Abstract
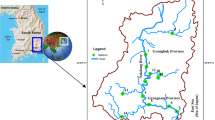
This research is aimed at generating a baseline monitoring data at different sites of the high-altitude Saiful Muluk Lake, Pakistan. The strength of this study is the provision of a wide range of measured physicochemical parameters in the unique environment where water-monitoring data is still not available and will be helpful for future comparison. Water and sediment samples from Saiful Muluk Lake (upstream) and Kunhar River (downstream) were collected during April/June 2019 and analyzed for various physicochemical parameters and metal content. Generally, the lake water quality is found to be clean from chemical contamination but elevated levels of BOD indicate that the degradation process has started. However, the concentrations of metals were lower in water samples but minor enrichment was found in the lake and river sediments. The metals were present in the following order: Fe > Na > Zn > Cr > Ni > Cu > Co > Pb > As > Cd indicating that the accumulation of metals in the sediment can affect the water chemistry of aquatic systems due to any physical or chemical process in the system. The metals can be released to overlying water and pose risk to human health and ecosystem. Moreover, during sample collection, we observed plastic debris along lake and river banks which can also be threatening for aquatic life and should be monitored in future studies along with metal speciation for the better assessment of toxicity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Association, A. P. H. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association.
Algül, F., & Beyhan, M. (2020). Concentrations and sources of heavy metals in shallow sediments in Lake Bafa Turkey. Scientific Reports, 10, 11782.
Arain, M., Kazi, T., Jamali, M., khan , Afridi, H., Baig, J., Jalbani, N. and Shah, A.Q. (2008). Evaluation of physico-chemical parameters of Manchar Lake water and their comparison with other global published values 9: 101–109.
Baran, A., & Tarnawski, M. (2015). Assessment of heavy metals mobility and toxicity in contaminated sediments by sequential extraction and a battery of bioassays. Ecotoxicology, 24(6), 1279–1293.
Bradney, L., Wijesekara, H., Palansooriya, K. N., Obadamudalige, N., Bolan, N. S., Ok, Y. S., Rinklebe, J., Kim, K.-H., & Kirkham, M. B. (2019). Particulate plastics as a vector for toxic trace-element uptake by aquatic and terrestrial organisms and human health risk. Environment International, 131, 104937.
BS EN ISO 11260. (1994). Determination of effective cation exchange capacity and base saturation level using barium chloride solution.
Eggleton, J., & Thomas, K. V. (2004). A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environment International, 30(7), 973–980.
European Comission. (2018). LARGER THAN TIGERS: Inputs for a strategic approach to biodiversity conservation in Asia–Synthesis report. 148.
Ghumman, A. R. (2011). Assessment of water quality of Rawal Lake by long-time monitoring. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 180(1–4), 115–126.
Heiri, O., Lotter, A. F., & Lemcke, G. (2001). Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: Reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology, 25(1), 101–110.
Hodson, M. E., Duffus-Hodson, C. A., Clark, A., Prendergast-Miller, M. T., & Thorpe, K. L. (2017). Plastic bag derived-microplastics as a vector for metal exposure in terrestrial invertebrates. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(8), 4714–4721.
Iqbal, J., Tirmizi, S. A., & Shah, M. H. (2013). Statistical apportionment and risk assessment of selected metals in sediments from Rawal Lake (Pakistan). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(1), 729–743.
ISO 11466. (1995). Extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia.
Jamal, Z. (2009). Biodiversity, ethnobotany and conservation status of the flora of Kaghan Valley Mansehra, NWFP Pakistan. Quaid-i-Azam University.
Khan, N. A. (2017). Saiful Muluk National Park: A picture of neglect, Dawn News. Dawn.
Kumar, R., & Sharma, R. C. (2019). Assessment of the water quality of Glacier-fed lake Neel Tal of Garhwal Himalaya India. Water Science, 33(1), 22–28.
Liang, B., Qian, X., Peng, S., Liu, X., Bai, L., Cui, B., & Bai, J. (2018). Speciation variation and comprehensive risk assessment of metal(loid)s in surface sediments of intertidal zones. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(10), 2125.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39(1), 20–31.
Malik, A., Yasar, A., Tabinda, A. B., & Abubakar, M. (2012). Water-borne diseases, cost of illness and willingness to pay for diseases interventions in rural communities of developing countries. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 41(6), 39–49.
Romero, E., Le Gendre, R., Garnier, J., Billen, G., Fisson, C., Silvestre, M., & Riou, P. (2016). Long-term water quality in the lower Seine: Lessons learned over 4 decades of monitoring. Environmental Science & Policy, 58, 141–154.
Saleem, M., Iqbal, J., & Shah, M. H. (2015). Geochemical speciation, anthropogenic contamination, risk assessment and source identification of selected metals in freshwater sediments—A case study from Mangla Lake, Pakistan. Environmental Nanotechnology Monitoring & Management, 4, 27–36.
Shah, S., Sher, K., Shah, M., & Hussain, A. (2013). Socio-economic and biological conditions of Saif-ul-Malook National Park, Pakistan. 3, 21–29.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7), 844–851.
UNICEF and WHO. (2017). Progress on drinking water, sanitation and hygiene-A joint monitoring progress report Geneva, Switzerland.
Varol, M., & Şen, B. (2012). Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. CATENA, 92, 1–10.
Vincent, W. F. (2009). Effects of climate change on lakes Encyclopedia of Inland Waters (pp. 55–60). Elsevier.
Wen, Y., Schoups, G., & van de Giesen, N. (2017). Organic pollution of rivers: Combined threats of urbanization, livestock farming and global climate change. Scientific Reports, 7, 43289.
World Bank. (2019). Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Integrated Tourism Development Project, Technical Note 139.
Wu, Z., Zhang, D., Cai, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, L., & Chen, Y. (2017). Water quality assessment based on the water quality index method in Lake Poyang: The largest freshwater lake in China. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 17999.
Yasutomi, N., Hamada, A., & Yatagai, A. (2011). Development of a long-term daily gridded temperature dataset and its application to rain/snow discrimination of daily precipitation. Global Environmental Research, 15(2), 165–172.
Yatagai, A., Kamiguchi, K., Arakawa, O., Hamada, A., Yasutomi, N., & Kitoh, A. (2012). APHRODITE: Constructing a long-term daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 93(9), 1401–1415.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Dr. Muhammad Daud and Mr. Munib Ahmed Shafique from Central Analytical Facility Division (CAFD), Pakistan Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology (PINSTECH), Islamabad, Pakistan for the provision of analysis facilities.
Funding
The study was financially supported by Kurita Water and Environment Foundation, Japan, Grant No. 18P009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taneez, M., Jamil, S. & Ramzan, M. Water Quality Assessment and Identification of Pollution Risk in High-Altitude Saiful Muluk Lake, North East, Pakistan. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 230 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05191-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05191-3