Abstract
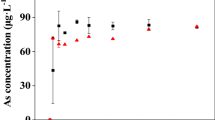
The release of arsenic (As) from sediments poses a risk to human health especially at high pH levels. Despite this, the distribution and kinetic response of mobile As remains unclear under varying pH conditions. In this study, a microcosm incubation experiment was performed, using sediment cores in combination with dialysis (Peeper) and thin film diffusive gradients (DGT), to investigate the distributions of mobile As (soluble As in pore water and DGT-labile As) at high vertical resolutions (2–4 mm). Results show that the concentrations of soluble As present in the water column increased 1.5-fold with an increase in pH from 5.4 to 11.2. Both soluble As in pore water and DGT-labile As exhibited stable low-level distributions in the uppermost layer beneath the sediment-water interface, followed by increasing concentration distribution with decreasing layers to middle depths. The mean concentrations of mobile As species increased with increased water pH in both sediment profiles and with upward diffusion gradients, showing a 0.2-fold increase of soluble As in the top 20-mm layer and a 0.6-fold increase in deeper 20–52-mm layers, while DGT-labile As showed a 1.0- and 1.1-fold increase in these two layers, respectively. Modeling of DGT-induced flux in sediments (DIFS) showed that the desorption rate constant increased more rapidly than the absorption rate constant, resulting in the increased availability of solid As pools, therefore resupplying the soluble As in pore water from sediments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar, J., Dorronsoro, C., Fernández, E., Fernández, J., García, I., Martín, F., Sierra, M., & Simón, M. (2007). Arsenic contamination in soils affected by a pyrite-mine spill (Aznalcóllar, SW Spain). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 180(1–4), 271–281.
Aziz, Z., Bostick, B. C., Zheng, Y., Huq, M. R., Rahman, M. M., Ahmed, K. M., & van Geen, A. (2017). Evidence of decoupling between arsenic and phosphate in shallow groundwater of Bangladesh and potential implications. Applied Geochemistry, 77, 167–177.
Bennett, W. W., Teasdale, P. R., Panther, J. G., Welsh, D. T., Zhao, H. J., & Jolley, D. F. (2012a). Investigating arsenic speciation and mobilization in sediments with DGT and DET: a mesocosm evaluation of oxic-anoxic transitions. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(7), 3981–3989.
Bennett, W. W., Teasdale, P. R., Welsh, D. T., Panther, J. G., Stewart, R. R., Price, H. L., & Jolley, D. F. (2012b). Inorganic arsenic and iron(II) distributions in sediment porewaters investigated by a combined DGT-colourimetric DET technique. Environmental Chemistry, 9(1), 31–40.
Bose, P., & Sharma, A. (2002). Role of iron in controlling speciation and mobilization of arsenic in subsurface environment. Water Research, 36(19), 4916–4926.
Ding, S. M., Qin, S., & Di, X. (2010a). Development of the DET technique for high-resolution determination of soluble reactive phosphate profiles in sediment pore waters. International Journal of Environmental and Analytical Chemistry, 90, 1130–1138.
Ding, S., Xu, D., Sun, Q., Yin, H., & Zhang, C. (2010b). Measurement of dissolved reactive phosphorus using the diffusive gradients in thin films technique with a high-capacity binding phase. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(21), 8169–8174.
Ding, S., Han, C., Wang, Y., Yao, L., Wang, Y., Xu, D., Sun, Q., Williams, P. N., & Zhang, C. (2015). In situ, high-resolution imaging of labile phosphorus in sediments of a large eutrophic lake. Water Research, 74(0), 100–109.
Ding, S., Xu, D., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Gong, M., & Zhang, C. (2016). Simultaneous measurements of eight oxyanions using high-capacity diffusive gradients in thin films (Zr-oxide DGT) with a high-efficiency elution procedure. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(14), 7572.
Dixit, S., & Hering, J. G. (2003). Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(18), 4182–4189.
Du, M., Wei, D., Tan, Z., Lin, A., & Du, Y. (2015). The potential risk assessment for different arsenic species in the aquatic environment. Journal Environmental Sciences, 27(1), 1–8.
Ernstberger, H., Zhang, H., Tye, A., Young, S., & Davison, W. (2005). Desorption kinetics of Cd, Zn, and Ni measured in soils by DGT. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(6), 1591–1597.
Gao, X., Su, C., Wang, Y., & Hu, Q. (2013). Mobility of arsenic in aquifer sediments at Datong Basin, northern China: effect of bicarbonate and phosphate. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 135, 93–103.
Gorchev, H. G., & Ozolins, G. (2004). WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization.
Guerra, P., Gonzalez, C., Escauriaza, C., Pizarro, G., & Pasten, P. (2016). Incomplete mixing in the fate and transport of arsenic at a river affected by acid drainage. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227(3), 1–20.
Guo, H., Wen, D., Liu, Z., Jia, Y., & Guo, Q. (2014). A review of high arsenic groundwater in Mainland and Taiwan, China: distribution, characteristics and geochemical processes. Applied Geochemistry, 41(1), 196–217.
Hafeznezami, S., Zimmer-Faust, A. G., Dunne, A., Tran, T., Yang, C., & Lam, J. (2016). Adsorption and desorption of arsenate on sandy sediments from contaminated and uncontaminated saturated zones: kinetic and equilibrium modeling. Environmental Pollution, 215, 290–301.
Handley, K. M., McBeth, J. M., Charnock, J. M., Vaughan, D. J., Wincott, P. L., Polya, D. A., & Lloyd, J. R. (2013). Effect of iron redox transformations on arsenic solid-phase associations in an arsenic-rich, ferruginous hydrothermal sediment. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 102(2), 124–142.
Harper, M. P., Davison, W., Zhang, H., & Tych, W. (1998). Kinetics of metal exchange between solids and solutions in sediments and soils interpreted from DGT measured fluxes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(16), 2757–2770.
Harper, M. P., Davison, W., & Tych, W. (2000). DIFS—a modelling and simulation tool for DGT induced trace metal remobilisation in sediments and soils. Environmental Modelling & Software, 15(1), 55–66.
Hinsinger, P., Plassard, C., Tang, C., & Jaillard, B. (2003). Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: a review. Plant and Soil, 248(1), 43–59.
Jia, Y., Xu, L., Wang, X., & Demopoulos, G. P. (2007). Infrared spectroscopic and X-ray diffraction characterization of the nature of adsorbed arsenate on ferrihydrite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(7), 1643–1654.
Kaur, S., Kamli, M. R., & Ali, A. (2011). Role of arsenic and its resistance in nature. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 57, 769–774.
Lock, A., Wallschläger, D., Belzile, N., Spiers, G., & Gueguen, C. (2017). Rates and processes affecting As speciation and mobility in lake sediments during aging. Journal of Environmental Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.05.003.
Ma, J., Guo, H., Lei, M., Zhou, X., Li, F., & Yu. (2015). Arsenic adsorption and its fractions on aquifer sediment: effect of pH, arsenic species, and iron/manganese minerals. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 226(260), 1–15.
Maji, S. K., Pal, A., Pal, T., & Adak, A. (2007). Adsorption thermodynamics of arsenic on laterite soil. Journal of Surface Science & Technology, 22(3), 161–176.
Mamindy-Pajany, Y., Hurel, C., Marmier, N., & Roméo, M. (2011). Arsenic (V) adsorption from aqueous solution onto goethite, hematite, magnetite and zero-valent iron: effects of pH, concentration and reversibility. Desalination, 281(20), 93–99.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta, 58(1), 201–235.
Matera, V., Hécho, I. L., Selim, H. M., & Sparks, D. L. (2001). Heavy metals release in soils (pp. 207–235). USA: Vadose Zone Journal.
Mittal, P., Chhillar, D., Dhattarwal, S. K., Singla, K., Merry, V., & Singh, S. (2014). Criminal arsenic poisoning: a case report. Anil Aggrawals Internet Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology, 15 (2), 11 p.
O'Day, P. A., Vlassopoulos, D., Root, R., & Rivera, N. (2004). The influence of sulfur and iron on dissolved arsenic concentrations in the shallow subsurface under changing redox conditions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(38), 13703–13708.
Pedersen, H. D., Postma, D., & Jakobsen, R. (2006). Release of arsenic associated with the reduction and transformation of iron oxides. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(16), 4116–4129.
Qiao, J., Jiang, Z., Sun, B., Sun, Y., & Wang, Q. (2012). Arsenate and arsenite removal by FeCl 3 : effects of pH, As/Fe ratio, initial As concentration and co-existing solutes. Separation and Purification Technology, 92(1), 106–114.
Roggenbeck, B. A., Banerjee, M., & Leslie, E. M. (2016). Cellular arsenic transport pathways in mammals. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 49, 38–58.
Root, R. A., Dixit, S., Campbell, K. M., Jew, A. D., Hering, J. G., & O'Day, P. A. (2007). Arsenic sequestration by sorption processes in high-iron sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(23), 5782–5803.
Rubinos, D. A., Iglesias, L., Díaz-Fierros, F., & Barral, M. T. (2011). Interacting effect of pH, phosphate and time on the release of arsenic from polluted river sediments (Anllóns River, Spain). Aquatic Geochemistry, 17(3), 281–306.
Santner, J., Larsen, M., Kreuzeder, A., & Glud, R. N. (2015). Two decades of chemical imaging of solutes in sediments and soils—a review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 878, 9–42.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17(5), 517–568.
Stockdale, A., Davison, W., & Zhang, H. (2009). Micro-scale biogeochemical heterogeneity in sediments: a review of available technology and observed evidence. Earth-Science Reviews, 92(1–2), 81–97.
Sun, Q., Chen, J., Zhang, H., Ding, S., Li, Z., & Williams. (2014). Improved diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) measurement of total dissolved inorganic arsenic in waters and soils using a hydrous zirconium oxide binding layer. Analytical Chemistry, 86(6), 3060–3067.
Sun, Q., Ding, S., Wang, Y., Xu, L., Wang, D., Chen, J., & Zhang, C. (2016). In-situ characterization and assessment of arsenic mobility in lake sediments. Environmental Pollution, 214, 314–323.
Sun, Q., Ding, S., Zhang, L., Cheng, M., & Zhang, C. (2017). A millimeter-scale observation of the competitive effect of phosphate on promotion of arsenic mobilization in sediments. Chemosphere, 180, 285–294.
Tufano, K. J., Reyes, C., Saltikov, C. W., & Fendorf, S. (2008). Reductive processes controlling arsenic retention: revealing the relative importance of iron and arsenic reduction. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(22), 8283–8289.
Wang, Z. H., & Liang, Y. (2015). Growth and alkaline phosphatase activity of Chattonella marina and Heterosigma akashiwo in response to phosphorus limitation. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 28(2), 1–7.
Wang, S., & Mulligan, C. N. (2006). Effect of natural organic matter on arsenic release from soils and sediments into groundwater. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28(3), 197–214.
Wang, S., Cao, X., Lin, C., & Chen, X. (2010). Arsenic content and fractionation in the surface sediments of the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River in Southern China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183(1), 264–270.
Wang, C., Yao, Y., Wang, P., Hou, J., Qian, J., Yuan, Y., & Fan, X. (2016). In situ high-resolution evaluation of labile arsenic and mercury in sediment of a large shallow lake. Science of the Total Environment, 541, 83–91.
Xu, D., Wu, W., Ding, S., Sun, Q., & Zhang, C. (2012). A high-resolution dialysis technique for rapid determination of dissolved reactive phosphate and ferrous iron in pore water of sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 421, 245–252.
Yao, Y., Wang, C., Wang, P., Hou, J., Wang, T., Liu, C., & Yuan, Y. (2016). In situ, high resolution ZrO-Chelex DGT for the investigation of iron-coupled inactivation of arsenic in sediments by macrozoobenthos bioturbation and hydrodynamic interactions. Science of the Total Environment, 562, 451–462.
Zhang, W., Singh, P., Paling, E. I., & Delides, S. (2004). Arsenic removal from contaminated water by natural iron ores. Minerals Engineering, 17(4), 517–524.
Zhou, A., Tang, H., & Wang, D. (2005). Phosphorus adsorption on natural sediments: modeling and effects of pH and sediment composition. Water Research, 39(7), 1245–1254.
Acknowledgements
This study was jointly sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41621002, 41571465, 41322011) and National High-level Personnel of Special Support Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Sun, Q., Ding, S. et al. Mobile Arsenic Distribution and Release Kinetics in Sediment Profiles under Varying pH Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 413 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3601-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3601-4