Abstract
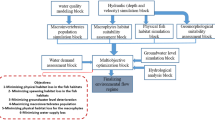
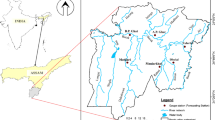
The design of stepped spillways is a multi-objective optimization problem in which the uncertainty of parameters plays a key role in the stepped spillways’ design. A Fuzzy Transformation Method (FTM), as a first attempt, was employed to address the uncertainty through a multi-objective optimization of the stepped spillway. The proposed methodology comprises two parts. A numerical model is developed by FLOW3D® and the Multi-Layer Perceptron artificial neural network (MLP-ANN) meta-model was trained and validated to substitute the numerical model. Then, the meta-model is coupled with a multi-objective optimization model to find the optimal design scenarios in each α-cut level. Finally, two multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) models are applied to achieve the lower and upper bounds of optimum solutions. The application of proposed methodology in Jarreh dam, Iran, shows its capability in satisfying the objectives and also addressing the uncertainty in stepped spillways’ design.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadeh MR, Nikoo MR, Rakhshandehroo GR (2017) Hydro-environmental management of groundwater resources: a fuzzy-based multi-objective compromise approach. J Hydrol 551:540–554
Bayon A, Toro JP, Bombardelli FA, Matos J, López-Jiménez PA (2018) Influence of VOF technique, turbulence model and discretization scheme on the numerical simulation of the non-aerated, skimming flow in stepped spillways. J Hydro Environ Res 19:137–149
Boes RM, Hager WH (2003) Two-phase flow characteristics of stepped spillways. J Hydraul Eng 129(9):661–670
Cheng X, Gulliver JS, Zhu D (2014) Application of displacement height and surface roughness length to determination boundary layer development length over stepped spillway. Water 6(12):3888–3912
Deardorff JW (1970) A numerical study of three-dimensional turbulent channel flow at large Reynolds numbers. J Fluid Mech 41(2):453–480
Deb K, Agrawal S, Pratap A, Meyarivan T (2000) A fast elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization: NSGA-II. International conference on parallel problem solving from nature (pp. 849–858). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Farhadi S, Nikoo MR, Rakhshandehroo GR, Akhbari M, Alizadeh MR (2016) An agent-based-Nash modeling framework for sustainable groundwater management: a case study. Agric Water Manag 177:348–358
Frizell KW, Renna FM, Matos J (2012) Cavitation potential of flow on stepped spillways. J Hydraul Eng 139(6):630–636
Haddad OB, Mirmomeni M, Mariño MA (2010) Optimal design of stepped spillways using the HBMO algorithm. Civ Eng Environ Syst 27(1):81–94
Harlow FH, Nakayama PI (1968) Transport of turbulence energy decay rate (no. LA-3854). Los Alamos Scientific Lab, N. Mex
Hwang CL, Yoon KS (1981) Multiple attribute decision making: methods and applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Kavianpour MR, Masoumi HR (2008) New approach for estimating of energy dissipation over stepped spillways. Int J Civil Eng 6(3):230–237
Kazakis N, Spiliotis M, Voudouris K, Pliakas FK, Papadopoulos B (2018) A fuzzy multicriteria categorization of the GALDIT method to assess seawater intrusion vulnerability of coastal aquifers. Sci Total Environ 621:524–534
Khoramshokooh N, Veiskarami M, Nikoo MR, Roshandeh SP (2018) Multi-objective hydraulic optimization of diversion Dam’s cut-off. Water Resour Manag: 1–14
Kramer M, Chanson H (2018) Transition flow regime on stepped spillways: air–water flow characteristics and step-cavity fluctuations. Environ Fluid Mech: 1–19
Kuang H, Kilgour DM, Hipel KW (2015) Grey-based PROMETHEE II with application to evaluation of source water protection strategies. Inf Sci 294:376–389
Lu HW, Huang GH, He L (2010) Development of an interval-valued fuzzy linear-programming method based on infinite α-cuts for water resources management. Environ Model Softw 25(3):354–361
Mareschal B, Brans JP, Vincke P (1984) PROMETHEE: A new family of outranking methods in multicriteria analysis (no. 2013/9305). ULB--Universite Libre de Bruxelles
Musavi-Jahromi H, Bina M, Salmasi F (2008) Physical and numerical modeling of the nappe flow in the stepped spillways. J Appl Sci 8(9):1720–1725
Rad IN, Teimouri M (2010) An investigation of flow energy dissipation in simple stepped spillways by numerical model. European Journal of Scientific Research 47
Naserizade SS, Nikoo MR, Montaseri H (2018) A risk-based multi-objective model for optimal placement of sensors in water distribution system. J Hydrol 557:147–159
Nikoo MR, Kerachian R, Karimi A, Azadnia AA (2013) Optimal water and waste-load allocations in rivers using a fuzzy transformation technique: a case study. Environ Monit Assess 185(3):2483–2502
Nikoo MR, Varjavand I, Kerachian R, Pirooz MD, Karimi A (2014) Multi-objective optimumA design of double-layer perforated-wall breakwaters: application of NSGA-II and bargaining models. Appl Ocean Res 47:47–52
Nikoo MR, Khorramshokouh N, Monghasemi S (2015) Optimal design of detention rockfill dams using a simulation-based optimization approach with mixed sediment in the flow. Water Resour Manag 29(15):5469–5488
Nikoo MR, Gavahi K, Khoramshokooh N (2017) A multi-objective simulation–optimization approach for Design of Cutoff Walls and Apron of diversion dams. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Civil Engineering: 1–12
Parsaie A, Haghiabi AH, Saneie M, Torabi H (2016) Prediction of energy dissipation on the stepped spillway using the multivariate adaptive regression splines. ISH J Hydraul Eng 22(3):281–292
Revelli R, Ridolfi L (2002) Fuzzy approach for analysis of pipe networks. J Hydraul Eng 128(1):93–101
Roushangar K, Akhgar S, Salmasi F, Shiri J (2014) Modeling energy dissipation over stepped spillways using machine learning approaches. J Hydrol 508:254–265
Roushangar K, Akhgar S, Salmasi F, Shiri J (2017) Neural networks-and neuro-fuzzy-based determination of influential parameters on energy dissipation over stepped spillways under nappe flow regime. ISH J Hydraul Eng 23(1):57–62
Sadegh M, Kerachian R (2011) Water resources allocation using solution concepts of fuzzy cooperative games: fuzzy least core and fuzzy weak least core. Water Resour Manag 25(10):2543–2573
Sapkota M, Arora M, Malano H, Sharma A, Moglia M (2018) Integrated evaluation of hybrid Water supply systems using a PROMETHEE–GAIA approach. Water 10(5):610
Sarkardeh H, Marosi M, Roshan R (2015) Stepped spillway optimization through numerical and physical modeling. Int J Energy Environ 6(6):597
Shrestha B, Cochrane TA, Caruso BS, Arias ME, Piman T (2016) Uncertainty in flow and sediment projections due to future climate scenarios for the 3S Rivers in the Mekong Basin. J Hydrol 540:1088–1104
Simões ALA, Schulz HE, Lobosco RJ, de Melo Porto R (2012) Stepped spillways: theoretical, experimental and numerical studies. Hydrodynamics-natural Water bodies. InTech
Spiliotis M, Tsakiris G (2010) Water distribution system analysis: Newton-Raphson method revisited. J Hydraul Eng 137(8):852–855
Spiliotis M, Skoulikaris C (2018) A hybrid multicriteria 0/1 programming methodology for prioritizing the measures of River Basin management plans. Multidisciplin Digit Publ Instit Proc 2(11):624
Srdjevic B, Medeiros YDP, Faria AS (2004) An objective multi-criteria evaluation of water management scenarios. Water Resour Manag 18(1):35–54
Terrier S (2016) Hydraulic performance of stepped spillway aerators and related downstream flow features (no. BOOK). EPFL-LCH
Toro JP, Bombardelli FA, Paik J, Meireles I, Amador A (2016) Characterization of turbulence statistics on the non-aerated skimming flow over stepped spillways: a numerical study. Environ Fluid Mech 16(6):1195–1221
Tsakiris G, Spiliotis M (2017) Uncertainty in the analysis of urban water supply and distribution systems. J Hydroinf 19(6):823–837
Yakhot V, Orszag SA (1986) Renormalization group analysis of turbulence. I. Basic theory. J Sci Comput 1(1):3–51
Yakhot V, Smith LM (1992) The renormalization group, the ɛ-expansion and derivation of turbulence models. J Sci Comput 7(1):35–61
Zhang K, Kluck C, Achari G (2009) A comparative approach for ranking contaminated sites based on the risk assessment paradigm using fuzzy PROMETHEE. Environ Manag 44(5):952
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 792 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorbani Mooselu, M., Nikoo, M.R., Bakhtiari Rayani, N. et al. Fuzzy Multi-Objective Simulation-Optimization of Stepped Spillways Considering Flood Uncertainty. Water Resour Manage 33, 2261–2275 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02263-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02263-2