Abstract
Plasma has been introduced in recent years as a promising method for modification of carbon materials in comparing with traditional wet chemical method, thanks to reduced energy combustion, shortened synthesis duration and undestroyed bulk structure. In this review, we present the modification of carbons on surface chemistry and the recent progress in the applications of these modified carbons in catalyst supports and electrode materials. Plasma methods show promise as a means of enhancing surface properties without destroying the bulk structure of the carbon. Interaction can occur with oxygen, nitrogen and halogens and the chemical modification at the surface can often lead to the provision of sites that can be used to anchor small (nano) particles of metals and active components. This in turn can lead to enhanced catalytic behavior, including electrocatalysis. Hydrophilic/hydrophobic properties can also be tuned via this approach, Carbons modified in this way have also shown promise as high performance electrode materials and pseudocapacitors. The review also mentions challenges and opportunities for further modification of carbons by plasma treatment and for broadening their applications.

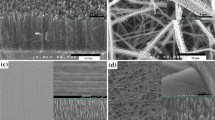
Reprinted with permission from the American Chemical Society

Reproduced with permission from Elsevier Publ. Co

Reproduced with permission from Elsevier Publ. Co

Reproduced with permission from Elsevier Publ. Co

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, de Heer WA (2002) Carbon nanotubes-the route toward applications. Science 297(5582):787–792
Mauter MS, Elimelech M (2008) Environmental applications of carbon-based nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 42(16):5843–5859
Bessel CA, Laubernds K, Rodriguez NM, Baker, R. T. K. (2001) Graphite nanofibers as an electrode for fuel cell applications. J Phys Chem B 105(6):1115–1118
Yoo E, Kim J, Hosono E, Zhou HS, Kudo T, Honma I (2008) Large reversible Li storage of graphene nanosheet families for use in rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Nano Lett 8(8):2277–2282
Prasad KE, Das B, Maitra U, Ramamurty U, Rao, C. N. R. (2009) Extraordinary synergy in the mechanical properties of polymer matrix composites reinforced with 2 nanocarbons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(32):13186–13189
Fernández-Rossier J, Palacios JJ (2007) Magnetism in graphene nanoislands. Phys Rev Lett 99(17):177204
Pourfayaz F, Jafari SH, Khodadadi AA, Mortazavi Y, Khonakdar HA (2013) On the dispersion of CNTs in polyamide 6 matrix via solution methods: assessment through electrical, rheological, thermal and morphological analyses. Polym Bull 70(8):2387–2398
Boiani M, Gonzalez M (2005) Imidazole and benzimidazole derivatives as chemotherapeutic agents. Mini Rev Med Chem 5(4):409–424
Datsyuk V, Kalyva M, Papagelis K, Parthenios J, Tasis D, Siokou A, Kallitsis I, Galiotis C (2008) Chemical oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 46(6):833–840
Chin, C. J. M., Shih LC, Tsai HJ, Liu TK (2007) Adsorption of o-xylene and p-xylene from water by SWCNTs. Carbon 45(6):1254–1260
Marshall MW, Popa-Nita S, Shapter JG (2006) Measurement of functionalised carbon nanotube carboxylic acid groups using a simple chemical process. Carbon 44(7):1137–1141
Wu ZX, Webley PA, Zhao DY (2012) Post-enrichment of nitrogen in soft-templated order mesoporous carbon materials for high efficient phenol removal and CO2 capture. J Mater Chem 22:11379
Liu L, Deng QF, Ma TY, Lin XZ, Hou XX, Liu YP, Yuan ZY (2011) Ordered mesoporous carbons: citric acid-catalyzed synthesis, nitrogen doping and CO2 capture. J Mater Chem 21:16001
Meng FY, Ogata S, Xu DS, Shibutani Y, Shi SQ (2007) Thermal conductivity of an ultrathin carbon nanotube with an X-shaped junction. Phys Rev B 75(20):205403
Rosca ID, Hoa SV (2009) Highly conductive multiwall carbon nanotube and epoxy composites produced by three-roll milling. Carbon 47(8):1958–1968
Bogoeva-Gaceva G, Mäder E, Haüssler,L, Dekanski A (1997) Characterization of the surface and interphase of plasma-treated HM carbon fibres. Composites Part A 28(5):445–452
De Torre LC, Bottani EJ, Martinez-Alonso A, Cuesta A, Garcia AB, Tascon JMD (1998) Effects of oxygen plasma treatment on the surface of graphitized carbon black. Carbon 36(3):277–282
Takada T, Nakahara M, Kumagai H, Sanada Y (1996) Surface modification and characterization of carbon black with oxygen plasma. Carbon 34(9):1087–1091
Montes-Morán MA, Martınez-Alonso A, Tascón JMD, Paiva MC, Bernardo CA (2001) Effects of plasma oxidation on the surface and interfacial properties of carbon fibres/polycarbonate composites. Carbon 39(7):1057–1068
Zhi CY, Bai XD, Wang EG (2002) Enhanced field emission from carbon nanotubes by hydrogen plasma treatment. Appl Phys Lett 81(9):1690–1692
Ávila-Orta CA, Cruz-Delgado VJ, Neira-Velázquez MG, Hernández-Hernández E, Méndez-Padilla MG, Medellín-Rodríguez FJ (2009) Surface modification of carbon nanotubes with ethylene glycol plasma. Carbon 47(8):1916–1921
Boudou JP, Paredes JI, Cuesta A, Martınez-Alonso A, Tascon JMD (2003) Oxygen plasma modification of pitch-based isotropic carbon fibres. Carbon 41(1):41–56
Kyung SJ, Park JB, Voronko M, Lee JH, Yeom GY (2007) The effect of atmospheric pressure plasma treatment on the field emission characteristics of screen printed carbon nanotubes. Carbon 45(3):649–654
Lin CC, Huang HC (2009) Radio frequency oxygen–plasma treatment of carbon nanotube electrodes for electrochemical capacitors. J Power Sources 188(1):332–337
Ghamouss F, Luais E, Thobie-Gautier C, Tessier PY, Boujtita M (2009) Argon plasma treatment to enhance the electrochemical reactivity of screen-printed carbon surfaces. Electrochim Acta 54(11):3026–3032
Tang Z, Li Q, Lu G (2007) The effect of plasma pre-treatment of carbon used as a Pt catalyst support for methanol electrooxidation. Carbon 45(1):41–46
Jiang Z, Jiang ZJ (2011) Improvements of electrocatalytic activity of PtRu nanoparticles on multi-walled carbon nanotubes by a H2 plasma treatment in methanol and formic acid oxidation. Electrochim Acta 56(24):8662–8673
Ionescu R, Espinosa EH, Sotter E, Llobet E, Vilanova X, Correig X, Felten A, Bittencourt C, Van Lier G, Charlier J-C, Pireaux JJ (2006) Oxygen functionalisation of MWNT and their use as gas sensitive thick-film layers. Sens Actuators B 113(1):36–46
Okpalugo, TIT, Papakonstantinou P, Murphy H, Mclaughlin J, Brown NMD (2005) Oxidative functionalization of carbon nanotubes in atmospheric pressure filamentary dielectric barrier discharge (APDBD). Carbon 43(14):2951–2959
Hinokuma S, Misumi S, Yoshida H, Machida M (2015) Nanoparticle catalyst preparation using pulsed arc plasma deposition. Catal Sci Technol 5(9):4249–4257
Wang Q, Wang X, Chai Z, Hu W (2013) Low-temperature plasma synthesis of carbon nanotubes and graphene based materials and their fuel cell applications. Chem Soc Rev 42(23):8821–8834
Bo Z, Yang Y, Chen J, Yu K, Yan J, Cen K (2013) Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition synthesis of vertically oriented graphene nanosheets. Nanoscale 5(12):5180–5204
Chu W, Xu J, Hong J, Lin T, Khodakov A (2015) Design of efficient Fischer Tropsch cobalt catalysts via plasma enhancement: reducibility and performance (Review). Catal Today 256:41–48
Tendero C, Tixier C, Tristant P, Desmaison J, Leprince P (2006) Atmospheric pressure plasmas: A review. Spectrochim Acta Part B 61(1):2–30
Chen C, Liang B, Ogino A, Wang X, Nagatsu M (2009) Oxygen functionalization of multiwall carbon nanotubes by microwave-excited surface-wave plasma treatment. J Phys Chem C 113(18):7659–7665
Ago H, Kugler T, Cacialli F, Salaneck WR, Shaffer MS, Windle AH, Friend RH (1999) Work functions and surface functional groups of multiwall carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 103(38):8116–8121
Tang S, Lu N, Wang JK, Ryu SK, Choi HS (2007) Novel effects of surface modification on activated carbon fibers using a low pressure plasma treatment. J Phys Chem C 111(4):1820–1829
Lee H, Ohsawa I, Takahashi J (2015) Effect of plasma surface treatment of recycled carbon fiber on carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP) interfacial properties. Appl Surf Sci 328:241–246
Naseh MV, Khodadadi AA, Mortazavi Y, Pourfayaz F, Alizadeh O, Maghrebi M (2010) Fast and clean functionalization of carbon nanotubes by dielectric barrier discharge plasma in air compared to acid treatment. Carbon 48(5):1369–1379
Rider AN, Yeo E, Gopalakrishna J, Thostenson ET, Brack N (2015) Hierarchical composites with high-volume fractions of carbon nanotubes: Influence of plasma surface treatment and thermoplastic nanophase-modified epoxy. Carbon 94:971–981
Yook JY, Jun J, Kwak S (2010) Amino functionalization of carbon nanotube surfaces with NH 3 plasma treatment. Appl Surf Sci 256(23):6941–6944
Chen C, Liang B, Lu D, Ogino A, Wang X, Nagatsu M (2010) Amino group introduction onto multiwall carbon nanotubes by NH3/Ar plasma treatment. Carbon 48(4):939–948
Inagaki N, Narushima K, Hashimoto H, Tamura K (2007) Implantation of amino functionality into amorphous carbon sheet surfaces by NH3 plasma. Carbon 45(4):797–804
Abdelkader VK, Scelfo S, García-Gallarín C, Godino-Salido ML, Domingo-García M, López-Garzón FJ, Pérez-Mendoza M (2013) Carbon tetrachloride cold plasma for extensive chlorination of carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 117(32):16677–16685
Abdelkader VK, Domingo-García M, Gutiérrez-Valero MD, López-Garzón R, Melguizo M, García-Gallarín C, Javier Lopez-Garzon F, Pérez-Mendoza MJ (2014) Sidewall chlorination of carbon nanotubes by iodine trichloride. J Phys Chem C 118(5):2641–2649
Shioyama H, Honjo K, Kiuchi M, Yamada Y, Ueda A, Kuriyama N, Kobayashi T (2006) C2F6 plasma treatment of a carbon support for a PEM fuel cell electrocatalyst. J Power Sources 161(2):836–838
Abdelkader VK, Domingo-García M, Melguizo M, López-Garzón R, López-Garzón FJ, Pérez-Mendoza M (2015) Covalent bromination of multi-walled carbon nanotubes by iodine bromide and cold plasma treatments. Carbon 93:276–285
Vinu A, Hossian KZ, Srinivasu P, Miyahara M, Anandan S, Gokulakrishnan N, Mori T, Ariga K, Balasubramanian VV (2007) Carboxy-mesoporous carbon and its excellent adsorption capability for proteins. J Mater Chem 17(18):1819–1825
Ma TY, Liu L, Yuan ZY (2013) Direct synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbons. Chem Soc Rev 42(9):3977–4003
Liu L, Zhu YP, Su M, Yuan ZY (2015) Metal-Free carbonaceous materials as promising heterogeneous catalysts. ChemCatChem 7(18):2765–2787
Liu L, Deng QF, Liu YP, Ren TZ, Yuan ZY (2011) HNO3-activated mesoporous carbon catalyst for direct dehydrogenation of propane to propylene. Catal Commun 16(1):81–85
Loganathan K, Bose D, Weinkauf D (2014) Surface modification of carbon black by nitrogen and allylamine plasma treatment for fuel cell electrocatalyst. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39(28):15766–15771
Ruelle B, Felten A, Ghijsen J, Drube W, Johnson RL, Liang D, Erni R, Tendeloo GV, Dubois P, Hecq M, Bittencourt C (2008) Functionalization of MWCNTs with atomic nitrogen: electronic structure. J Phys D 41(4):045202
Kim S, Cho MH, Lee JR, Park SJ (2006) Influence of plasma treatment of carbon blacks on electrochemical activity of Pt/carbon blacks catalysts for DMFCs. J Power Sources 159(1):46–48
Chen G, Neupane S, Li W, Chen L, Zhang J (2013) An increase in the field emission from vertically aligned multiwalled carbon nanotubes caused by NH3 plasma treatment. Carbon 52:468–475
Felten A, Ghijsen J, Pireaux JJ, Johnson RL, Whelan CM, Liang D, Tendeloo GV, Bittencourt C (2008) Photoemission study of CF4 rf-Plasma treated multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 46(10):1271–1275
Friedrich JF, Wettmarshausen S, Hanelt S, Mach R, Mix R, Zeynalov EB, Meyer-Plath A (2010) Plasma-chemical bromination of graphitic materials and its use for subsequent functionalization and grafting of organic molecules. Carbon 48(13):3884–3894
Okajima K, Ohta K, Sudoh M (2005) Capacitance behavior of activated carbon fibers with oxygen-plasma treatment. Electrochim Acta 50(11):2227–2231
Ma C, Song Y, Shi J, Zhang D, Zhai X, Zhong M, Guo Q, Liu L (2013) Preparation and one-step activation of microporous carbon nanofibers for use as supercapacitor electrodes. Carbon 51:290–300
Hsieh CT, Teng H (2002) Influence of oxygen treatment on electric double-layer capacitance of activated carbon fabrics. Carbon 40(5):667–674
Bahr JL, Tour JM (2002) Covalent chemistry of single-wall carbon nanotubes. J Mater Chem 12(7):1952–1958
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Sadanandam, G., Liu, X. et al. Carbon Surface Modifications by Plasma for Catalyst Support and Electrode Materials Applications. Top Catal 60, 823–830 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-017-0747-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-017-0747-7