Abstract
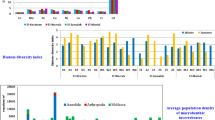
Although much previous research effort has examined the impacts of metal contamination on macrobenthic assemblages in subtidal sediments, little attention has been directed at macroinvertebrate responses in intertidal mangrove habitats. Thus, in order to assess the unique responses of mangrove macroinvertebrate assemblages to sediment metal(loid) contamination, total, normalised and bioavailable metal(loid)s (Mn, Pb, Cr, Cd, As, Se, Co, Ni, Zn and Cu) were assessed within and between four mangrove locations in Lake Macquarie, NSW, Australia, and compared to resident macroinvertebrate assemblages over two sampling occasions. Mangrove biomass and physicochemical properties of sediment are known to influence macroinvertebrate assemblages, and as such, were also assessed to account for any potential confounding effect on macroinvertebrate assemblage composition. Significant differences in total and bioavailable metal(loid) contamination were found between and within locations and were consistent over time. Sediments at contaminated locations presented a high risk to biota with bioavailable concentrations of Pb, Cd, Zn found to exceed sediment quality guidelines and concentrations of Se capable of adverse impacts to biota. Macroinvertebrate assemblage composition varied with metal(loid) contamination loads present at study locations. Metal(loid) contamination was significantly correlated with macroinvertebrate assemblages over two sampling periods. Further analysis revealed that 71% of macroinvertebrate assemblage composition could best be explained by a combination of five variables namely, bioavailable Mn, Zn, and Se, number of mangrove seedlings and mean mangrove biomass. Rather than tolerant polychaetes dominating metal(loid)-contaminated sediments (as is found generally in subtidal sediments), polychaetes in intertidal mangroves appeared to be relatively sensitive to metal(loid) stress. Further, decapod crustaceans in the family, Varunidae, and gastropod molluscs, in the family, Amphibolidae, were found to be metal-sensitive taxa and may be employed in future studies as indicator taxa of sediment metal(loid)-related impacts in south-eastern Australian mangrove forests.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi, D. (2009). The energetics of mangrove forests. Springer Netherlands.
Amin, B., Ismail, A., Arshad, A., Yap, C. K., & Kamarudin, M. S. (2009). Gastropod assemblages as indicators of sediment metal contamination in mangroves of Dumai, Sumatra, Indonesia. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 201(1–4), 9–18.
Anderson, M. (2001). A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecology, 26, 32–46.
ANZECC/ARMCANZ. (2000). Australian water quality guidelines for fresh and marine waters. Canberra: Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council and Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand.
Barwick, M., & Maher, W. (2003). Biotransference and biomagnification of selenium, copper, cadmium, zinc, arsenic and lead in a temperate Seagrass ecosystem from Lake Macquarie estuary, NSW, Australia. Marine Environmental Research, 56(4), 471–502.
Batley, G. (1987). Heavy metal speciation in waters, sediments and biota from Lake Macquarie NSW. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 38, 591–606.
Batley, G., Simpson, S. (2016). Chapter 2. Sediment sampling, sample preparation and general analysis. In: Sediment quality assessment: a practical guide. 2nd edition. Clayton South, Vic.: CSIRO Publishing; 2016.
Birch, G. F., O'Donnell, M. A., & McCready, S. (2018). Complex relationships between shallow muddy benthic assemblages, sediment chemistry and toxicity in estuaries in southern New South Wales, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 129(2), 573–591.
Bloomfield, A., & Gillanders, B. (2005). Fish and invertebrate assemblages in seagrass, mangrove, saltmarsh and non-vegetated habitats. Estuaries, 28(1), 63–77.
Brady, J., Ayoko, G., Martins, W., & Goonetilleke, A. (2015). Weak acid extractable metals in Bramble Bay Queensland, Australia: temporal behaviour, enrichment and source appointment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 91(1), 380–388.
Brady, J., Kinaev, I., Goonetilleke, A., & Ayoko, G. (2016). Comparison of partial extraction reagents for assessing potential bioavailability of heavy metals in sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 106, 329–334.
Briggs, S. (1977). Estimates of biomass in a temperate mangrove community. Australian Journal of Ecology, 2, 369–373.
Burt, A., Maher, W., Roach, A., Krikowa, F., Honkoop, P., & Bayne, B. (2007). The accumulation of Zn, Se, Cd, and Pb and physiological condition of Anadara trapezia transplanted to a contamination gradient in Lake Macquarie, New South Wales, Australia. Marine Environmental Research, 64(1), 54–78.
Caregnato, F., Koller, C., MacFarlane, G., & Moreira, J. (2008). The glutathione antioxidant system as a biomarker suite for the assessment of heavy metal exposure and effect in the Grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56(6), 1119–1127.
Carroll, B. (1999). Microbial and geochemical aspects of selenium cycling in an Estuarine System-Lake Macquarie NSW. PhD Thesis, University of Sydney Australia.
Chapman, P., & Wang, F. (2001). Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20(1), 3–22.
Chariton, A. A. (2005). Responses in estuarine macrobenthic invertebrate assemblages to trace metal contaminated sediments. PhD thesis, University of Canberra.
Chariton, A. A., Roach, A. C., Simpson, S. L., & Batley, G. E. (2010). Influence of the choice of physical and chemistry variables on interpreting patterns of sediment contaminants and their relationships with estuarine macrobenthic communities. Marine and Freshwater Research, 61(10), 1109–1122.
Chariton, A. A., Maher, W. A., & Roach, A. C. (2011). Recolonisation of translocated metal-contaminated sediments by estuarine macrobenthic assemblages. Ecotoxicology, 20(4), 706–718.
Clarke, M., McConchie, D., Lewis, D., & Saenger, P. (1998). Redox stratification and heavy metal partitioning in Avicennia - dominated mangrove sediments: a geochemical model. Chemical Geology, 149(3–4), 147–171.
Clarke, K., Gorley, R., Somerfield, P., & Warwick, R. (2014). Change in marine communities: An approach to statistical analysis and interpretation (3rd ed.). Plymouth: PRIMER-E.
Cuong, D., Bayen, S., Wurl, O., Subramanian, K., Wong, K., Sivasothi, N., & Obbard, J. (2005). Heavy metal contamination in mangrove habitats of Singapore. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(12), 1732–1138.
Dafforn, K. A., Kelaher, B. P., Simpson, S. L., Coleman, M. A., Hutchings, P. A., Clark, G. F., et al. (2013). Polychaete richness and abundance enhanced in anthropogenically modified estuaries despite high concentrations of toxic contaminants. PLoS One, 8(9), e77018.
Duodu, G., Goonetilleke A., Ayoko, G. (2017). Potential Bioavailability Assessment, Source Apportionment and Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of Brisbane River Estuary, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 117(1- 2): 523–531.
Harbison, P. (1986). Mangrove muds – a sink and a source for trace metals. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 17(6), 246–250.
He, Y., DeSutter, T., Prunty, L., Hopkins, D., Jia, X., & Wysocki, D. (2012). Evaluation of 1:5 soil to water extract electrical conductivity methods. Geoderma, 185-186, 12–17.
Hu, C., Yang, X., Dong, J., & Zhang, X. (2018). Heavy metal concentrations and chemical fractions in sediment from swan lagoon, China: their relation to the physiochemical properties of sediment. Chemosphere, 209, 848–856.
Johnston, E. L., & Roberts, D. A. (2009). Contaminants reduce the richness and evenness of marine communities: a review and meta-analysis. Environmental Pollution, 157(6), 1745–1752.
Kathiresan, K., & Bingham, B. (2001). Biology of mangroves and mangrove ecosystems. Advances in Marine Biology, 40, 81–251.
Kirby, J., Maher, W., & Krikowa, F. (2001a). Selenium, cadmium, copper and zinc concentrations in sediments and mullet (Mugil cephalus) from the Southern Basin of Lake Macquarie, NSW, Australia. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 40, 246–256.
Kirby, J., Maher, W., & Harasti, D. (2001b). Changes in selenium, copper, cadmium and zinc concentrations in mullet (Mugil cephalus) from the Southern Basin of Lake Macquarie in response to alteration of coal-fired power station fly ash handling procedures. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 41, 171–181.
Kristensen, E., Bouillon, S., Dittmar, T., & Marchand, C. (2008). Organic carbon dynamics in mangrove ecosystems: a review. Aquatic Botany, 89(2), 201–219.
Laing, G., De Vos, R., Vandecasteele, B., Lesage, E., Tack, F., & Verloo, M. (2008). Effect of salinity on heavy metal mobility and availability in intertidal sediments of the Scheldt estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 77(4), 589–602.
Lopez, L., Couture, P., Maher, W., Krikowa, F., Jolley, D., & Davis, A. (2014). Response of the hairy mussel Trichomya hirsute to sediment-metal contamination in the presence of a Bioturbator. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 88(1–2), 180–187.
MacFarlane, G., & Booth, D. (2000). Estuarine macrobenthic community structure in the Hawkesbury River, Australia: relationships with sediment physiochemical and anthropogenic parameters. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 72, 51–78.
Nagelkerken, I., Blaber, S., Bouillon, S., Green, P., Haywood, M., Kirton, L., Meynecke, J., Pawlik, J., Penrose, H., Sasekumar, A., & Somerfield, P. (2008). The habitat function of mangroves for terrestrial and marine Fauna: a review. Aquatic Botany, 89(2), 155–185.
Naser, H. (2010). Testing taxonomic resolution levels for detecting environmental impacts using macrobenthic assemblages in tropical waters. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 170, 435–444.
NSW Department of Planning and Environment (DP&E). (2018). Proposed State Environmental Planning Policy Amendment (Remediation of Land).
Office of Environment and Heritage. (2018). Lake Macquarie: estuary characteristics. https://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/topics/water/estuaries/estuaries-of-nsw/lake-macquarie. Accessed 5 Nov 2017.
Olsgard, F., Somerfield, P., & Carr, M. (1998). Relationships between taxonomic resolution, macrobenthic community patterns and disturbance. Marine Ecology Progess Series, 172, 25–36.
Parvaresh, H., Abedi, Z., Farshchi, P., Karami, M., Khorasani, N., & Karbassi, A. (2011). Bioavailability and concentration of heavy metals in the sediments and leaves of grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh, in Sirik Azini Creek, Iran. Biology Trace Element Research, 143(2), 1121–1130.
Peters, E., Gassman, N., Firman, J., Richmond, R., & Power, E. (1997). Ecotoxicology of tropical marine ecosystems. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 16(1), 12–40.
Peters, G., Maher, W., Krikowa, F., Roach, A., Jeswani, H., Barford, J., Gomes, V., & Reible, D. (1999). Selenium in sediments, pore waters and benthic infauna of Lake Macquarie, New South Wales, Australia. Marine Environmental Research, 47(5), 491–508.
Pilo, D., Pereira, G., Carrico, A., Curdia, J., Pereira, P., Gaspar, M., & Carvalho, D. (2015). Temporal variability of biodiversity patterns and trophic structure of estuarine macrobenthic assemblages along a gradient of metal contamination. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 167(Part A), 286–299.
Pocklington, P., & Wells, P. G. (1992). Polychaetes key taxa for marine environmental quality monitoring. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 24(12), 593–598.
Qu, X., Wu, N., Tang, T., Cai, Q., & Park, Y. (2010). Effects of heavy metals on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in high mountain streams. Annales Limnology – International Journal of Limnology, 46, 291–302.
Roach, A. (2005). Assessment of metals in sediments from Lake Macquarie, New South Wales, Australia, using normalisation models and sediment quality guidelines. Marine Environmental Research, 59(5), 453–472.
Rochow, J. (1974). Estimates of above-ground biomass and primary productivity in a Missouri Forest. Journal of Ecology, 62, 567–577.
Roy, P., & Crawford, E. (1984). Heavy metals in a contaminated Australian estuary – dispersion and accumulation trend. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 19(3), 341–358.
Rumisha, C., Elskens, M., Leermakers, M., & Kochzius, M. (2012). Trace metal pollution and its influence on the community structure of soft bottom Molluscs in intertidal areas of the Dares Salaam Coast, Tanzania. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(3), 521–531.
Schneider, L., Maher, W., Potts, J., Gruber, B., Batley, G., Taylor, A., Chariton, A., Krikowa, F., Zawadzki, A., & Heijnis, H. (2014). Recent history of sediment metal contamination in Lake Macquarie, Australia, and an assessment of ash handling procedure effectiveness in mitigating metal contamination from coal-fired Power stations. Science of the Total Environment, 490, 659–670.
Schneider, L., Maher, W., Potts, J., Taylor, A., Batley, G., Krikowa, F., Adamack, A., Chariton, A., & Gruber, B. (2018). Trophic transfer of metals in a Seagrass food web: Bioaccumulation of essential and non-essential metals. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 131(Part A), 468–480.
Simpson, S., Batley, G., Chariton, A., Stauber, J., King, C., Chapman, J., Hyne, R., Gale, S., Roach, A., Maher, W. (2005). Handbook for sediment quality assessment (CSIRO: Bangor, NSW).
Smith, T., Chan, H., McIvor, C., & Robblee, M. (1989). Comparisons of seed predation in tropical tidal forests from three continents. Ecology, 70(1), 146–151.
Stark, J. (1998). Heavy metal pollution and macrobenthic assemblages in soft sediments in two Sydney estuaries, Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research, 49(6), 533–540.
Suh, J. Y., Birch, G. F., Hughes, K., & Matthai, C. (2004). Spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in reclaimed lands of Homebush Bay: the venue of the 2000 Olympic Games, Sydney, New South Wales. Australian Journal of Earth Science, 51(1), 53–66.
Sundaramanickam, A., Shanmugam, N., Cholan, S., Kumaresan, S., Madeswaran, P., & Balasubramanian, T. (2016). Spatial variability of heavy metals in estuarine, mangrove and coastal ecosystems along Parangipettai, southeast coast of India. Environmental Pollution, 218, 186–195.
Swain, D., & Goodarizi, F. (1995). Environmental aspects of trace elements in coal (Vol. 2). Dordrecht: Springer.
Tarin, P. (2006). Distribution, speciation and geochemistry of selenium in contaminated marine sediments - Port Kembla Harbour, NSW, Australia, PhD thesis, School of Earth & Environmental Sciences, University of Wollongong.
Tran, T. K. A., Islam, R., Le Van, D., Rahman, M. M., Yu, R. M. K., & MacFarlane, G. R. (2020). Accumulation and partitioning of metals and metalloids in the halophytic saltmarsh grass, saltwater couch, Sporobolus virginicus. Science of the Total Environment, 713, 136576.
Turkman, G., & Kazanci, N. (2010). Applications of various biodiversity indices to benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in streams of a National Park in Turkey. Review of Hydrobiology, 3(2), 111–125.
U.S. EPA. 1996. “Method 3050B: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils,” Revision 2. Washington, DC.
Vårhammar, A., McLean, C. M., Yu, R. M. K., & MacFarlane, G. R. (2019). Uptake and partitioning of metals in the Australian saltmarsh halophyte, samphire (Sarcocornia quinqueflora). Aquatic Botany, 156, 25–37.
Walters, B., Ronnback, P., Kovacs, J., Crona, B., Hussain, S., Badola, R., Primavera, J., Barbier, E., & Dahdouh-Guebas, F. (2008). Ethnobiology, socio-economics and management of mangrove forests: a review. Aquatic Botany, 89(2), 220–236.
Ward, T., & Hutchings, P. (1996). Effects of trace metals on infaunal species composition in polluted intertidal and subtidal marine sediments near a lead smelter, Spencer Gulf, South Australia. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 135(1–3), 123–135.
Wu, Z., He, M., Lin, C., & Fan, Y. (2011). Distribution and speciation of four heavy metals (Cd, Cr, Mn, and Ni) in the surficial sediments from estuary in Daliao River and Yingkou Bay. Environmental Earth Science, 63, 163–175.
Zhang, C., Yu, Z., Zeng, G., Jiang, M., Yang, Z., Cui, F., Zhu, M., Shen, L., & Hu, L. (2014). Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environment International, 73, 270–281.
Acknowledgments
Macroinvertebrate taxa were collected under a NSW Fisheries scientific collection permit P13/0037. Thanks to Cody Henderson and John Hembra for assistance with field sampling and laboratory analyses. Additional appreciation is extended to Tony Rothkirch for assistance in ICPMS analysis and to Mahmud Rahman from the Global Centre for Environmental Remediation, University of Newcastle, for assistance with CNS analysis. Thanks to Olivier Rey-Lescure for map preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 24 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roe, R.A.L., Tran, T.K.A., Schreider, M.J. et al. Assessment of the Effects of Sediment-Associated Metals and Metalloids on Mangrove Macroinvertebrate Assemblages. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 352 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04731-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04731-7