Abstract
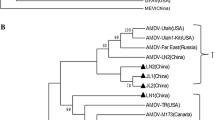
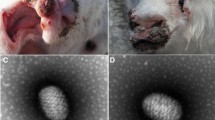
The genome of a highly pathogenic strain of Aleutian disease mink virus (AMDV-BJ) isolated from a domestic farm in North China has been determined and compared with other strains. Alignment analysis of the major structural protein VP2 revealed that AMDV-BJ is unique among 17 other AMDV strains. Compared with the nonpathogenic strain ADV-G, the 3′ end Y-shaped hairpin was highly conserved, while a 4-base deletion in the 5′ U-shaped terminal palindrome resulted in a different unpaired “bubble” group near the NS1-binding region of the 5′ end hairpin which may affect replication efficiency in vivo. We also performed a protein analysis of the NS1, NS2, and new-confirmed NS3 of AMDV-BJ with some related AMDV DNA sequence published, providing information on evolution of AMDV genes. This study shows a useful method to obtain the full-length genome of AMDV and some other parvoviruses.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Gorham, J.B. Henson, T.B. Crawford, G.A. Padgett, The epizootiology of aleutian disease. Front Biol. 44, 135–158 (1976)
S. Alexandersen, M.E. Bloom, Studies on the sequential development of acute interstitial pneumonia caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. J. Virol. 61, 81–86 (1987)
S. Alexandersen, M.E. Bloom, J. Wolfinbarger, R.E. Race, In situ molecular hybridization for detection of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus DNA by using strand-specific probes: identification of target cells for viral replication in cell cultures and in mink kits with virus-induced interstitial pneumonia. J. Virol. 61, 2407–2419 (1987)
S. Alexandersen, M.E. Bloom, J. Wolfinbarger, Evidence of restricted viral replication in adult mink infected with Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus. J. Virol. 62, 1495–1507 (1988)
W.J. Hadlow, R.E. Race, R.C. Kennedy, Comparative pathogenicity of four strains of Aleutian disease virus for pastel and sapphire mink. Infect. Immun. 41, 1016–1023 (1983)
B. Aasted, M.E. Bloom, Sensitive radioimmune assay for measuring Aleutian disease virus antigen and antibody. J. Clin. Microbiol. 18, 637–644 (1983)
M.E. Bloom, R.E. Race, W.J. Hadlow, B. Chesebro, Aleutian disease of mink: the antibody response of sapphire and pastel mink to Aleutian disease virus. J. Immunol. 115, 1034–1037 (1975)
D.D. Porter, A.E. Larsen, H.G. Porter, The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J. Exp. Med. 130, 575–593 (1969)
B. Aasted, S. Alexandersen, J. Christensen, Vaccination with Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (AMDV) capsid proteins enhances disease, while vaccination with the major non-structural AMDV protein causes partial protection from disease. Vaccine. 16, 1158–1165 (1998)
D.D. Porter, A.E. Larsen, Aleutian disease of mink—infectious virus-antibody complexes in serum. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 126, 680 (1967)
Y. Sang, J. Ma, Z. Hou, Y. Zhang, Phylogenetic analysis of the VP2 gene of Aleutian mink disease parvoviruses isolated from 2009 to 2011 in China. Virus Genes 45, 31–37 (2012)
L. Li, P.A. Pesavento, L. Woods, D.L. Clifford, J. Luff, C. Wang, E. Delwart, Novel amdovirus in gray foxes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17, 1876–1878 (2011)
S.F. Cotmore, M. Agbandje-McKenna, J.A. Chiorini, D.V. Mukha, D.J. Pintel, J. Qiu, M. Soderlund-Venermo, P. Tattersall, P. Tijssen, D. Gatherer, A.J. Davison, The family parvoviridae. Arch. Virol. 159, 1239–1247 (2014)
M.E. Bloom, S. Alexandersen, C.F. Garon, S. Mori, W. Wei, S. Perryman, J.B. Wolfinbarger, Nucleotide sequence of the 5′-terminal palindrome of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus and construction of an infectious molecular clone. J. Virol. 64, 3551–3556 (1990)
M.E. Bloom, S. Alexandersen, S. Perryman, D. Lechner, J.B. Wolfinbarger, Nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV): sequence comparisons between a nonpathogenic and a pathogenic strain of ADV. J. Virol. 62, 2903–2915 (1988)
S.F. Cotmore, P. Tattersall, The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv. Virus Res. 33, 91–174 (1987)
A. Knuuttila, K. Aaltonen, A.M.K. Virtala, H. Henttonen, M. Isomursu, A. Leimann, T. Maran, U. Saarma, P. Timonen, O. Vapalahti, T. Sironen, Aleutian mink disease virus in free-ranging mustelids in Finland—a cross-sectional epidemiological and phylogenetic study. J. Gen. Virol. 96, 1423–1435 (2015)
J.M. Qiu, F. Cheng, L.R. Burger, D. Pintel, The transcription profile of Aleutian mink disease virus in CRFK cells is generated by alternative processing of Pre-mRNAs produced from a single promoter. J. Virol. 80, 654–662 (2006)
Q. Huang, Y. Luo, F. Cheng, S.M. Best, M.E. Bloom, J. Qiu, Molecular characterization of the small nonstructural proteins of parvovirus Aleutian mink disease virus (AMDV) during infection. Virology 452, 23–31 (2014)
J.M. Qiu, F. Cheng, D. Pintel, The abundant R2 mRNA generated by aleutian mink disease parvovirus is tricistronic, encoding NS2, VP1, and VP2. J. Virol. 81, 6993–7000 (2007)
J. Christensen, M. Pedersen, B. Aasted, S. Alexandersen, Purification and characterization of the major nonstructural protein (NS-1) of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. J. Virol. 69, 1802–1809 (1995)
S.F. Cotmore, P. Tattersall, The NS-1 polypeptide of minute virus of mice is covalently attached to the 5′ termini of duplex replicative-form DNA and progeny single strands. J. Virol. 62, 851–860 (1988)
S.F. Cotmore, P. Tattersall, Alternate splicing in a parvoviral nonstructural gene links a common amino-terminal sequence to downstream domains which confer radically different localization and turnover characteristics. Virology 177, 477–487 (1990)
C.L. Miller, D.J. Pintel, Interaction between parvovirus NS2 protein and nuclear export factor Crm1 is important for viral egress from the nucleus of murine cells. J. Virol. 76, 3257–3266 (2002)
F. Costello, N. Steenfos, K.T. Jensen, J. Christensen, E. Gottschalck, A. Holm, B. Aasted, Epitope mapping of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus virion protein VP1 and 2. Scand. J. Immunol. 49, 347–354 (1999)
D.L. Clemens, J.B. Wolfinbarger, S. Mori, B.D. Berry, S.F. Hayes, M.E. Bloom, Expression of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus capsid proteins by a recombinant vaccinia virus: self-assembly of capsid proteins into particles. J. Virol. 66, 3077–3085 (1992)
J. Christensen, T. Storgaard, B. Bloch, S. Alexandersen, B. Aasted, Expression of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus proteins in a baculovirus vector system. J. Virol. 67, 229–238 (1993)
W.H. Wu, M.E. Bloom, B.D. Berry, M.J. McGinley, K.B. Platt, Expression of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus capsid proteins in a baculovirus expression system for potential diagnostic use. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 6, 23–29 (1994)
R. McKenna, N.H. Olson, P.R. Chipman, T.S. Baker, T.F. Booth, J. Christensen, B. Aasted, J.M. Fox, M.E. Bloom, J.B. Wolfinbarger, M. Agbandje-McKenna, Three-dimensional structure of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus: implications for disease pathogenicity. J. Virol. 73, 6882–6891 (1999)
M.E. Bloom, S.M. Best, S.F. Hayes, R.D. Wells, J.B. Wolfinbarger, R. McKenna, M. Agbandje-McKenna, Identification of aleutian mink disease parvovirus capsid sequences mediating antibody-dependent enhancement of infection, virus neutralization, and immune complex formation. J. Virol. 75, 11116–11127 (2001)
J.M. Fox, M.E. Bloom, Identification of a cell surface protein from Crandell feline kidney cells that specifically binds Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. J. Virol. 73, 3835–3842 (1999)
M.E. Bloom, D.A. Martin, K.L. Oie, M.E. Huhtanen, F. Costello, J.B. Wolfinbarger, S.F. Hayes, M. AgbandjeMcKenna, Expression of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus capsid proteins in defined segments: localization of immunoreactive sites and neutralizing epitopes to specific regions. J. Virol. 71, 705–714 (1997)
A.Q. Baldauf, K. Willwand, E. Mumtsidu, J.P.F. Nuesch, J. Rommelaere, Specific initiation of replication at the right-end telomere of the closed species of minute virus of mice replicative-form DNA. J. Virol. 71, 971–980 (1997)
S.F. Cotmore, P. Tattersall, High-mobility group 1/2 proteins are essential for initiating rolling-circle-type DNA replication at a parvovirus hairpin origin. J. Virol. 72, 8477–8484 (1998)
J. Christensen, P. Tattersall, Parvovirus initiator protein NS1 and RPA coordinate replication fork progression in a reconstituted DNA replication system. J. Virol. 76, 6518–6531 (2002)
S. Schuierer, M.E. Bloom, O.R. Kaaden, U. Truyen, Sequence analysis of the lymphotropic Aleutian disease parvovirus ADV-SL3. Arch. Virol. 142, 157–166 (1997)
J.H. Shien, Y.S. Wang, C.H. Chen, H.K. Shieh, C.C. Hu, P.C. Chang, Identification of sequence changes in live attenuated goose parvovirus vaccine strains developed in Asia and Europe. Avian Pathol. 37, 499–505 (2008)
A. Leimann, A. Knuuttila, T. Maran, O. Vapalahti, U. Saarma, Molecular epidemiology of Aleutian mink disease virus (AMDV) in Estonia, and a global phylogeny of AMDV. Virus Res. 199, 56–61 (2015)
M. Loechelt, H. Delius, O.R. Kaaden, A novel replicative form DNA of Aleutian disease virus: the covalently closed linear DNA of the parvoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 70, 1105–1116 (1989)
S.M. Best, J.F. Shelton, J.M. Pompey, J.B. Wolfinbarger, M.E. Bloom, Caspase cleavage of the nonstructural protein NS1 mediates replication of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. J. Virol. 77, 5305–5312 (2003)
J.P.F. Nuesch, P. Tattersall, Nuclear targeting of the parvoviral replicator molecule NS1: evidence for self-association prior to nuclear transport. Virology 196, 637–651 (1993)
Q.C. Yang, A. Kadam, J.P. Trempe, Mutational analysis of the adeno-associated virus rep gene. J. Virol. 66, 6058–6069 (1992)
J.A. Kleinschmidt, M. Mohler, F.W. Weindler, R. Heilbronn, Sequence elements of the adeno-associated virus rep gene required for suppression of herpes-simplex-virus-induced DNA amplification. Virology 206, 254–262 (1995)
E. Gottschalck, S. Alexandersen, T. Storgaard, M.E. Bloom, B. Aasted, Sequence comparison of the non-structural genes of four different types of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus indicates an unusual degree of variability. Arch. Virol. 138, 213–231 (1994)
K.L. Oie, G. Durrant, J.B. Wolfinbarger, D. Martin, F. Costello, S. Perryamn, D. Hogan, W.J. Hadlow, M.E. Bloom, The relationship between capsid protein (VP2) sequence and pathogenicity of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV): a possible role for raccoons in the transmission of ADV infections. J. Virol. 70, 852–861 (1996)
A. Knuuttila, P. Aronen, A. Saarinen, O. Vapalahti, Development and evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on recombinant VP2 capsids for the detection of antibodies to Aleutian mink disease virus. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 16, 1360–1365 (2009)
M.E. Bloom, B.D. Berry, W. Wei, S. Perryman, J.B. Wolfinbarger, Characterization of chimeric full-length molecular clones of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV): identification of a determinant governing replication of ADV in cell culture. J. Virol. 67, 5976–5988 (1993)
J.M. Fox, M.A.M. Stevenson, M.E. Bloom, Replication of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus in vivo is influenced by residues in the VP2 protein. J. Virol. 73, 8713–8719 (1999)
M.E. Bloom, J.M. Fox, B.D. Berry, K.L. Oie, J.B. Wolfinbarger, Construction of pathogenic molecular clones of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus that replicate both in vivo and in vitro. Virology 251, 288–296 (1998)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by 863 Project (2011AA10A213).
Funding
This study was funded by 863 Project (2011AA10A213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Edited by Juergen A. Richt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, J., Wang, J., Yu, Y. et al. Genetic characterization of the complete genome of an Aleutian mink disease virus isolated in north China. Virus Genes 52, 463–473 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-016-1320-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-016-1320-3