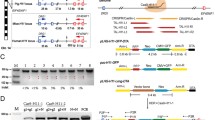
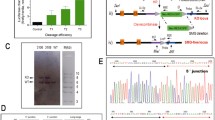
Abstract
Genetically modified (GM) pigs hold great promises for pig genetic improvement, human health and life science. When GM pigs are produced, selectable marker genes (SMGs) are usually introduced into their genomes for host cell or animal recognition. However, the SMGs that remain in GM pigs might have multiple side effects. To avoid the possible side effects caused by the SMGs, they should be removed from the genome of GM pigs before their commercialization. The Cre recombinase is commonly used to delete the LoxP sites-flanked SMGs from the genome of GM animals. Although SMG-free GM pigs have been generated by Cre-mediated recombination, more efficient and cost-effective approaches are essential for the commercialization of SMG-free GM pigs. In this article we describe the production of a recombinant Cre protein containing a cell-penetrating and a nuclear localization signal peptide in one construct. This engineered Cre enzyme can efficiently excise the LoxP-flanked SMGs in cultured fibroblasts isolated from a transgenic pig, which then can be used as nuclear donor cells to generate live SMG-free GM pigs harboring a desired transgene by somatic cell nuclear transfer. This study describes an efficient and far-less costly method for production of SMG-free GM pigs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki K, Araki M, Miyazaki J, Vassalli P (1995) Site-specific recombination of a transgene in fertilized eggs by transient expression of Cre recombinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(1):160–164
Bechara C, Sagan S (2013) Cell-penetrating peptides: 20 years later, where do we stand? FEBS Lett 587(12):1693–1702
Bi Y, Hua Z, Liu X, Hua W, Ren H, Xiao H, Zhang L, Li L, Wang Z, Laible G, Wang Y, Dong F, Zheng X (2016) Isozygous and selectable marker-free MSTN knockout cloned pigs generated by the combined use of CRISPR/Cas9 and Cre/LoxP. Sci Rep 6:31729
Brasseur R, Divita G (2010) Happy birthday cell penetrating peptides: already 20 years. Biochim Biophys Acta 1798(12):2177–2181
Cadinanos J, Bradley A (2007) Generation of an inducible and optimized piggyBac transposon system. Nucl Acids Res 35(12):e87
Gu H, Zou YR, Rajewsky K (1993) Independent control of immunoglobulin switch recombination at individual switch regions evidenced through Cre-loxP-mediated gene targeting. Cell 73(6):1155–1164
Hammer RE, Pursel VG, Rexroad CJ, Wall RJ, Bolt DJ, Ebert KM, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL (1985) Production of transgenic rabbits, sheep and pigs by microinjection. Nature 315(6021):680–683
Hoess RH, Abremski K (1984) Interaction of the bacteriophage P1 recombinase Cre with the recombining site loxP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81(4):1026–1029
Hoess RH, Ziese M, Sternberg N (1982) P1 site-specific recombination: nucleotide sequence of the recombining sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79(11):3398–3402
Jo D, Nashabi A, Doxsee C, Lin Q, Unutmaz D, Chen J, Ruley HE (2001) Epigenetic regulation of gene structure and function with a cell-permeable Cre recombinase. Nat Biotechnol 19(10):929–933
Kaartinen V, Nagy A (2001) Removal of the floxed neo gene from a conditional knockout allele by the adenoviral Cre recombinase in vivo. Genesis 31(3):126–129
Kalderon D, Roberts BL, Richardson WD, Smith AE (1984) A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell 39(3 Pt 2):499–509
Kang Q, Sun Z, Zou Z, Wang M, Li Q, Hu X, Li N (2018) Cell-penetrating peptide-driven Cre recombination in porcine primary cells and generation of marker-free pigs. PLoS ONE 13(1):e190690
Lai L, Park KW, Cheong HT, Kuhholzer B, Samuel M, Bonk A, Im GS, Rieke A, Day BN, Murphy CN, Carter DB, Prather RS (2002) Transgenic pig expressing the enhanced green fluorescent protein produced by nuclear transfer using colchicine-treated fibroblasts as donor cells. Mol Reprod Dev 62(3):300–306
Lan C, Ren L, Wu M, Liu S, Liu G, Xu X, Chen J, Ma H, Cheng G (2013) Deletion of marker gene in transgenic goat by Cre/LoxP system. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 29(12):1847–1854
Li Z, Shi J, Liu D, Zhou R, Zeng H, Zhou X, Mai R, Zeng S, Luo L, Yu W, Zhang S, Wu Z (2013) Effects of donor fibroblast cell type and transferred cloned embryo number on the efficiency of pig cloning. Cell Reprogram 15(1):35–42
Li Z, Zeng F, Meng F, Xu Z, Zhang X, Huang X, Tang F, Gao W, Shi J, He X, Liu D, Wang C, Urschitz J, Moisyadi S, Wu Z (2014) Generation of transgenic pigs by cytoplasmic injection of piggyBac transposase-based pmGENIE-3 plasmids. Biol Reprod 90(5):93
Lin Q, Jo D, Gebre-Amlak KD, Ruley HE (2004) Enhanced cell-permeant Cre protein for site-specific recombination in cultured cells. BMC Biotechnol 4:25
Mae M, Langel U (2006) Cell-penetrating peptides as vectors for peptide, protein and oligonucleotide delivery. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6(5):509–514
McLellan MA, Rosenthal NA, Pinto AR (2017) Cre-loxP-mediated recombination: general principles and experimental considerations. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol 7(1):1–12
Milletti F (2012) Cell-penetrating peptides: classes, origin, and current landscape. Drug Discov Today 17(15–16):850–860
Montag J, Petersen B, Flogel AK, Becker E, Lucas-Hahn A, Cost GJ, Muhlfeld C, Kraft T, Niemann H, Brenner B (2018) Successful knock-in of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy-mutation R723G into the MYH7 gene mimics HCM pathology in pigs. Sci Rep 8(1):4786
Naruse K, Ishikawa H, Kawano HO, Ueda H, Kurome M, Miyazaki K, Endo M, Sawasaki T, Nagashima H, Makuuchi M (2005) Production of a transgenic pig expressing human albumin and enhanced green fluorescent protein. J Reprod Dev 51(4):539–546
Park KW, Cheong HT, Lai L, Im GS, Kuhholzer B, Bonk A, Samuel M, Rieke A, Day BN, Murphy CN, Carter DB, Prather RS (2001) Production of nuclear transfer-derived swine that express the enhanced green fluorescent protein. Anim Biotechnol 12(2):173–181
Peitz M, Pfannkuche K, Rajewsky K, Edenhofer F (2002) Ability of the hydrophobic FGF and basic TAT peptides to promote cellular uptake of recombinant Cre recombinase: a tool for efficient genetic engineering of mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(7):4489–4494
Sauer B, Henderson N (1988) Site-specific DNA recombination in mammalian cells by the Cre recombinase of bacteriophage P1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85(14):5166–5170
Song Y, Lai L, Li L, Huang Y, Wang A, Tang X, Pang D, Li Z, Ouyang H (2016) Germ cell-specific expression of Cre recombinase using the VASA promoter in the pig. FEBS Open Bio 6(1):50–55
Sunaga S, Maki K, Komagata Y, Ikuta K, Miyazaki JI (1997) Efficient removal of loxP-flanked DNA sequences in a gene-targeted locus by transient expression of Cre recombinase in fertilized eggs. Mol Reprod Dev 46(2):109–113
Tong J, Wei H, Liu X, Hu W, Bi M, Wang Y, Li Q, Li N (2011) Production of recombinant human lysozyme in the milk of transgenic pigs. Transgenic Res 20(2):417–419
Vasey DB, Lillico SG, Sang HM, King TJ, Whitelaw CB (2009) CMV enhancer-promoter is preferentially active in exocrine cells in vivo. Transgenic Res 18(2):309–314
Vives E, Brodin P, Lebleu B (1997) A truncated HIV-1 Tat protein basic domain rapidly translocates through the plasma membrane and accumulates in the cell nucleus. J Biol Chem 272(25):16010–16017
Wadia JS, Dowdy SF (2005) Transmembrane delivery of protein and peptide drugs by TAT-mediated transduction in the treatment of cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57(4):579–596
Wadia JS, Stan RV, Dowdy SF (2004) Transducible TAT-HA fusogenic peptide enhances escape of TAT-fusion proteins after lipid raft macropinocytosis. Nat Med 10(3):310–315
Wang W, Lin C, Lu D, Ning Z, Cox T, Melvin D, Wang X, Bradley A, Liu P (2008) Chromosomal transposition of PiggyBac in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(27):9290–9295
Whitworth KM, Cecil R, Benne JA, Redel BK, Spate LD, Samuel MS, Prather RS, Wells KD (2018) Zygote injection of RNA encoding Cre recombinase results in efficient removal of LoxP flanked neomycin cassettes in pigs. Transgenic Res 27(2):167–178
Whyte JJ, Prather RS (2011) Genetic modifications of pigs for medicine and agriculture. Mol Reprod Dev 78(10–11):879–891
Wu Z, Xu Z, Zou X, Zeng F, Shi J, Liu D, Urschitz J, Moisyadi S, Li Z (2013) Pig transgenesis by piggyBac transposition in combination with somatic cell nuclear transfer. Transgenic Res 22(6):1107–1118
Xu Y, Liu S, Yu G, Chen J, Chen J, Xu X, Wu Y, Zhang A, Dowdy SF, Cheng G (2008) Excision of selectable genes from transgenic goat cells by a protein transducible TAT-Cre recombinase. Gene 419(1–2):70–74
Yoshioka K, Suzuki C, Itoh S, Kikuchi K, Iwamura S, Rodriguez-Martinez H (2003) Production of piglets derived from in vitro-produced blastocysts fertilized and cultured in chemically defined media: effects of theophylline, adenosine, and cysteine during in vitro fertilization. Biol Reprod 69(6):2092–2099
Zeng F, Li Z, Cai G, Gao W, Jiang G, Liu D, Urschitz J, Moisyadi S, Wu Z (2016) Characterization of growth and reproduction performance, transgene integration, expression, and transmission patterns in transgenic pigs produced by piggyBac transposition-mediated gene transfer. Anim Biotechnol 27(4):245–255
Zeng F, Li Z, Zhu Q, Dong R, Zhao C, Li G, Li G, Gao W, Jiang G, Zheng E, Cai G, Moisyadi S, Urschitz J, Yang H, Liu D, Wu Z (2017) Production of functional human nerve growth factor from the saliva of transgenic mice by using salivary glands as bioreactors. Sci Rep 7:41270
Zhang X, Li Z, Yang H, Liu D, Cai G, Li G, Mo J, Wang D, Zhong C, Wang H, Sun Y, Shi J, Zheng E, Meng F, Zhang M, He X, Zhou R, Zhang J, Huang M, Zhang R, Li N, Fan M, Yang J, Wu Z (2018) Novel transgenic pigs with enhanced growth and reduced environmental impact. Elife 7:e34286
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from a National Science and Technology Major Project of China (Grant Number: 2016ZX08006002), and two grants from the Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province, China (Grant Numbers: 2018B020203002 and 2018ML1101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Zou, X., Xu, Z. et al. Efficient deletion of LoxP-flanked selectable marker genes from the genome of transgenic pigs by an engineered Cre recombinase. Transgenic Res 29, 307–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-020-00200-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-020-00200-3