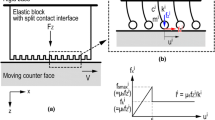
Abstract
This study develops a simplified model that can simulate the dynamics of a split contact interface at the transition from static to kinetic friction. The model has a contact interface formed by multiple contacting points connected to a rigid base via a spring. From a numerical analysis of this model, the effect of the stress distribution at the contact interface on the level of static friction force was investigated. Consequently, it was found that the existence of the stop-restart motion can act to increase the macroscopic (apparent) static friction force. Thus, the numerical analysis demonstrated that the macroscopic static friction coefficient could be changed without varying the local static friction coefficient. The type of tangential loading history, i.e., the existence of stop-restart motion, is an important factor for characterizing the level of the static friction force. In other words, this implies that we can adjust the level of the macroscopic static friction coefficient without changes to the local static friction. Furthermore, the above numerical prediction was confirmed by a model experiment focusing on the sliding contact interface of an object built from separated rubber blocks.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakano, K.: Two dimensionless parameters controlling the occurrence of stick–slip motion in a 1-DOF system with Coulomb friction. Tribol. Lett. 24, 91–98 (2006)
Nakano, K., Maegawa, S.: Safety-design criteria of sliding systems for preventing friction-induced vibration. J. Sound Vib. 324, 539–555 (2009)
Nakano, K., Maegawa, S.: Stick–slip in sliding systems with tangential contact compliance. Tribol. Int. 42, 1771–1780 (2009)
Maegawa, S., Nakano, K.: Mechanism of stick–slip associated with Schallamach waves. Wear 268, 924–930 (2010)
Maegawa, S., Itoigawa, F., Nakamura, T.: Dynamics in sliding friction of soft adhesive elastomer: Schallamach waves as a stress-relaxation mechanism. Tribol. Int. 96, 23–30 (2015)
Persson, B.N.J.: Sliding Friction: Physical Principles and Applications, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Rubinstein, S.M., Cohen, G., Fineberg, J.: Detachment fronts and the onset of dynamic friction. Nature 430, 1005–1009 (2004)
Varenberg, M., Gorb, S.: Hexagonal surface micropattern for dry and wet friction. Adv. Mater. 21, 483–486 (2009)
Popov, V.L.: Contact Mechanics and Friction: Physical Principals and Applications. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Maegawa, S., Suzuki, A., Nakano, K.: Precursors of global slip in a longitudinal line contact under non-uniform normal loading. Tribol. Lett. 38, 313–323 (2010)
Scheibert, J., Dysthe, D.K.: Role of friction-induced torque in stick–slip motion. Europhys. Lett. 92, 54001 (2010)
David, O.B., Fineberg, J.: Static friction coefficient is not a material constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 254301 (2011)
Murarash, B., Itovich, Y., Varenberg, M.: Tuning elastomer friction by hexagonal surface patterning. Soft Matter 7, 5553–5557 (2011)
Lorenz, B., Persson, B.N.J.: On the origin of why static or breakloose friction is larger than kinetic friction, and how to reduce it: the role of aging, elasticity and sequential interfacial slip. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 24, 225008 (2012)
Brormann, K., Barel, I., Urbakh, M., Bennewitz, R.: Friction on a microstructured elastomer surface. Tribol. Lett. 50, 3–15 (2013)
Otsuki, M., Matsukawa, H.: Systematic breakdown of Amonton’s law of friction for an elastic object locally obeying Amonton’s law. Sci. Rep. 3, 1586 (2013)
Ozaki, S., Inanobe, C., Nakano, K.: Finite element analysis of precursors to macroscopic stick–slip motion in elastic materials: analysis of friction test as a boundary value problem. Tribol. Lett. 55, 151–163 (2014)
Varenberg, M., Kligerman, Y.: Elimination of stick–slip motion in sliding of split or rough surface. Tribol. Lett. 53, 395–399 (2014)
Katano, Y., Nakano, K., Otsuki, M., Matsukawa, H.: Novel friction law for the static friction force based on local precursor slipping. Sci. Rep. 4, 06324 (2015)
Maegawa, S., Itoigawa, F., Nakamura, T.: A role of friction-induced torque on sliding friction of rubber materials. Tribol. Int. 93, 182–189 (2016)
Huthings, I.M.: Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials. Edward Arnold, London (1992)
Maegawa, S., Itoigawa, F., Nakamura, T.: Effect of normal load on friction coefficient for sliding contact between rough rubber surface and rigid smooth plane. Tribol. Int. 92, 335–343 (2015)
Dieterich, J.H., Kilgore, B.D.: Direct observation of frictional contacts: new insights for state-dependent properties. Pure. Appl. Geophys. 143, 283–302 (1994)
Bureau, L., Baumberger, T., Caroli, C.: Rheological aging and rejuvenation in solid friction contacts. Eur. Phys. J. E 8, 331–337 (2002)
Lorenz, B., Krick, B.A., Rodriguez, N., Sawyer, W.G., Mangiagalli, P., Persson, B.N.J.: Static or breakloose friction for lubricated contacts: the role of surface roughness and dwetting. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 25, 445013 (2013)
Chateauminois, A., Fretigny, C.: Local friction at a sliding interface between an elastomer and a rigid spherical probe. Eur. Phys. J. E 27, 221–227 (2008)
Prevost, A., Scheibert, J., Debregeas, G.: Probing the micromechanics of a multi-contact interface at the onset of frictional sliding. Eur. Phys. J. E 36, 17–29 (2013)
Tuononen, A.J.: Digital image correlation to analysis stick–slip behavior of tyre tread block. Tribol. Int. 69, 70–76 (2013)
Maegawa, S., Suzuki, A., Nakano, K.: Optical measurements of real contact area and tangential contact stiffness in rough contact interface between an adhesive elastomer and a glass plate. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manufact. 9, JAMDSM0069 (2015)
Kammer, D.S., Yastrebov, V.A., Spijker, P., Molinari, J.-F.: On the propagation of slip fronts at frictional interfaces. Tribol. Lett. 48, 27–32 (2012)
Bar-Sinai, Y., Brener, E.A., Bouchbinder, E.: Slow rupture of frictional interfaces. Geophys. Res. Lett. 39, L03308 (2012)
Bouchbinder, E., Brener, E.A., Barel, I., Urbakh, M.: Slow cracklike dynamics at the onset of frictional sliding. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 235501 (2011)
Bar-Sinai, Y., Spatschek, R., Brener, E.A., Bouchbinder, E.: Instabilities at frictional interfaces: creep patches, nucleation, and rupture fronts. Phys. Rev. E 88, 060403 (2013)
Rubinstein, S.M., Cohen, G., Fineberg, J.: Contact area measurements reveal loading-history dependence of static friction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 256103 (2006)
David, O.B., Cohen, G., Fineberg, J.: The dynamics of the onset of frictional slip. Science 330, 211–214 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maegawa, S., Itoigawa, F. & Nakamura, T. Effects of Stress Distribution at the Contact Interface on Static Friction Force: Numerical Simulation and Model Experiment. Tribol Lett 62, 15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0660-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0660-4