sciences, 74, 483–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-011-0242-3
Yiyong, Z., Jianqiu, L., & Min, Z. (2002). Temporal and spatial variations in kinetics of alkaline phosphatase in sediments of a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake (Lake Donghu). Water Research, 36, 2084–2090.
Zhou, Y., Li, J., Song, C., & Cao, X. (2004). Discharges and sediments as sources of alkaline phosphatase in shallow chinese eutrophic lake Water. Air and Soil Pollution, 159, 395–407.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larrea-Murrell, J.A., Romeu-Alvarez, B., Lugo-Moya, D. et al. Acid phosphatase activity in freshwater ecosystems of western Cuba and its relationship with water quality. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 57 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05514-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05514-y